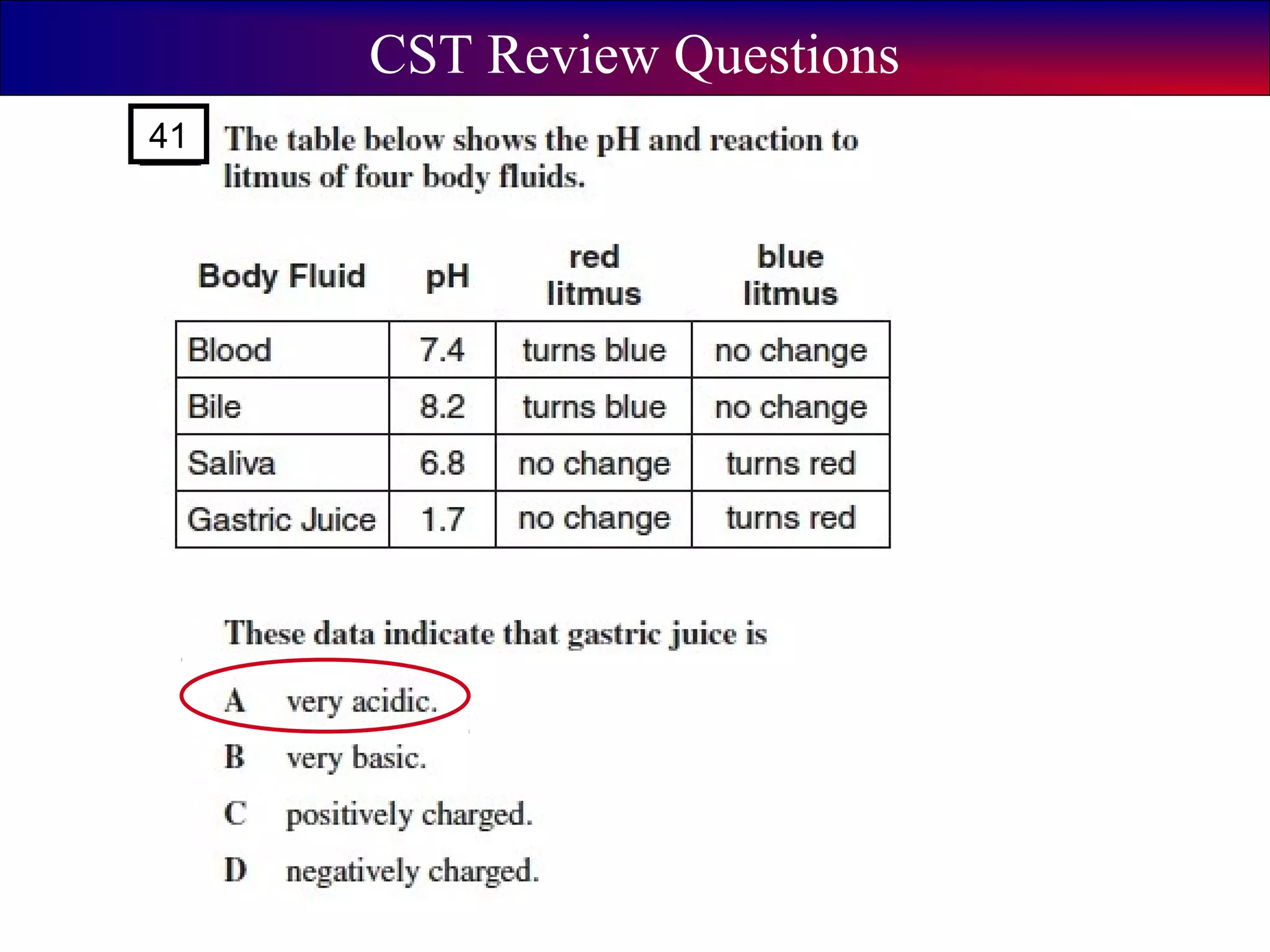
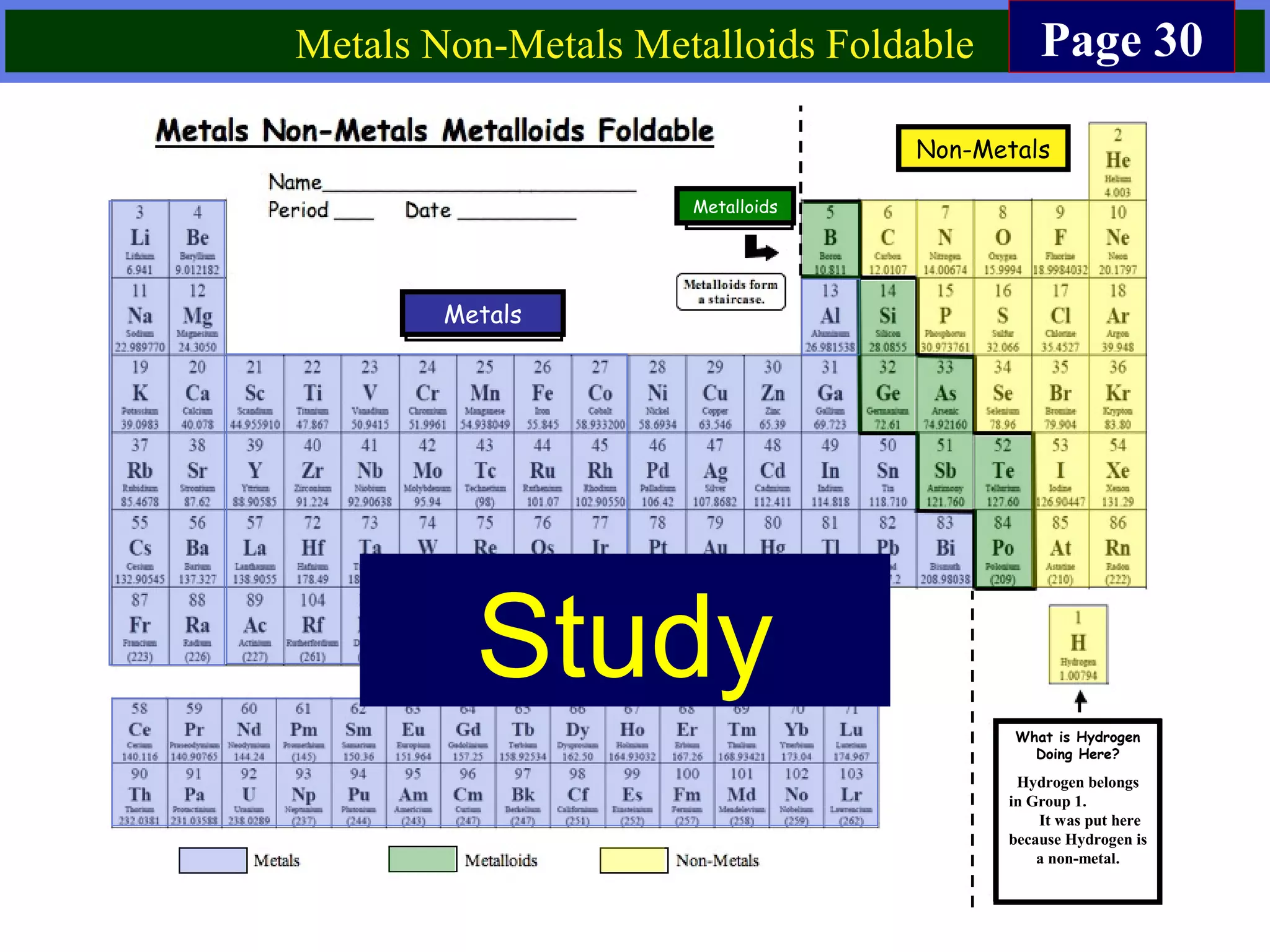
