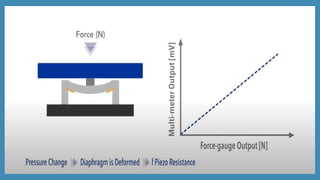
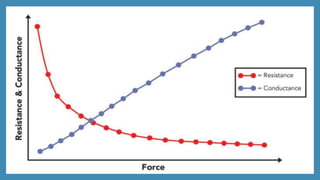
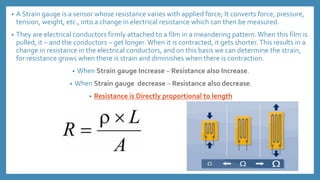
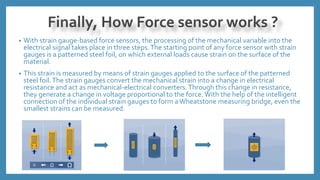
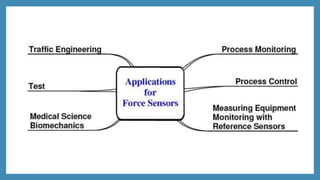
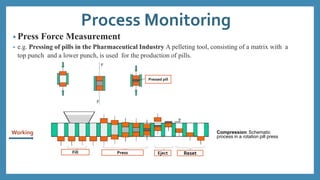
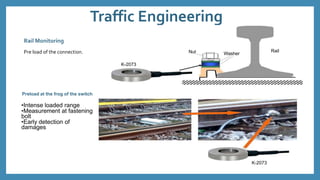
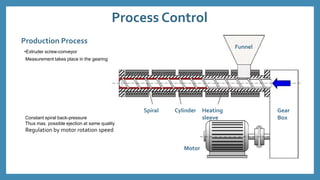
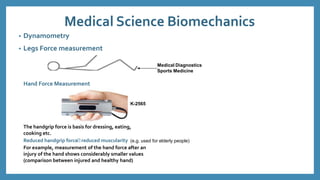
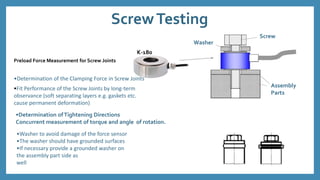
The document discusses force sensors, which convert mechanical forces into electrical signals using strain gauges. It explains that as force is applied, the resistance of the strain gauges changes proportionally, allowing for precise measurement of strain and force. Various applications of force sensors are also highlighted, including their use in process monitoring, medical diagnostics, and construction.