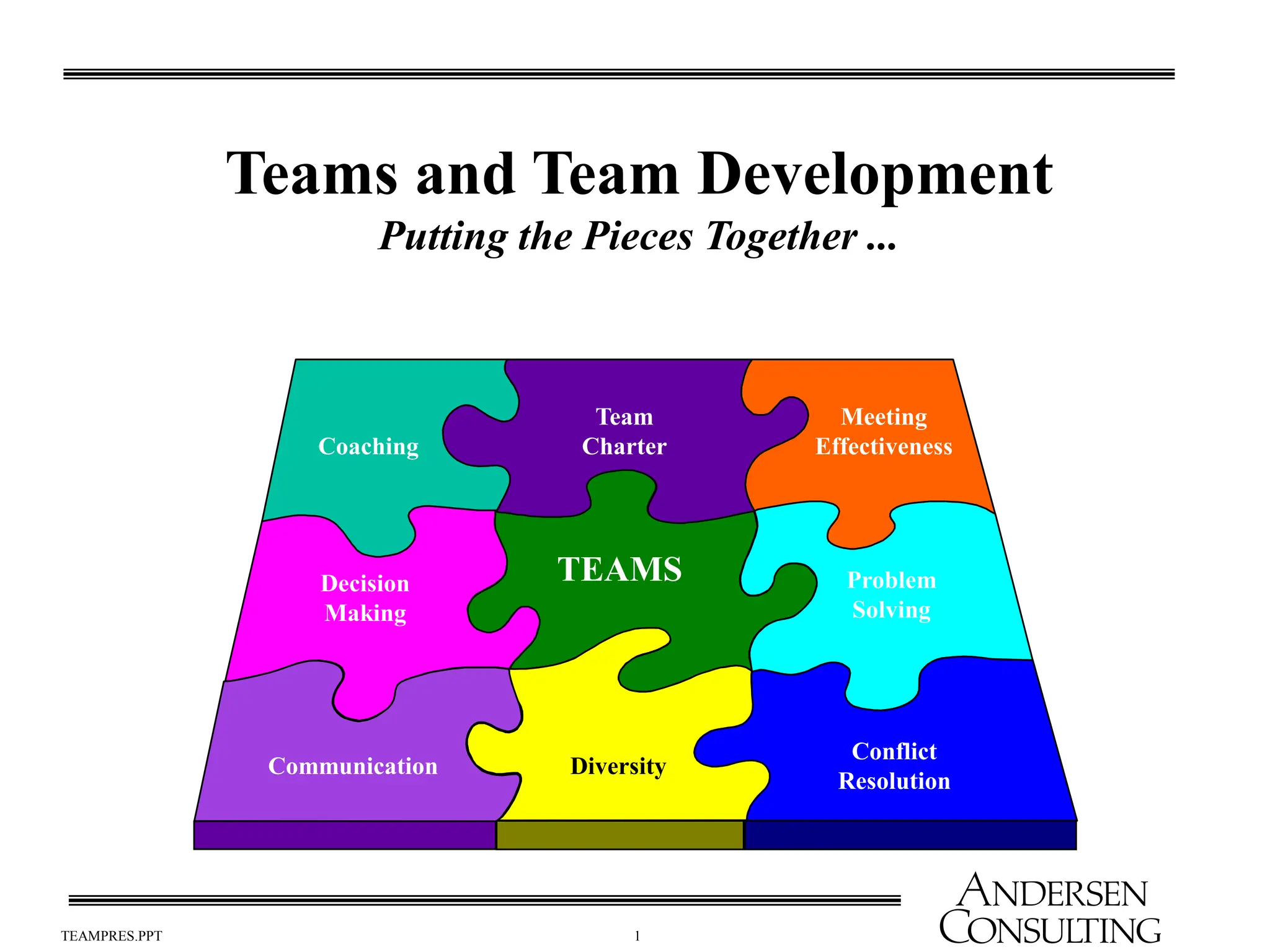
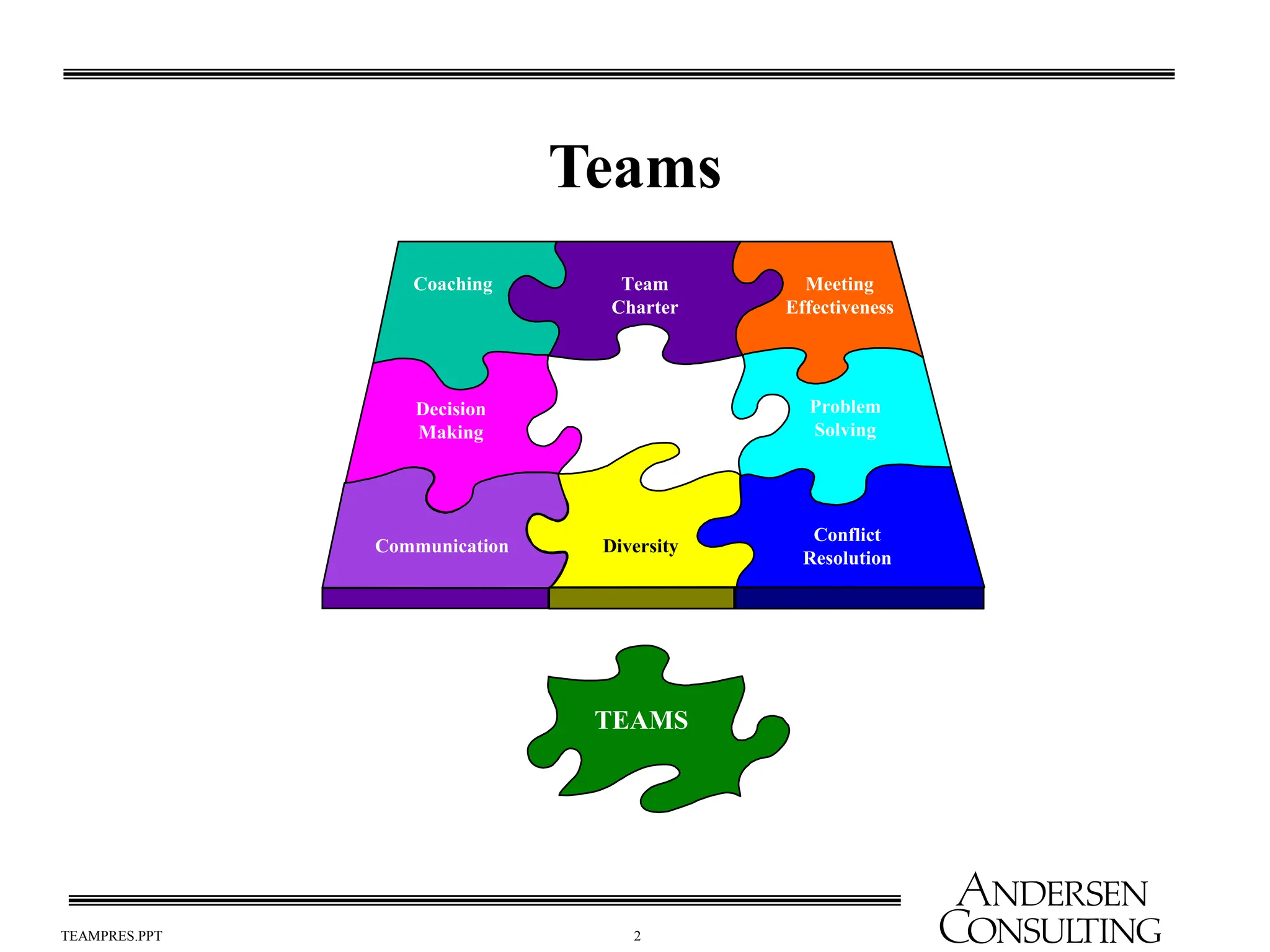
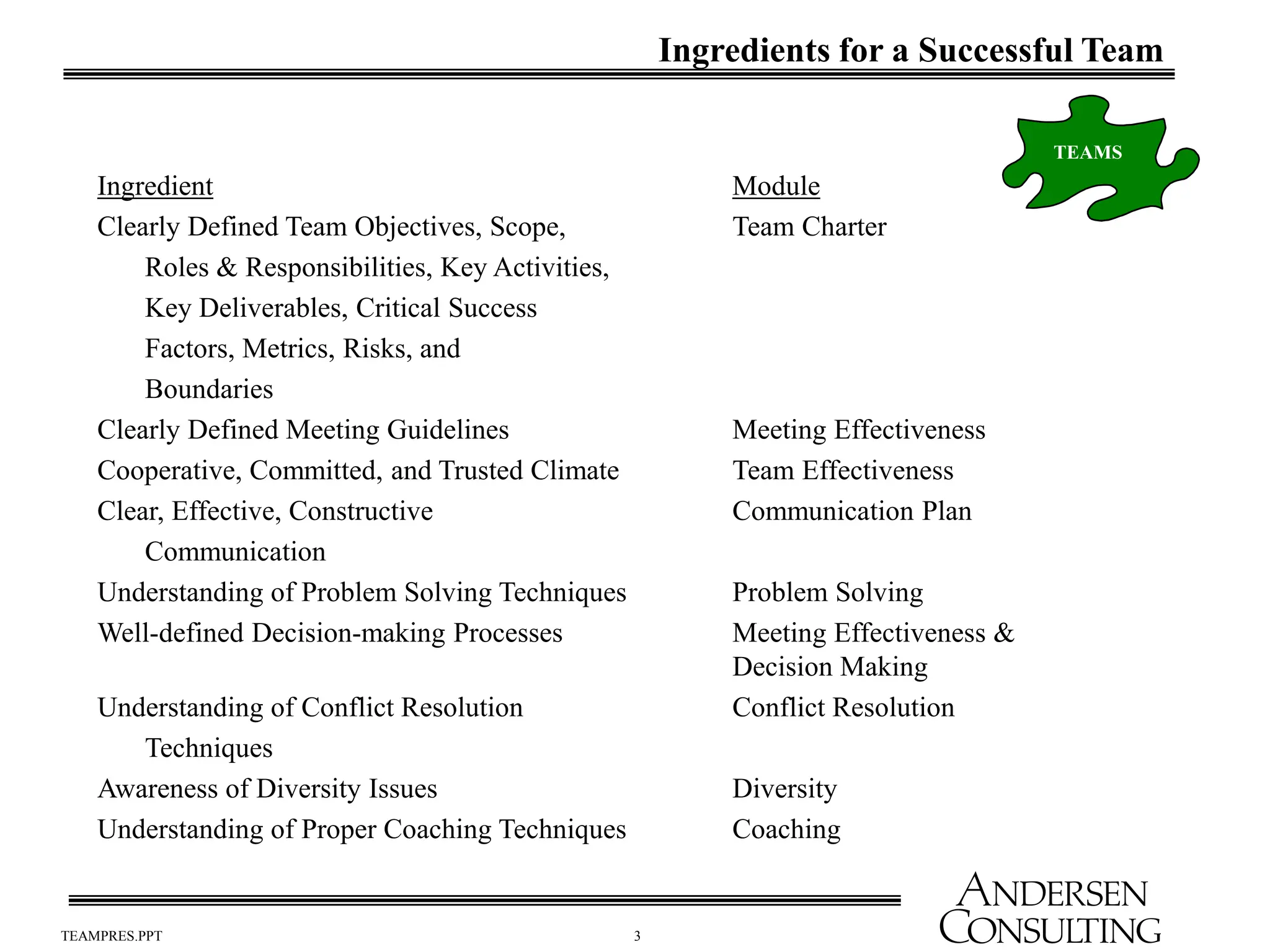