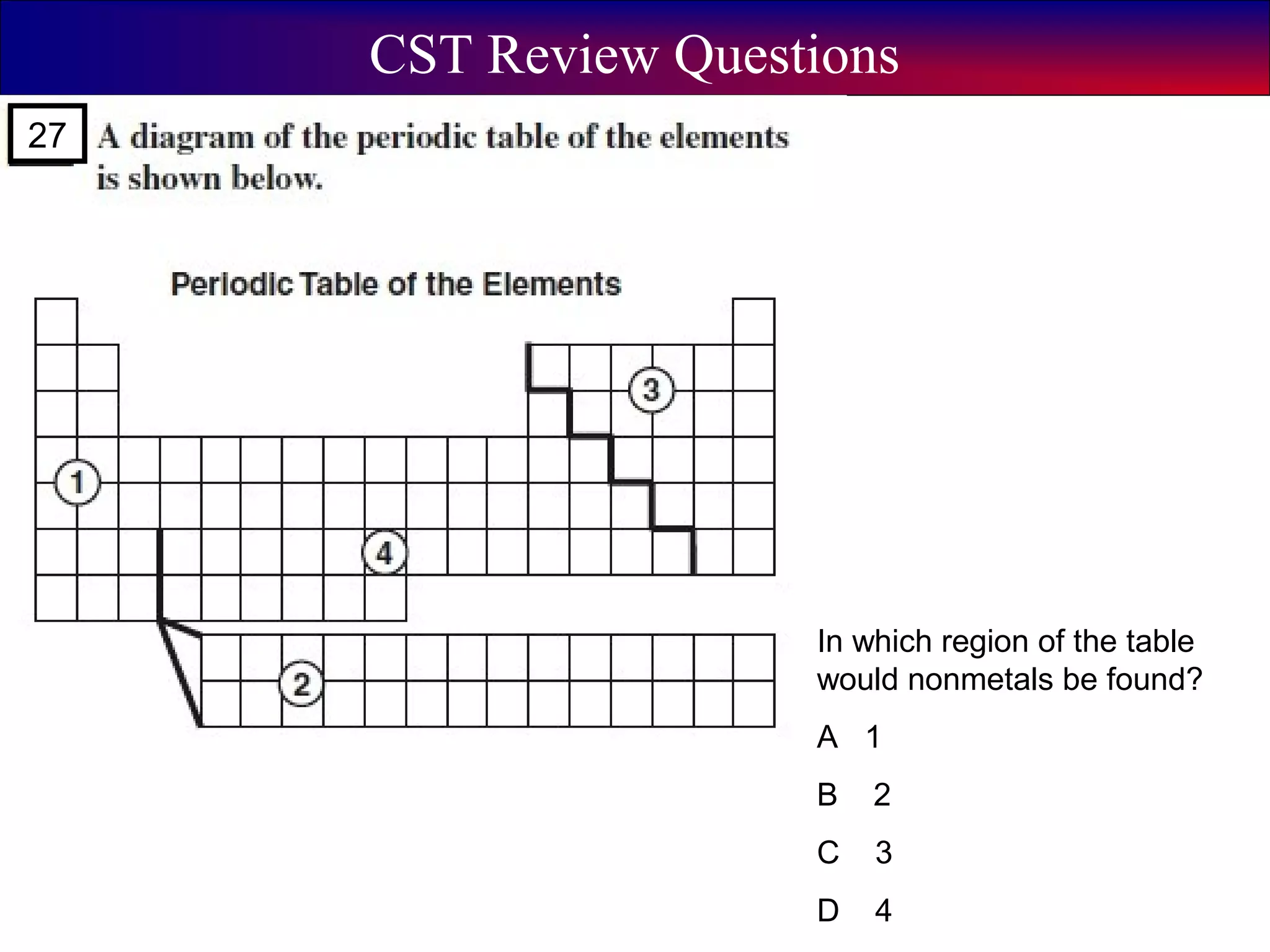
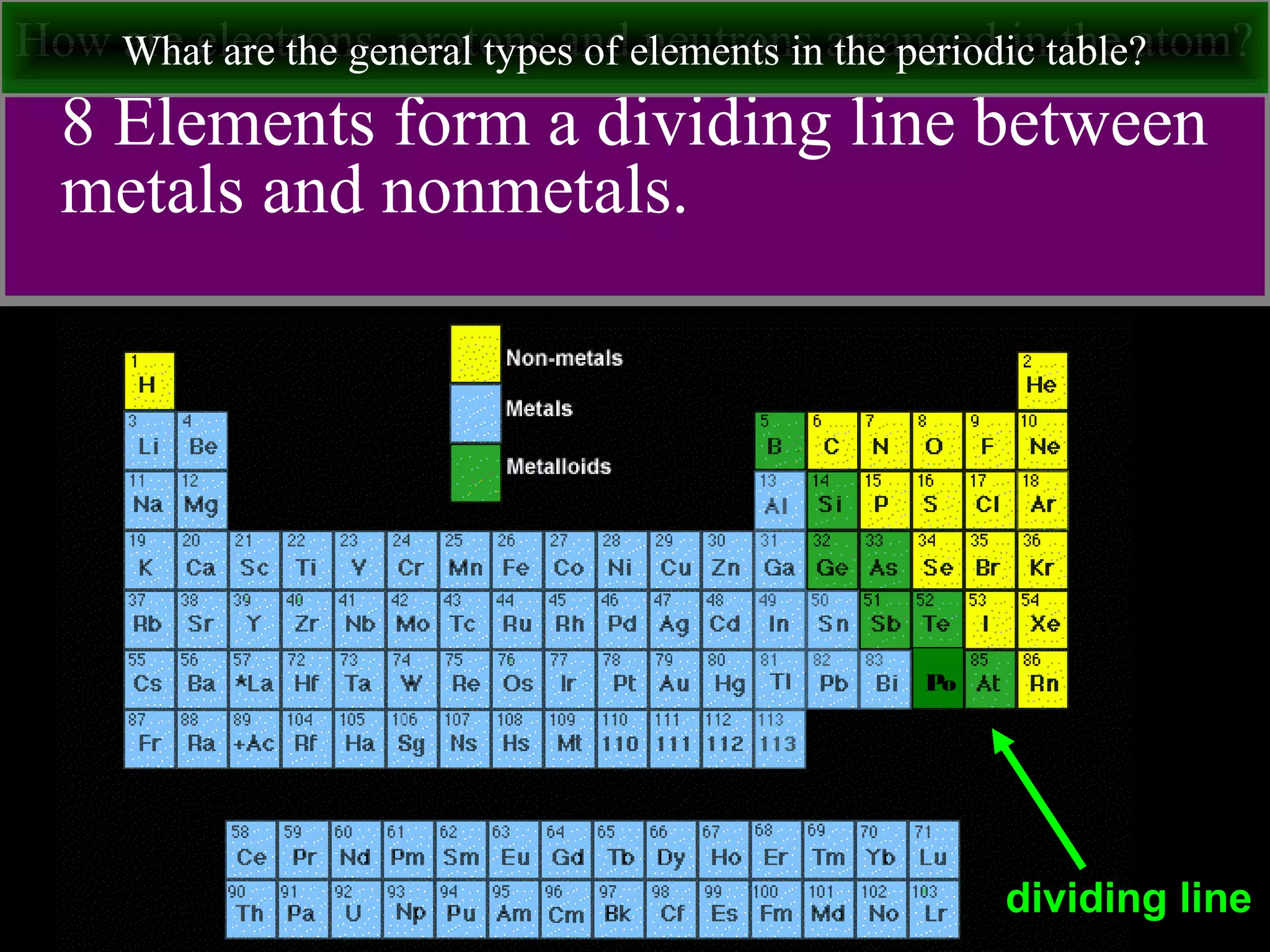
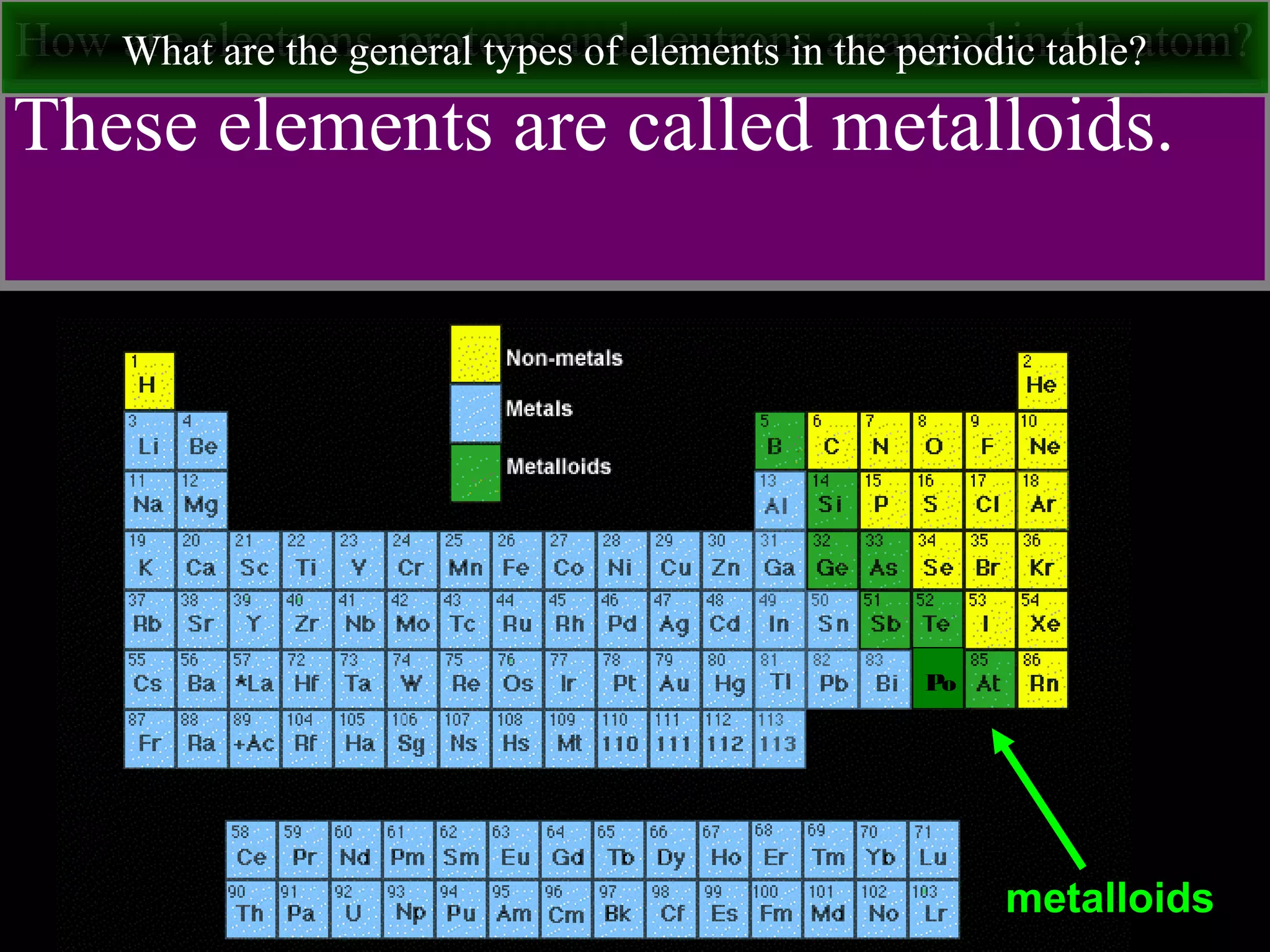
