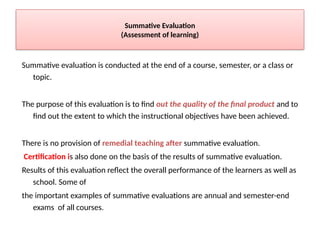
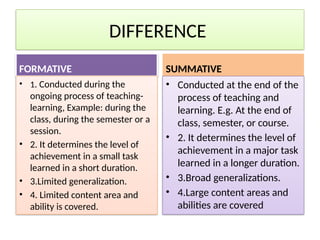
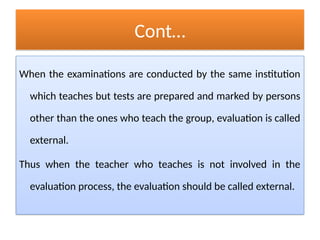
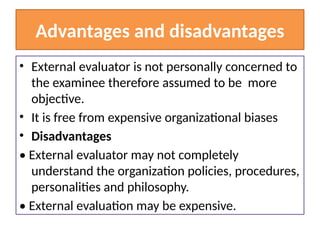
The document discusses two main types of evaluations in education: formative and summative. Formative evaluation occurs during the teaching process to monitor student progress and improve learning outcomes, while summative evaluation is conducted at the end of a course to assess overall performance and determine if instructional objectives have been met. Additionally, it contrasts internal and external evaluations, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages in objectivity and understanding of the learning environment.