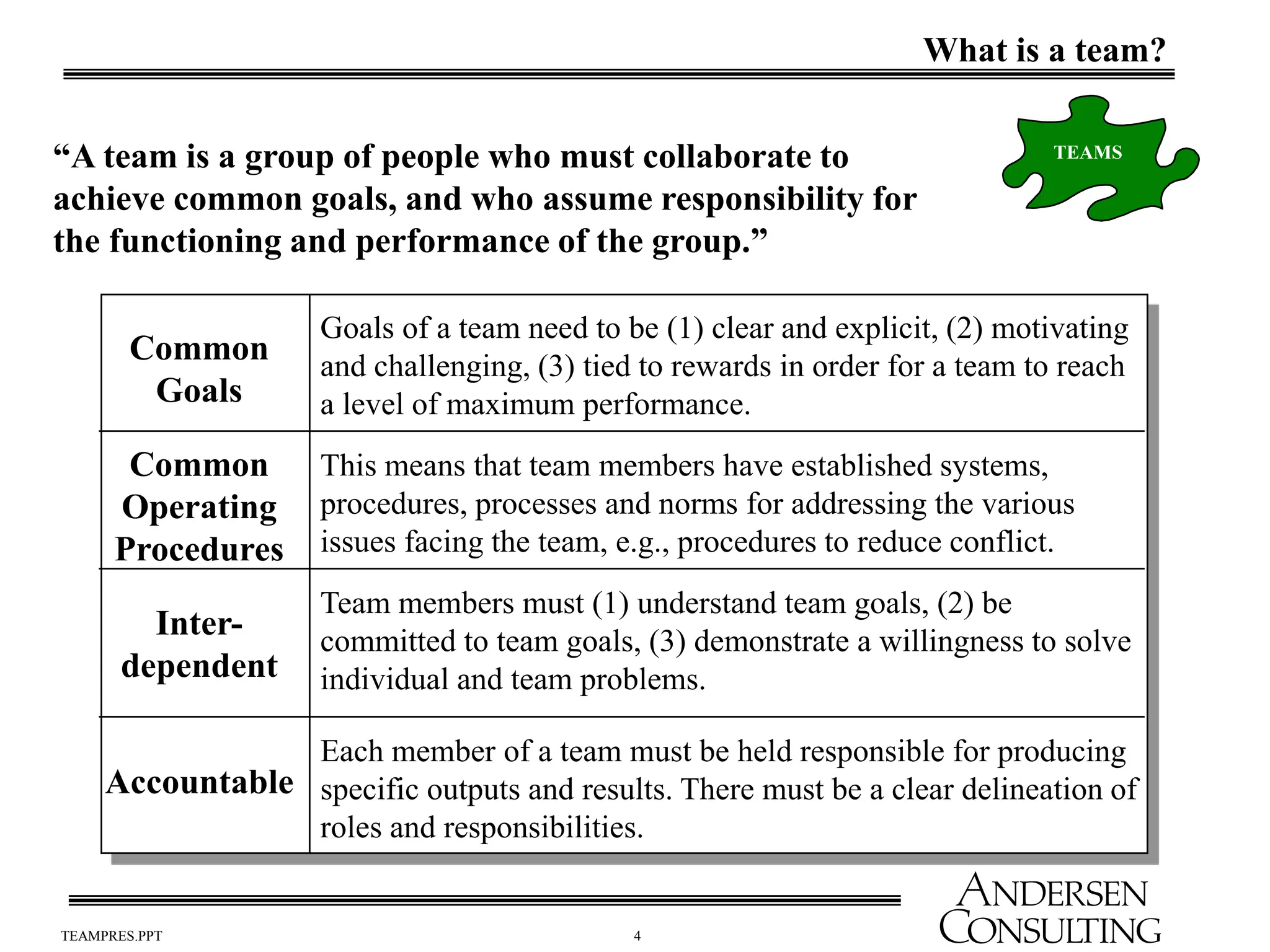
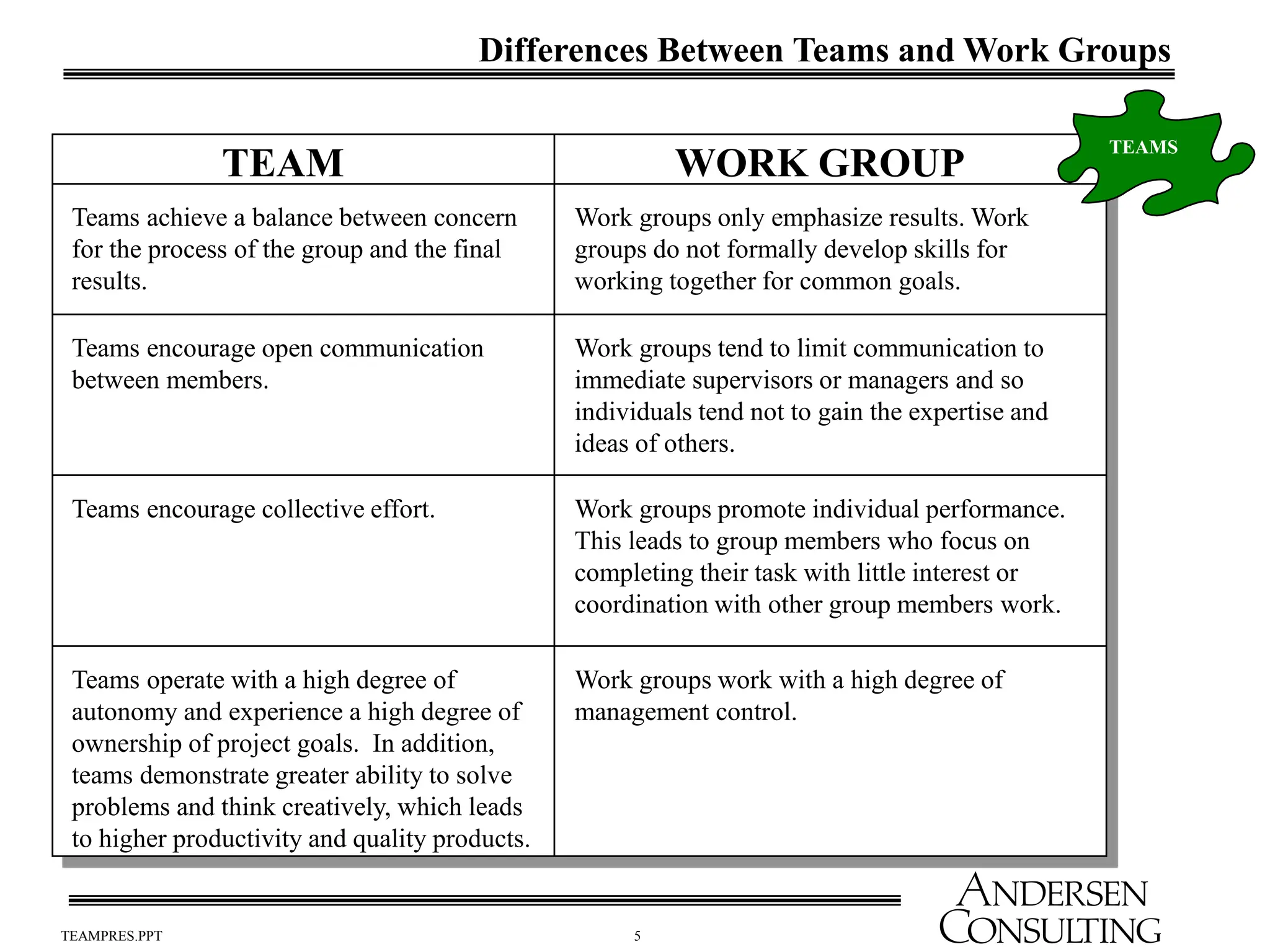