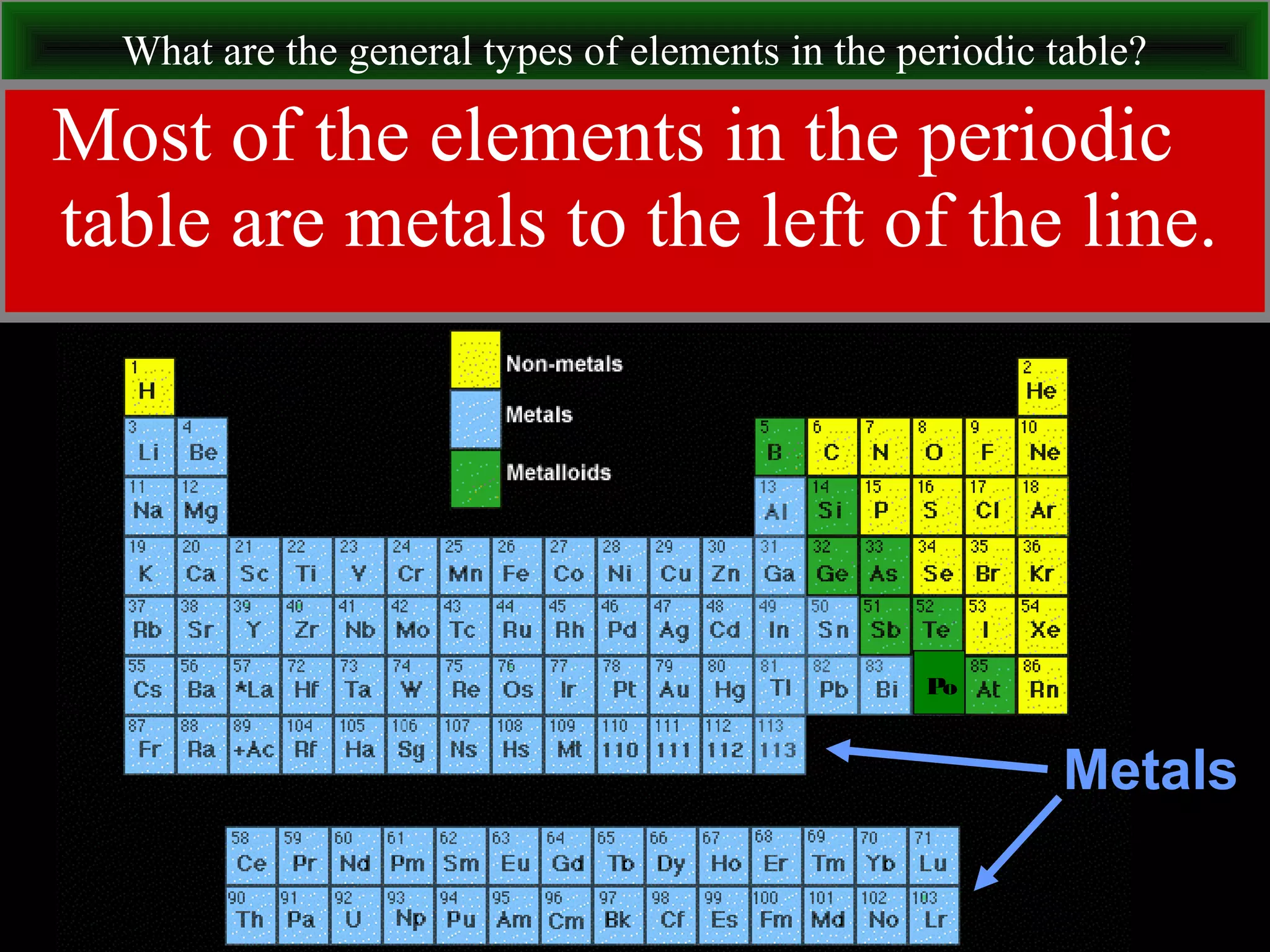
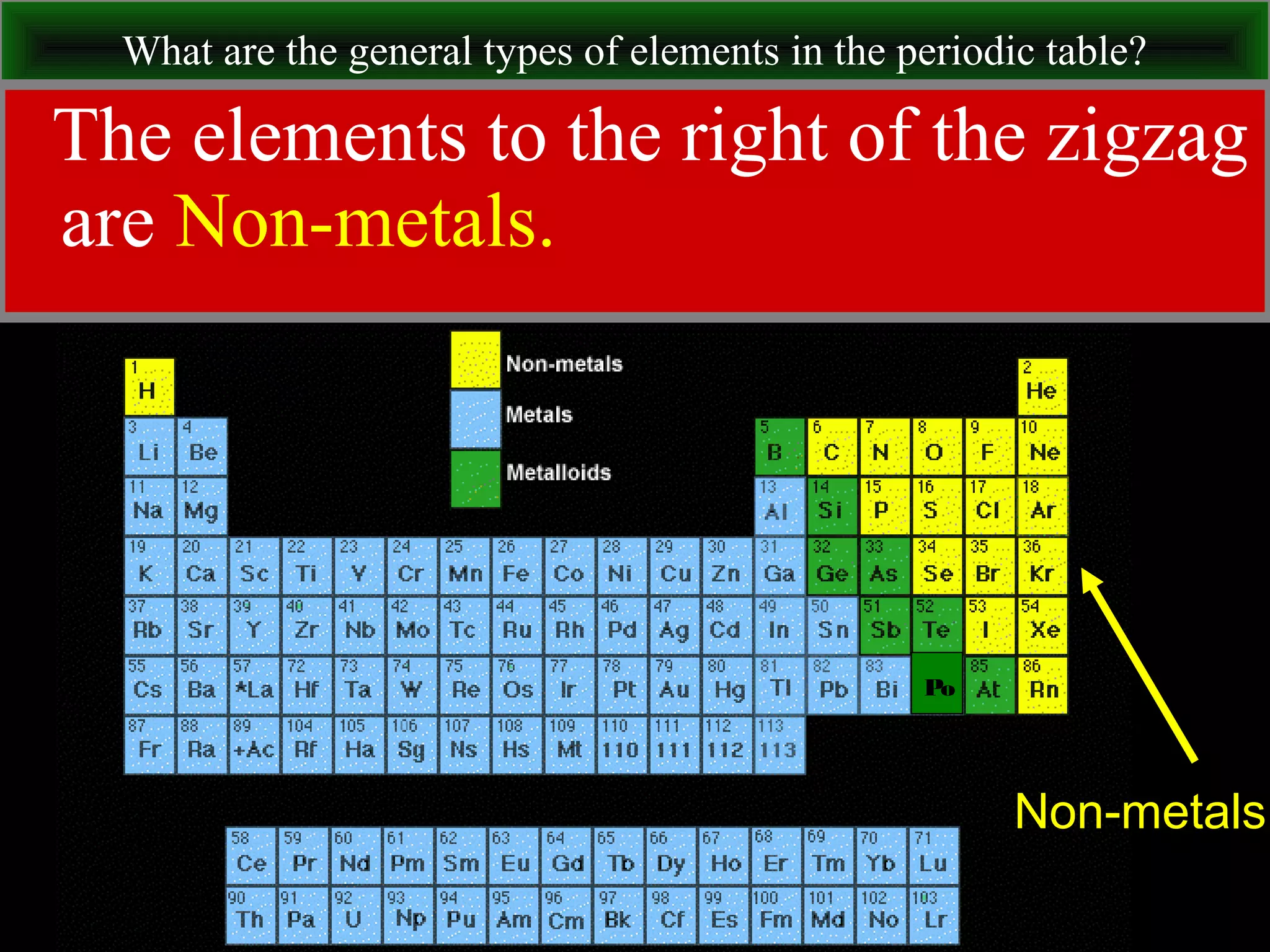
