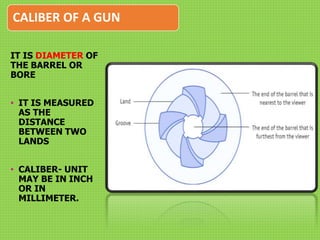
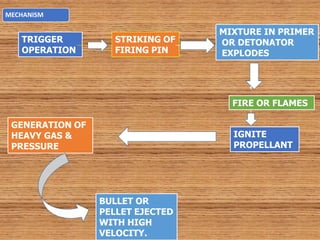
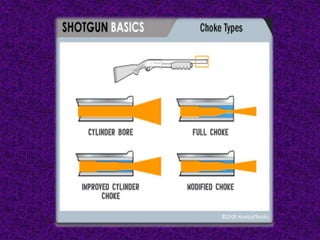
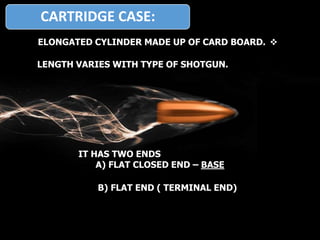
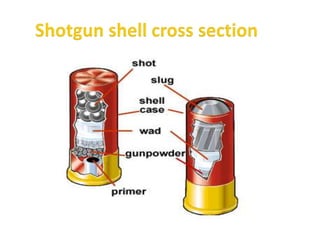
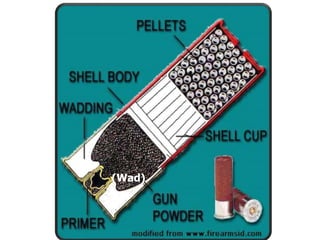
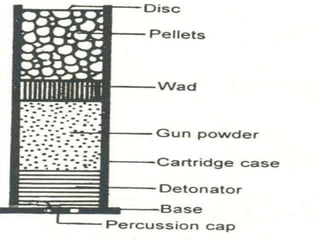
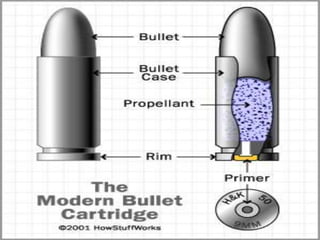
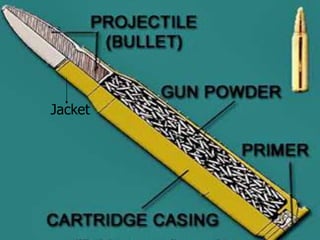
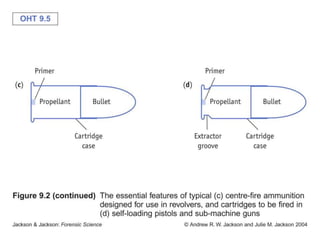
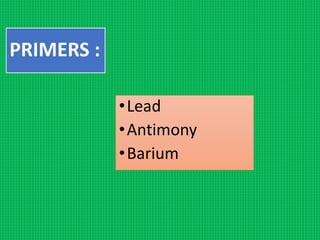
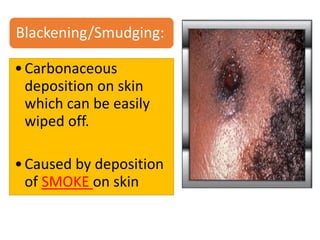
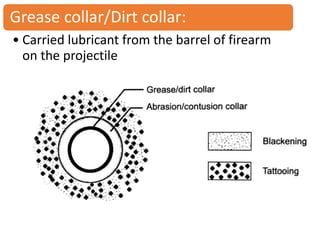
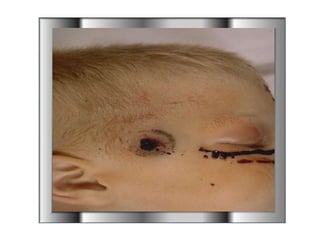
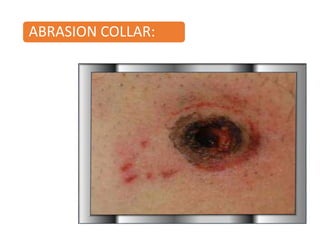
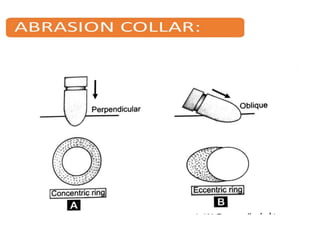
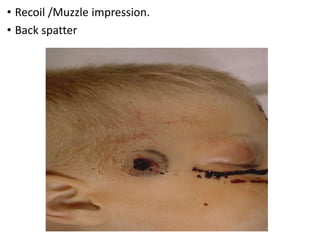
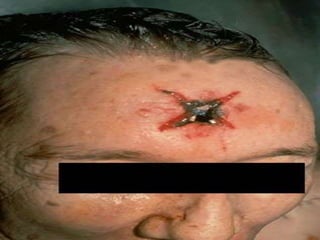
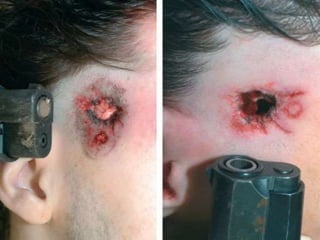
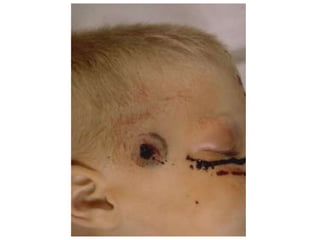
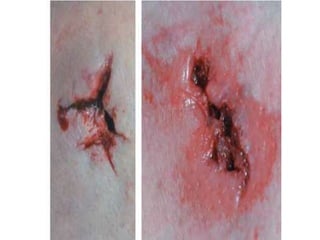