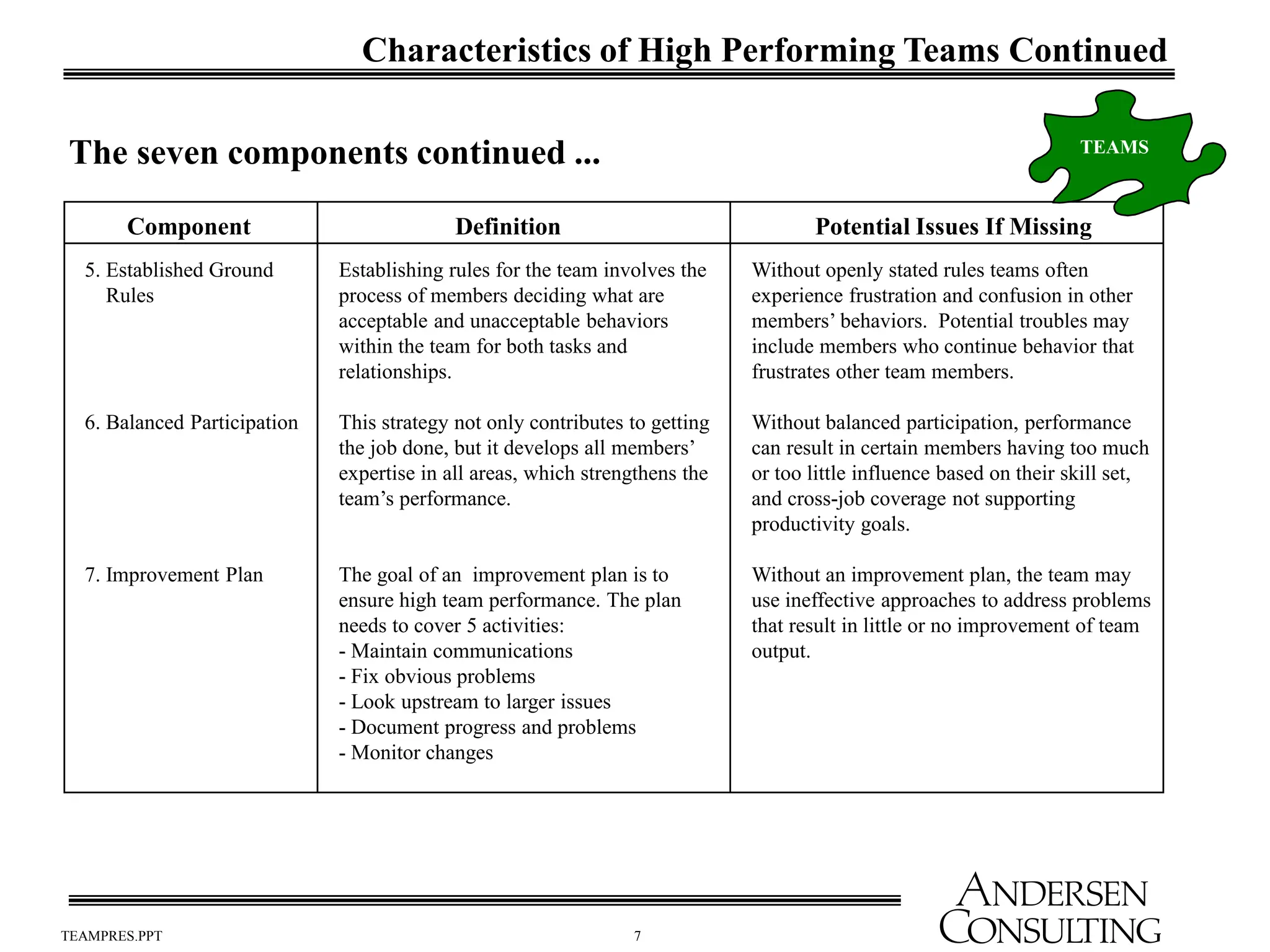
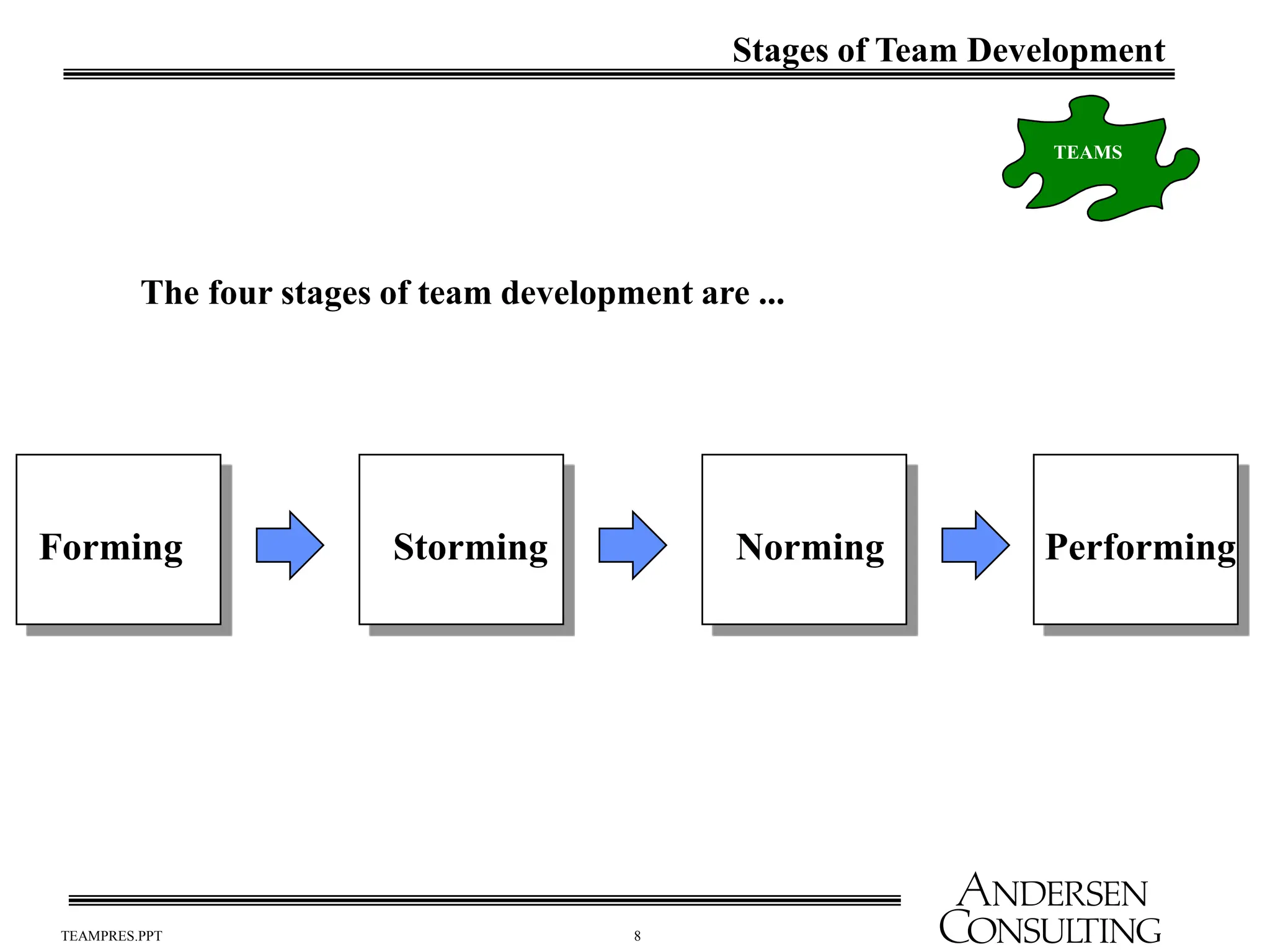
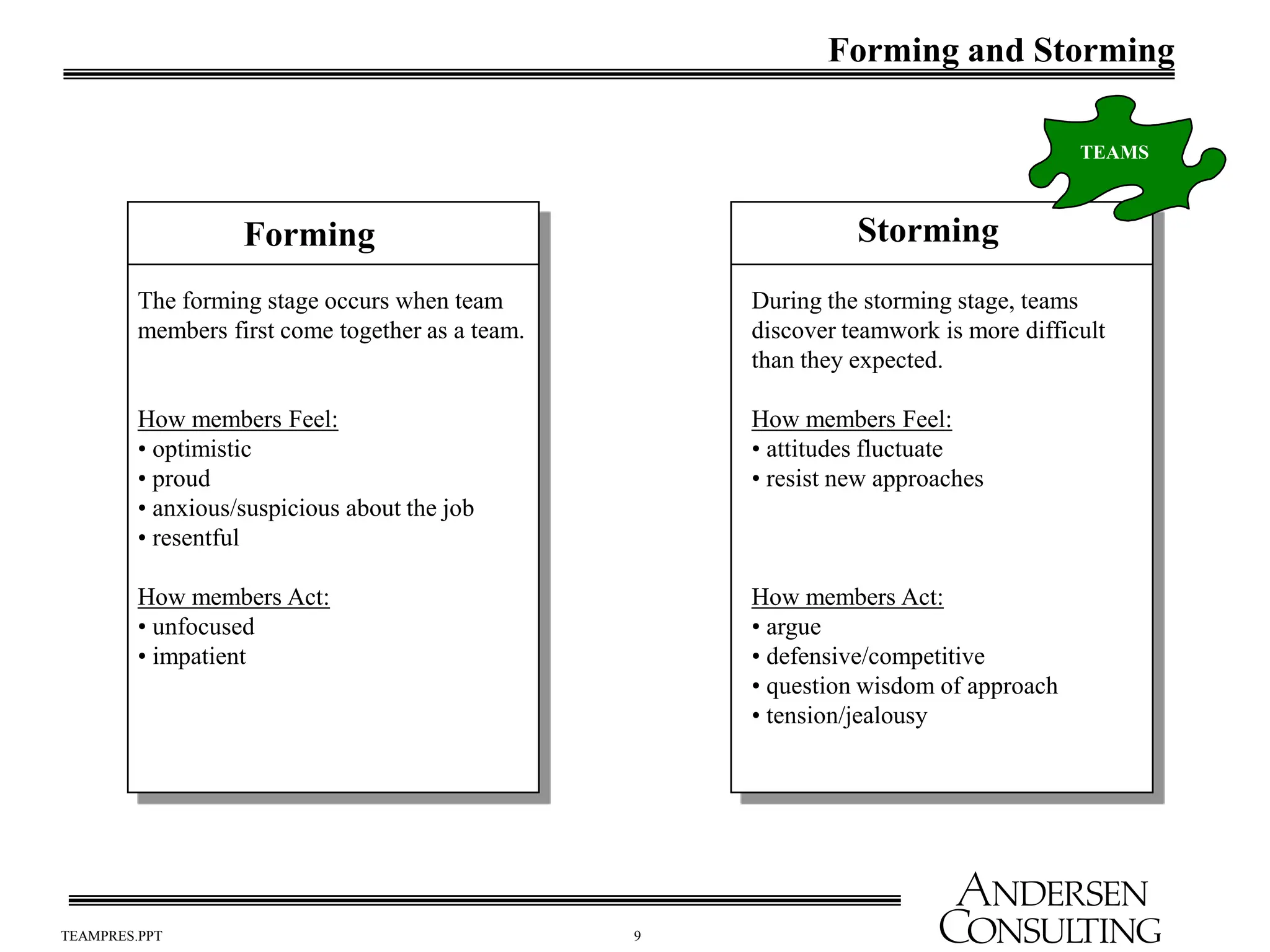