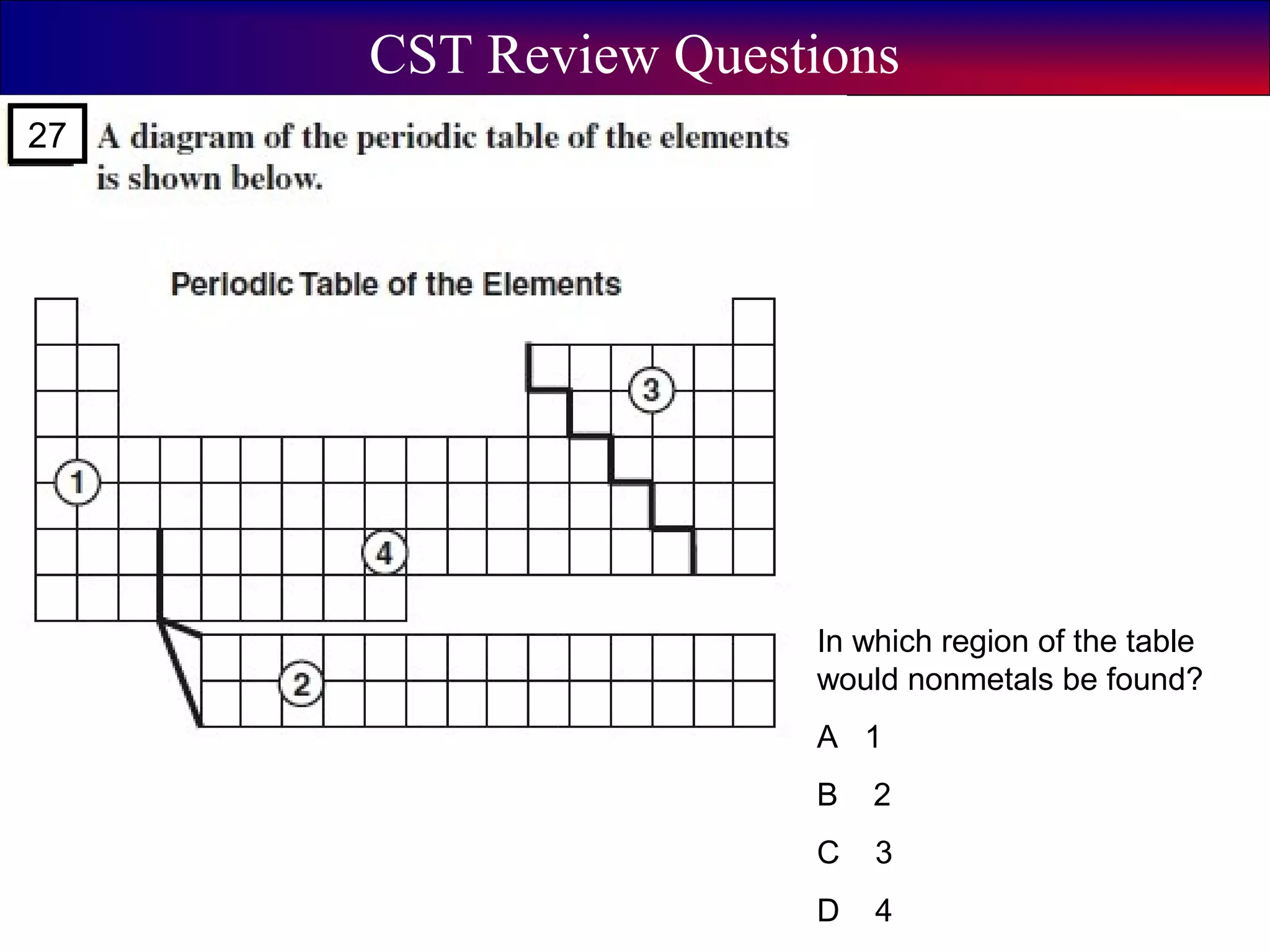
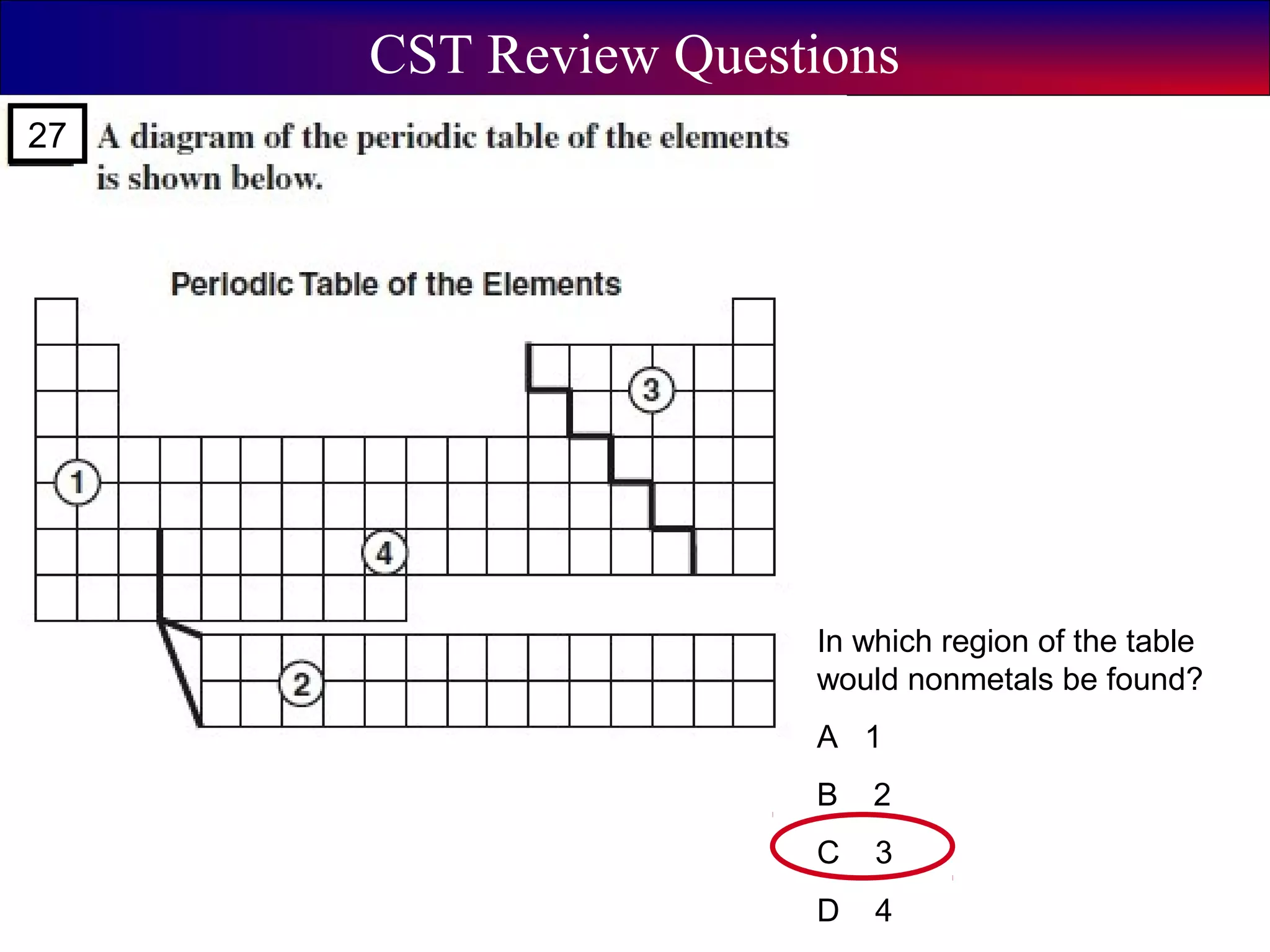
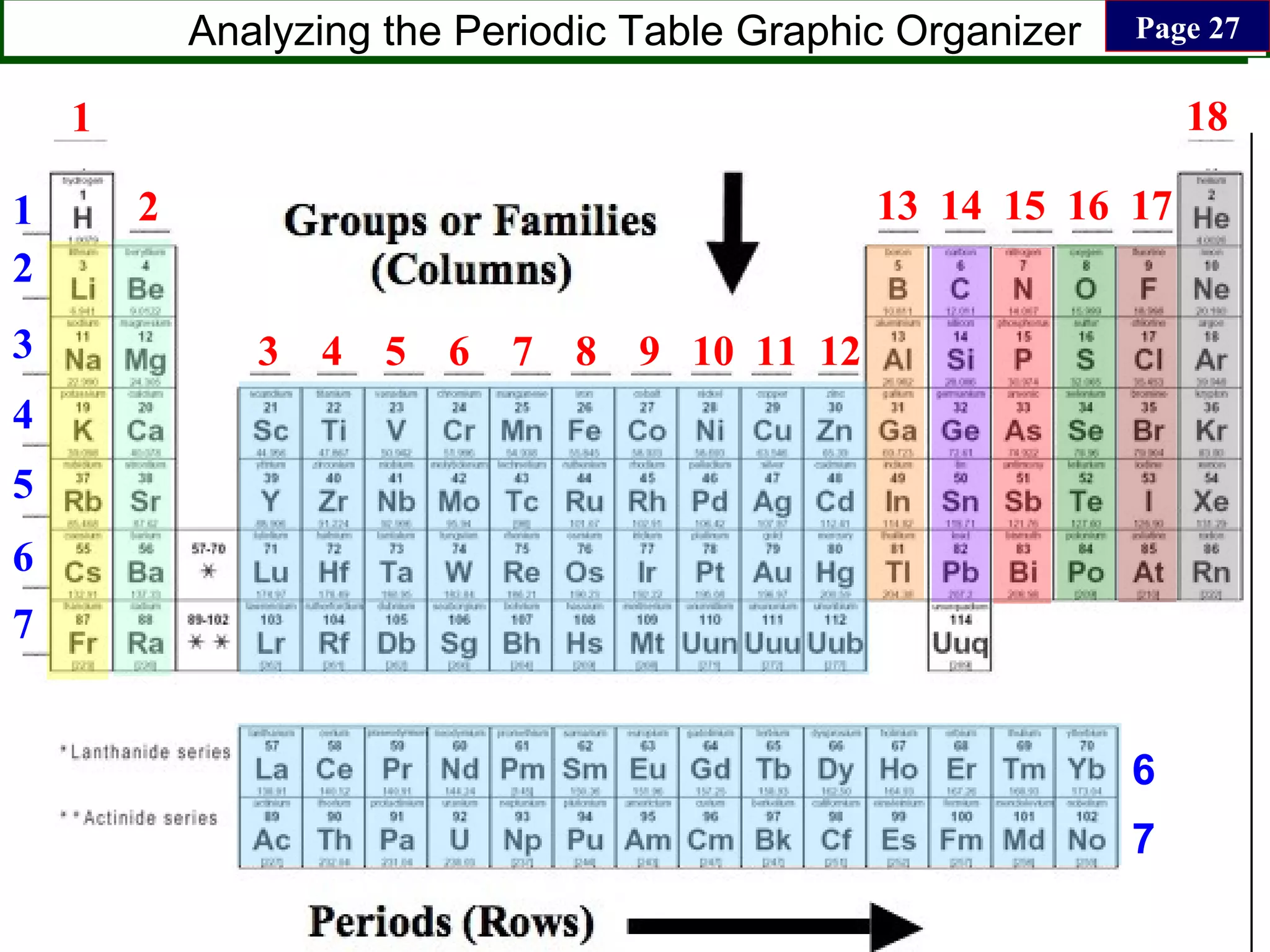
