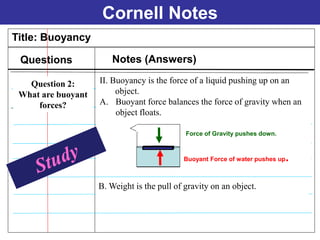
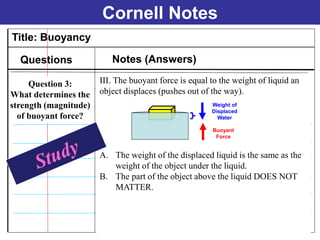
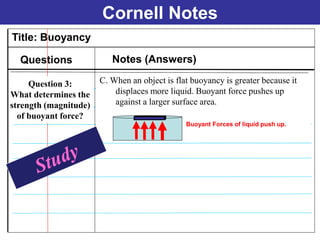
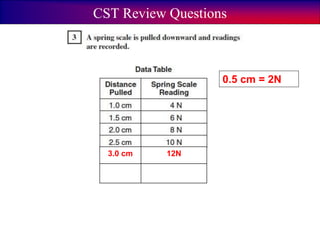
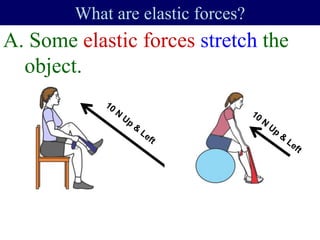
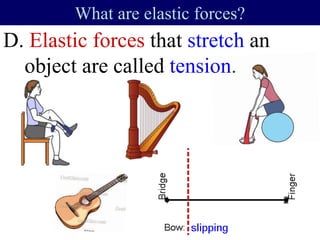
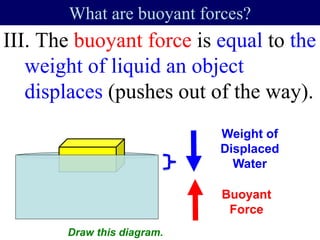
The documents discuss forces and concepts related to forces including:
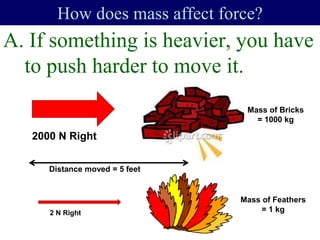
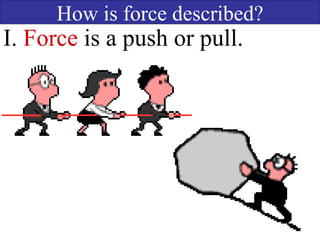
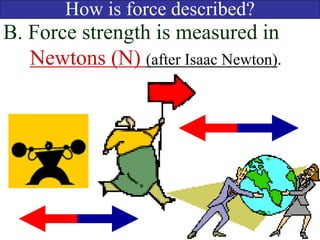
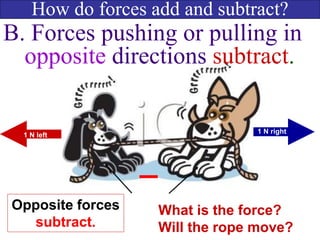
- Forces have both magnitude and direction. Forces in the same direction add while forces in opposite directions subtract.
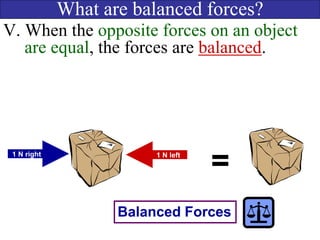
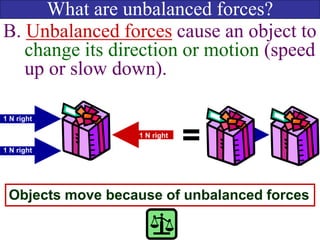
- Balanced forces occur when opposing forces are equal, resulting in no net force and no change in motion. Unbalanced forces occur when opposing forces are unequal, resulting in a net force and a change in motion.
- Friction is a force that opposes motion between objects in contact. It always acts in the opposite direction of motion.
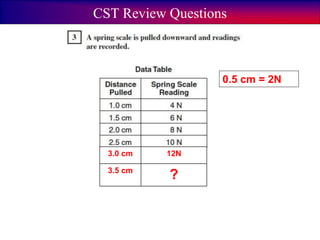
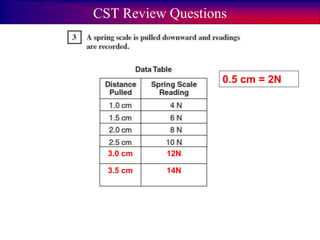
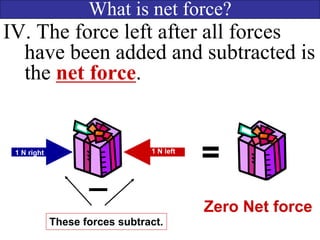
- Examples are provided to demonstrate how to calculate net force by adding and subtracting forces in the same and opposite directions.