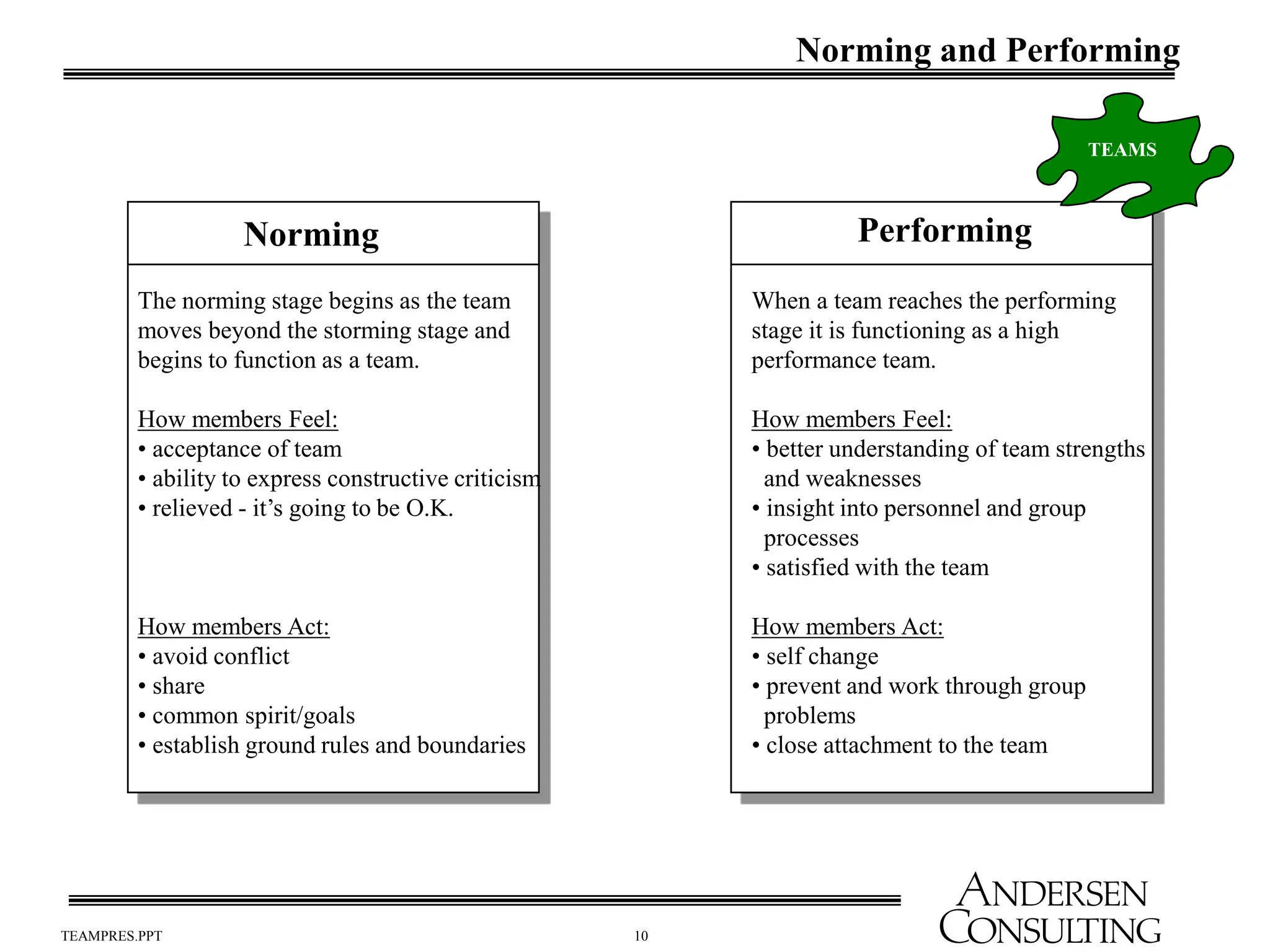
The document outlines the essential components of effective teams, including clear goals, defined roles, and effective communication techniques. It discusses the stages of team development (forming, storming, norming, performing) and provides guidance on creating a team charter to define objectives and responsibilities. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of meeting effectiveness and conflict resolution within teams to enhance performance and collaboration.