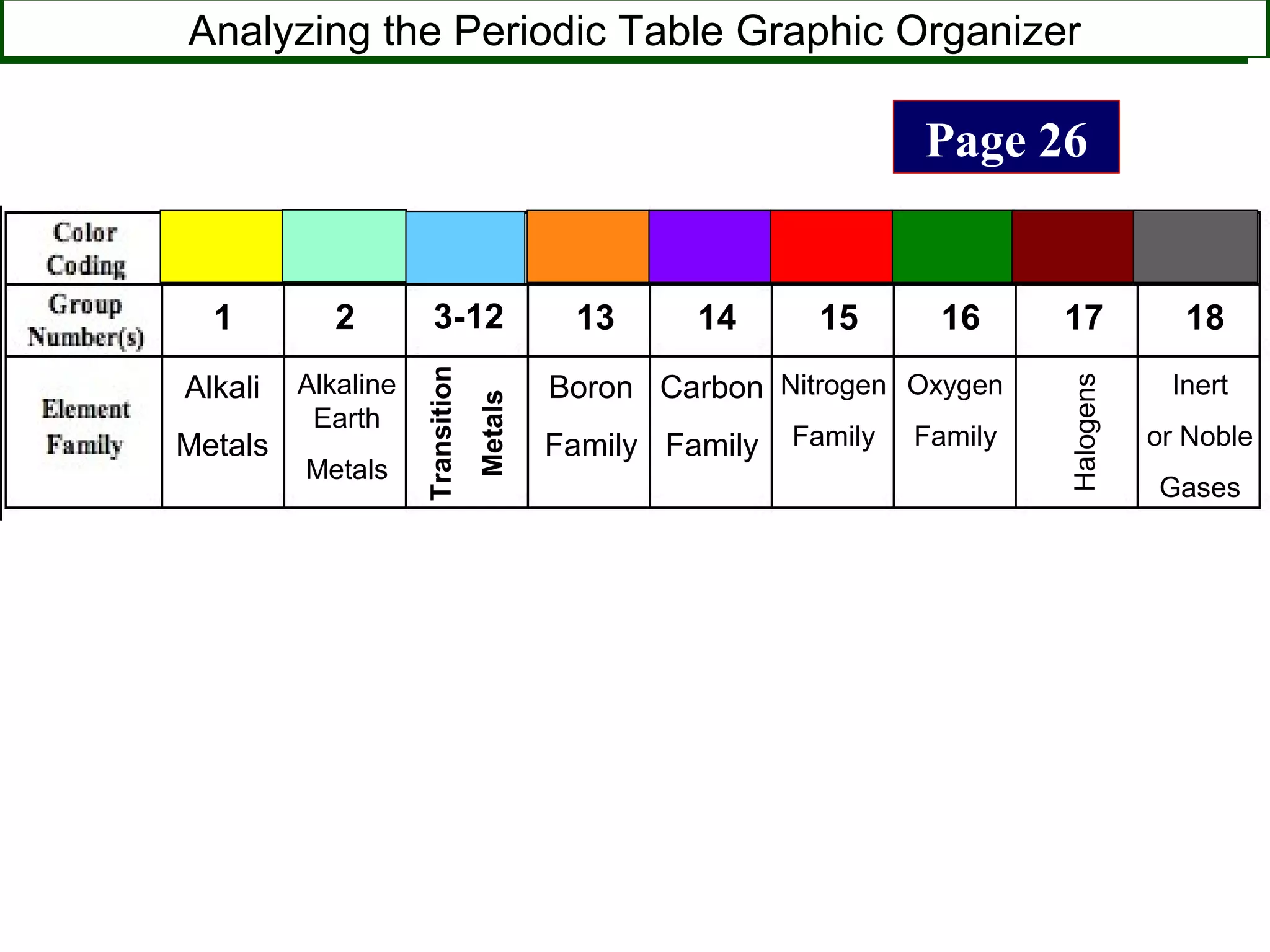
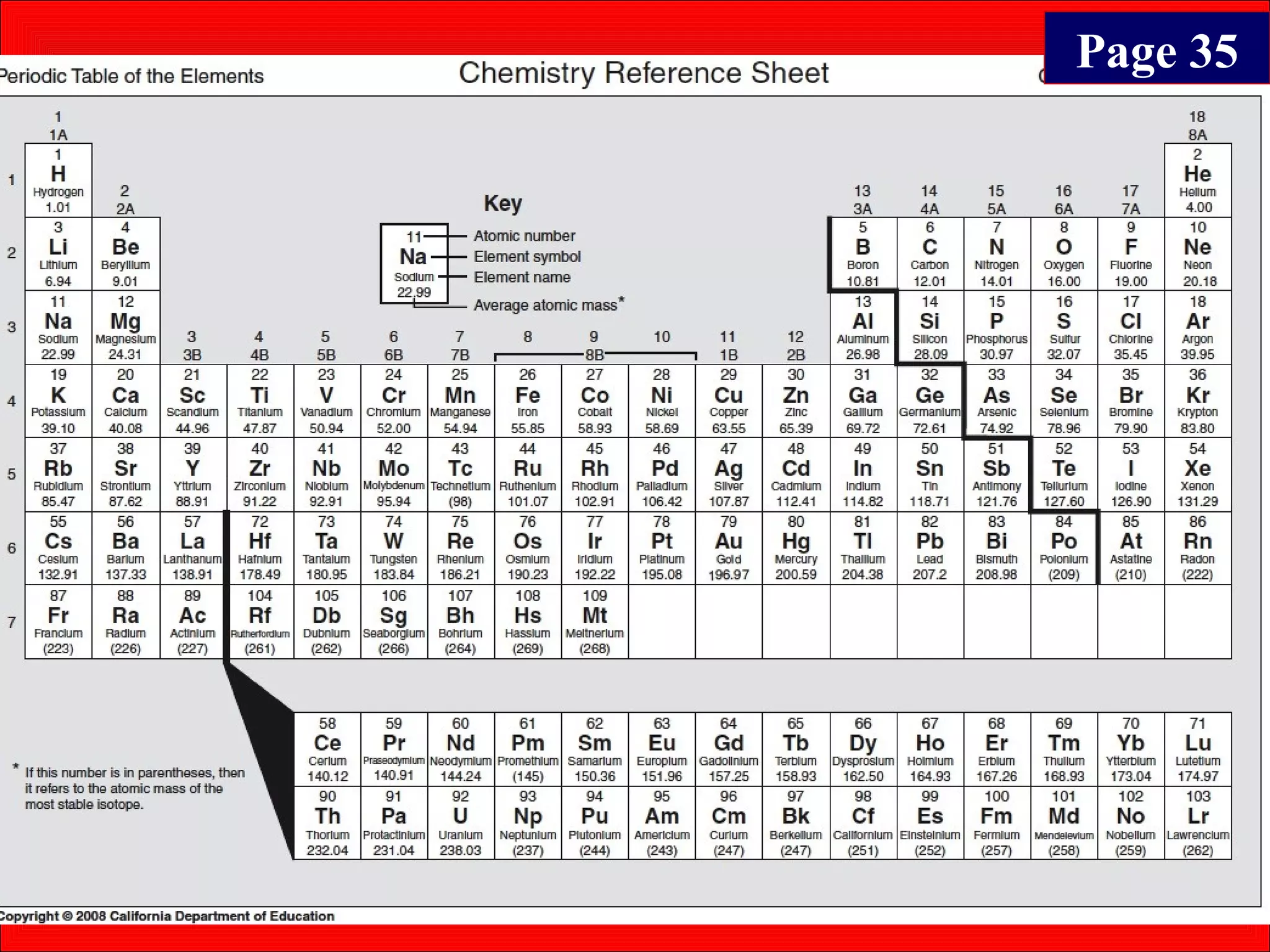