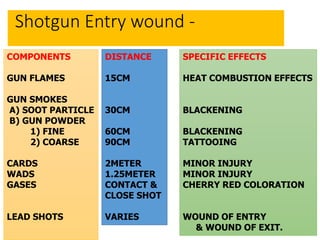
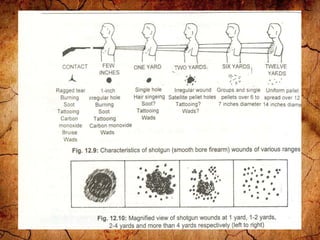
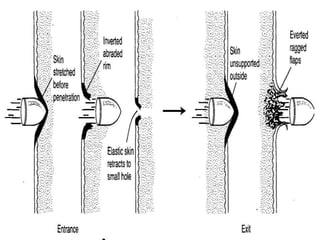
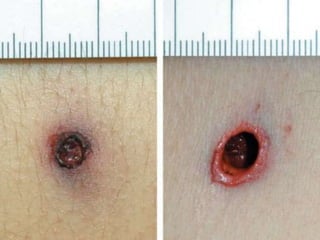
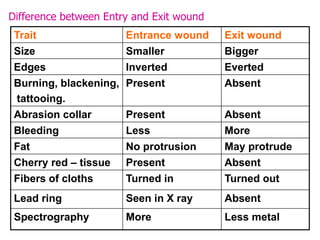
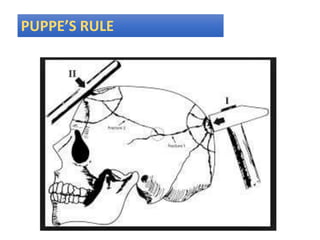
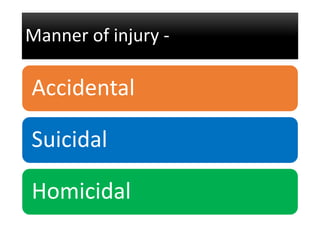
Firearm injuries can be analyzed based on wound characteristics to determine details like the type of firearm, firing range, and manner of injury. Entry wounds are usually smaller and have inverted edges while exit wounds are larger with everted edges. Tattooing and soot deposition can indicate a close firing range. The presence of an abrasion collar or lead residue in wounds and on the hand helps determine if the person recently fired a gun. Analyzing the bullet, wound ballistics, and performing dermal nitrate tests on the hand are important for the medico-legal investigation of firearm-related deaths.