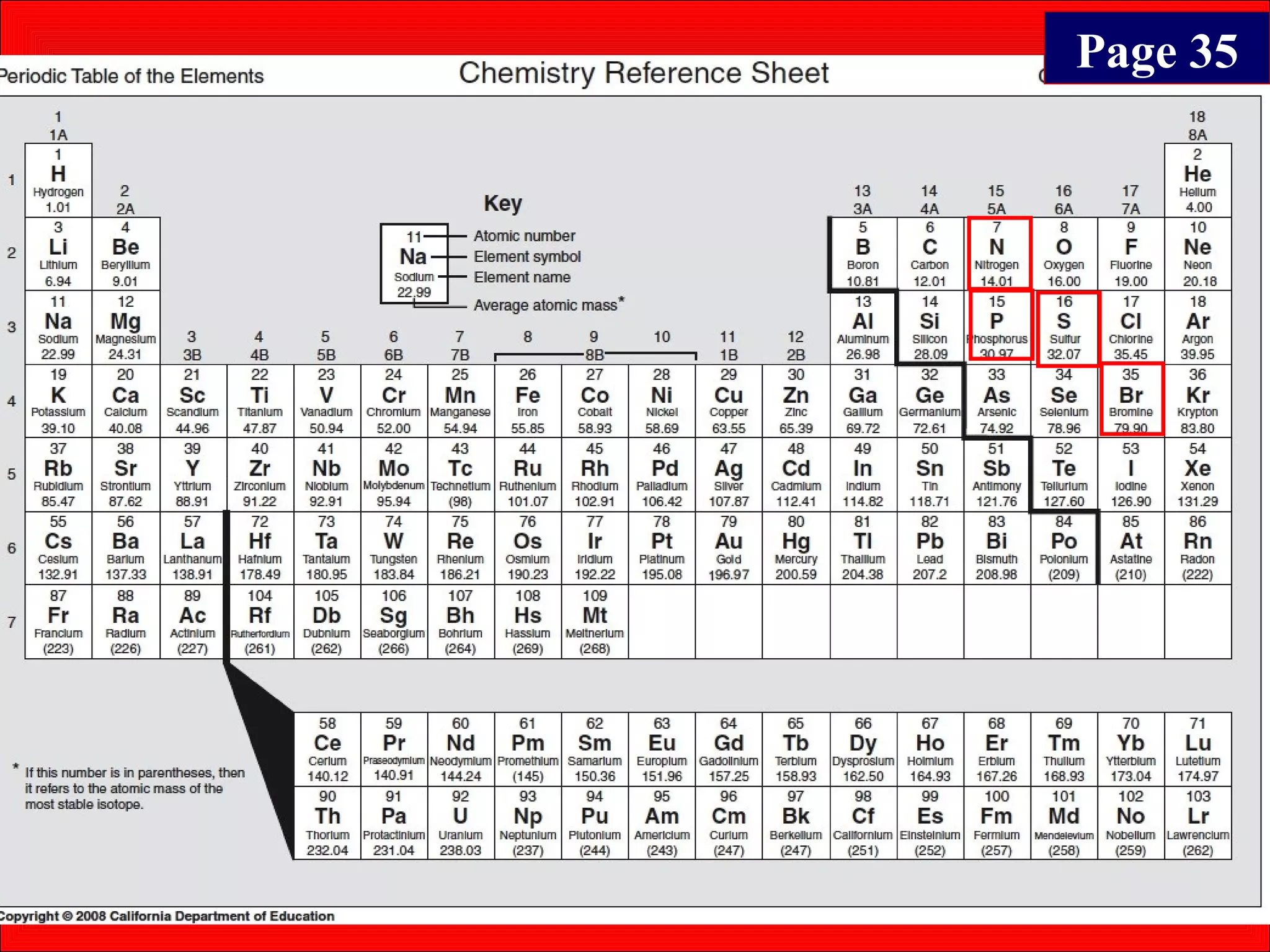
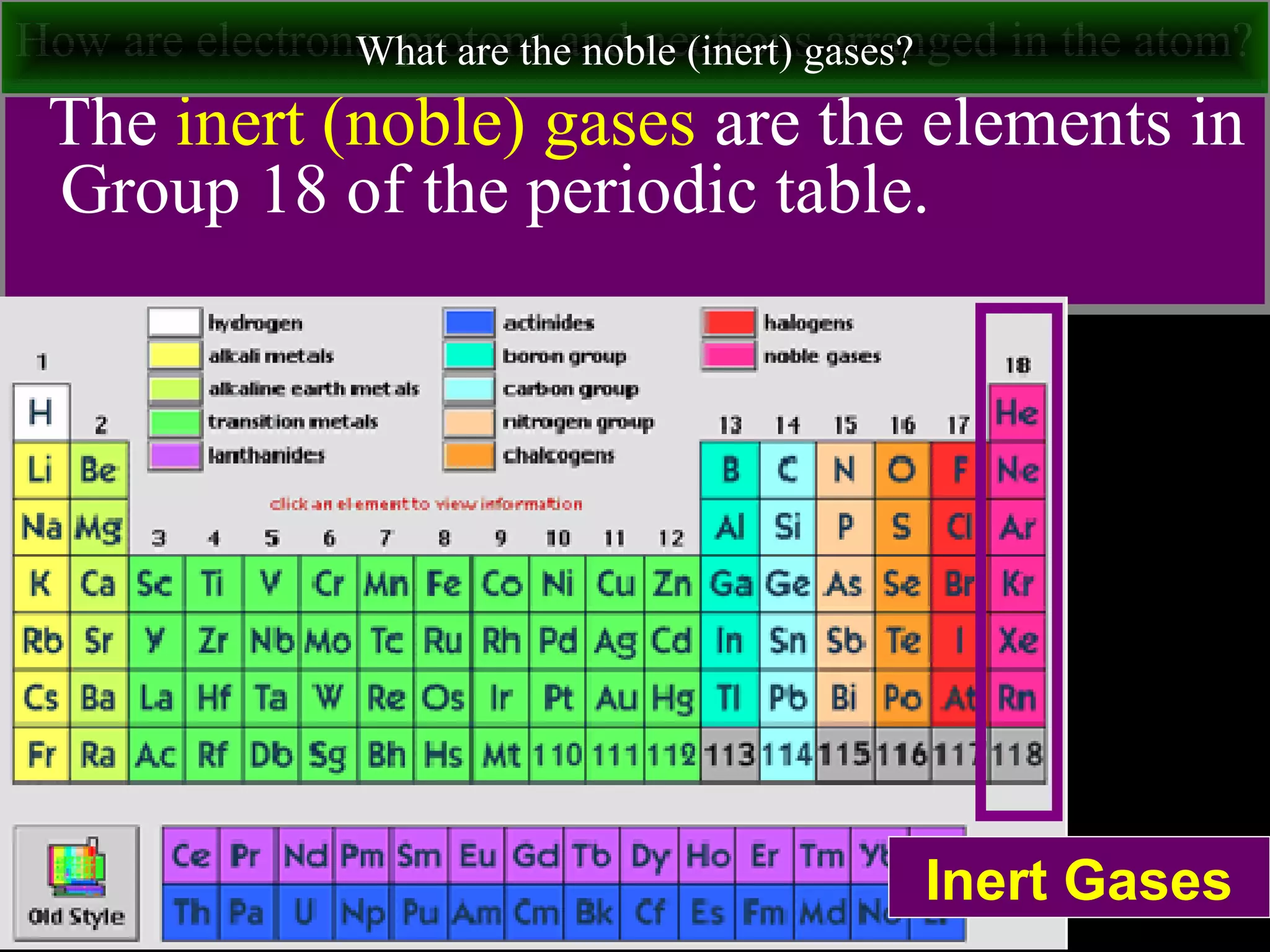
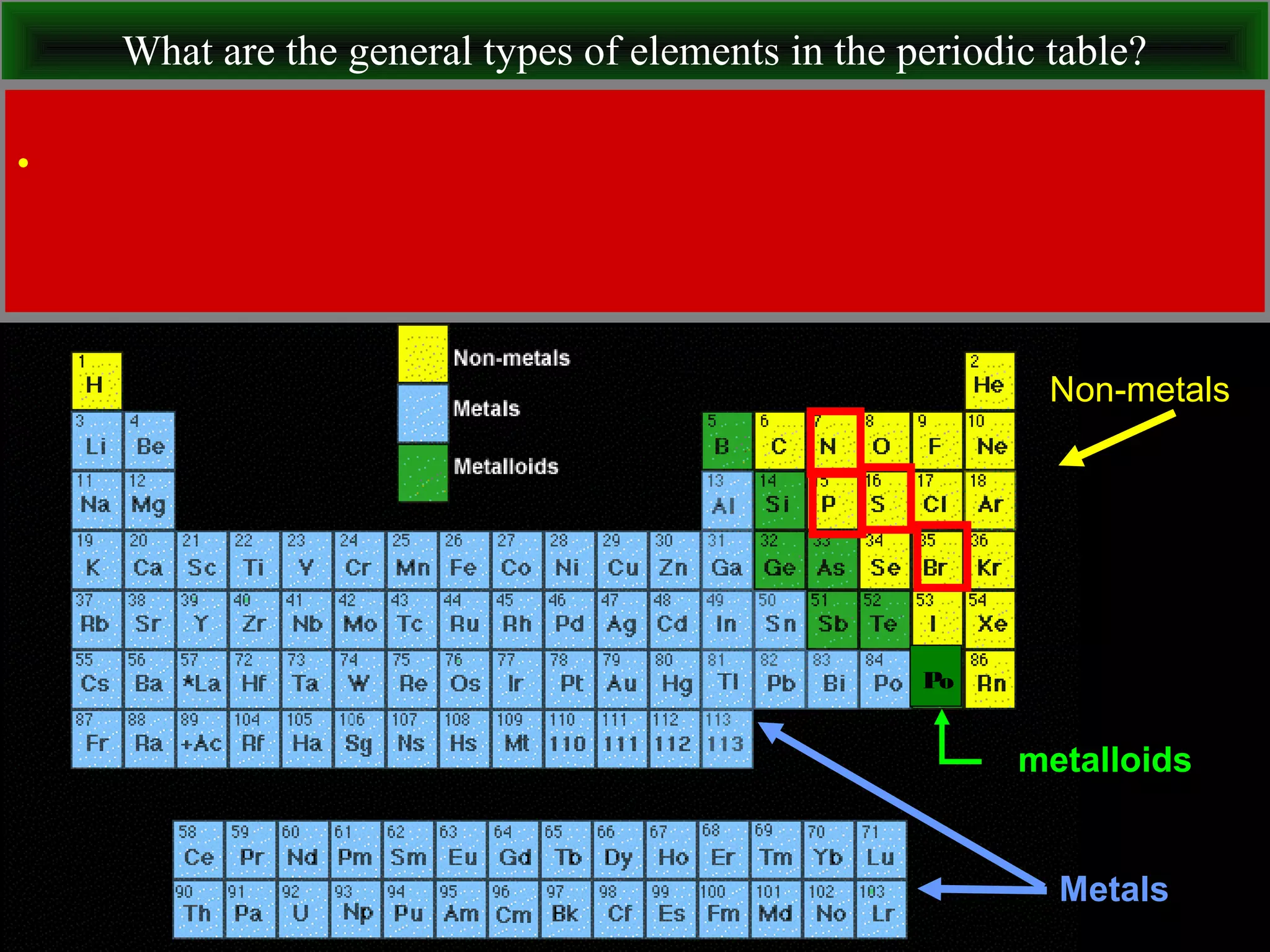
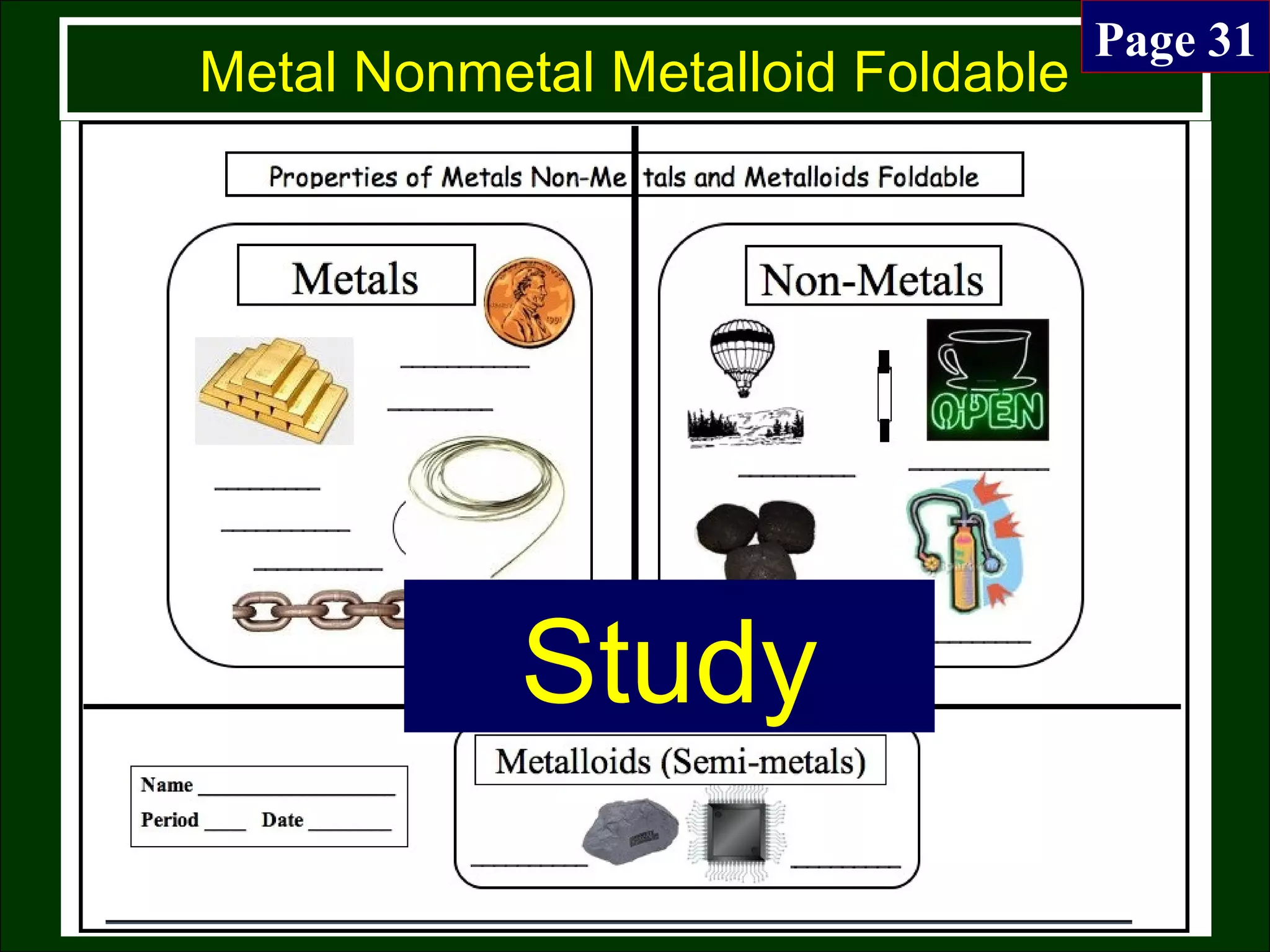
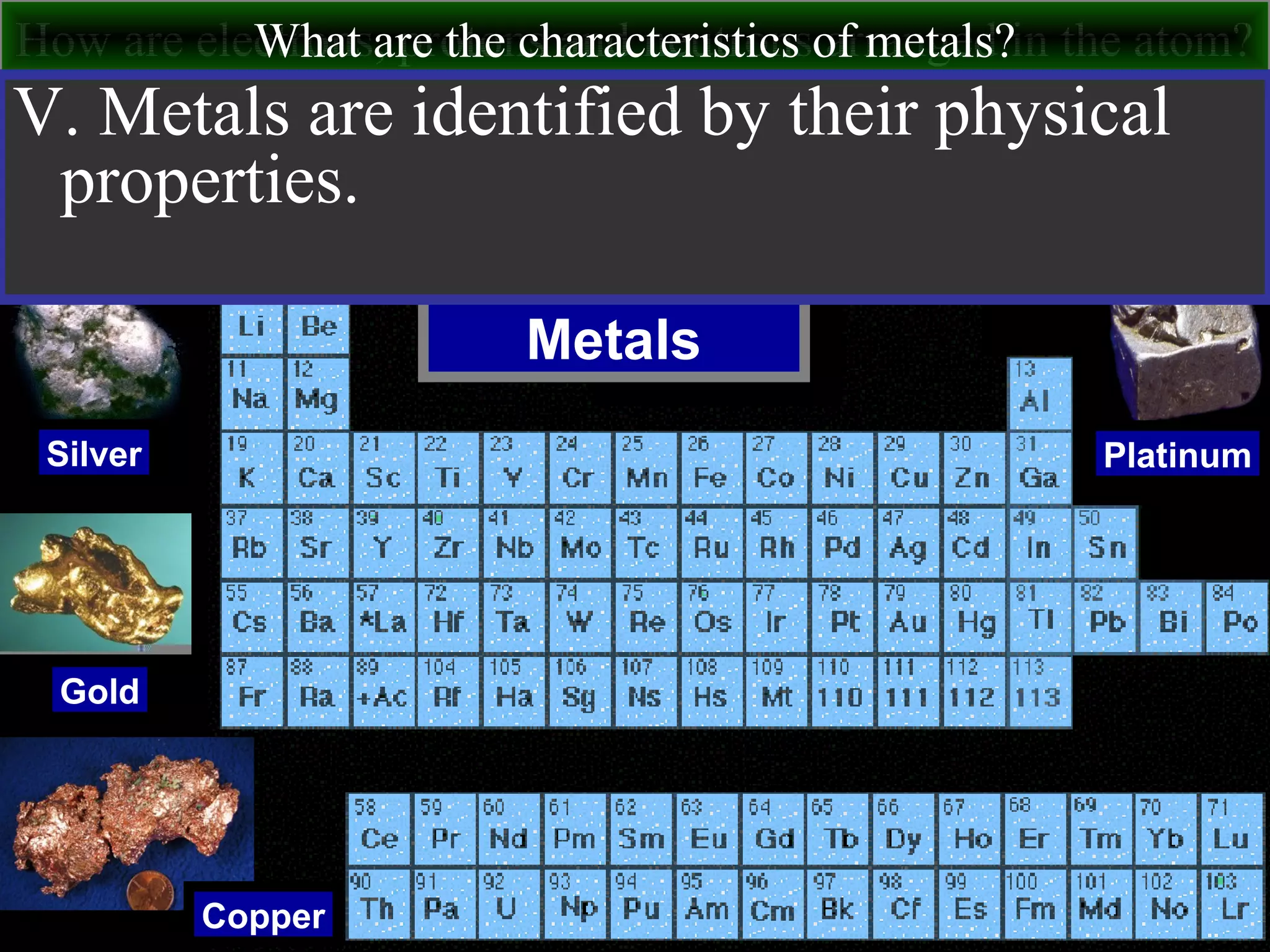
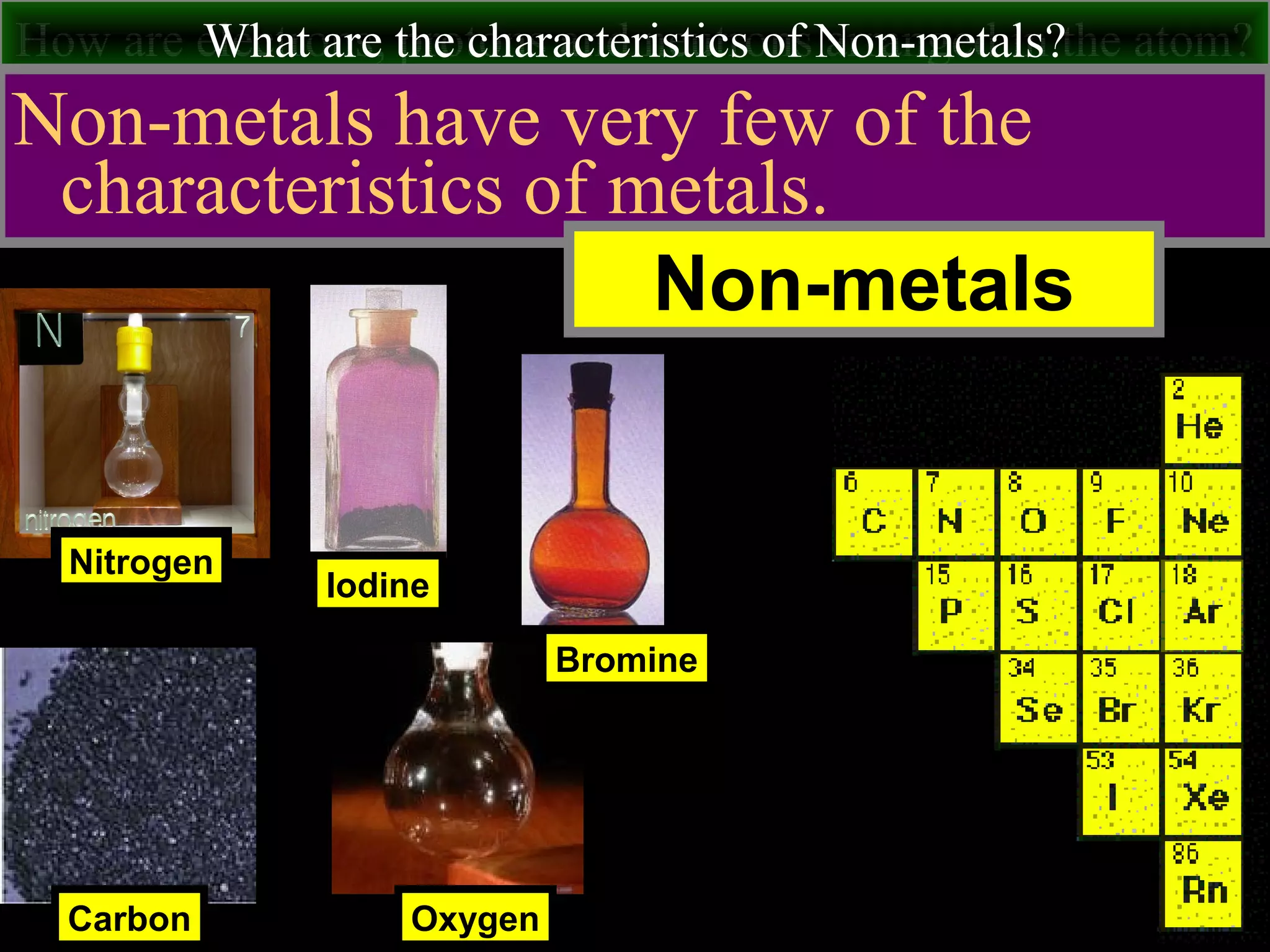
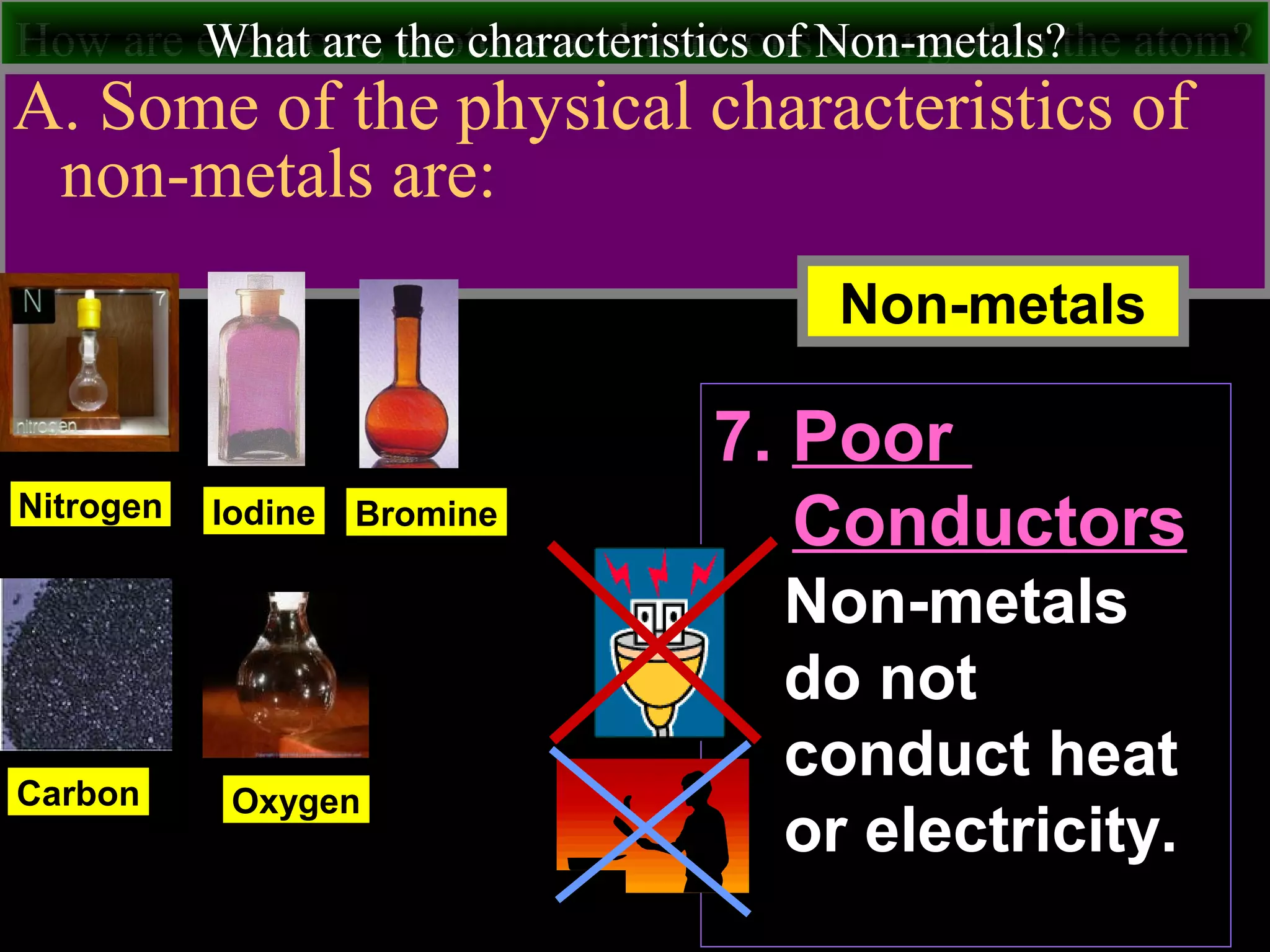
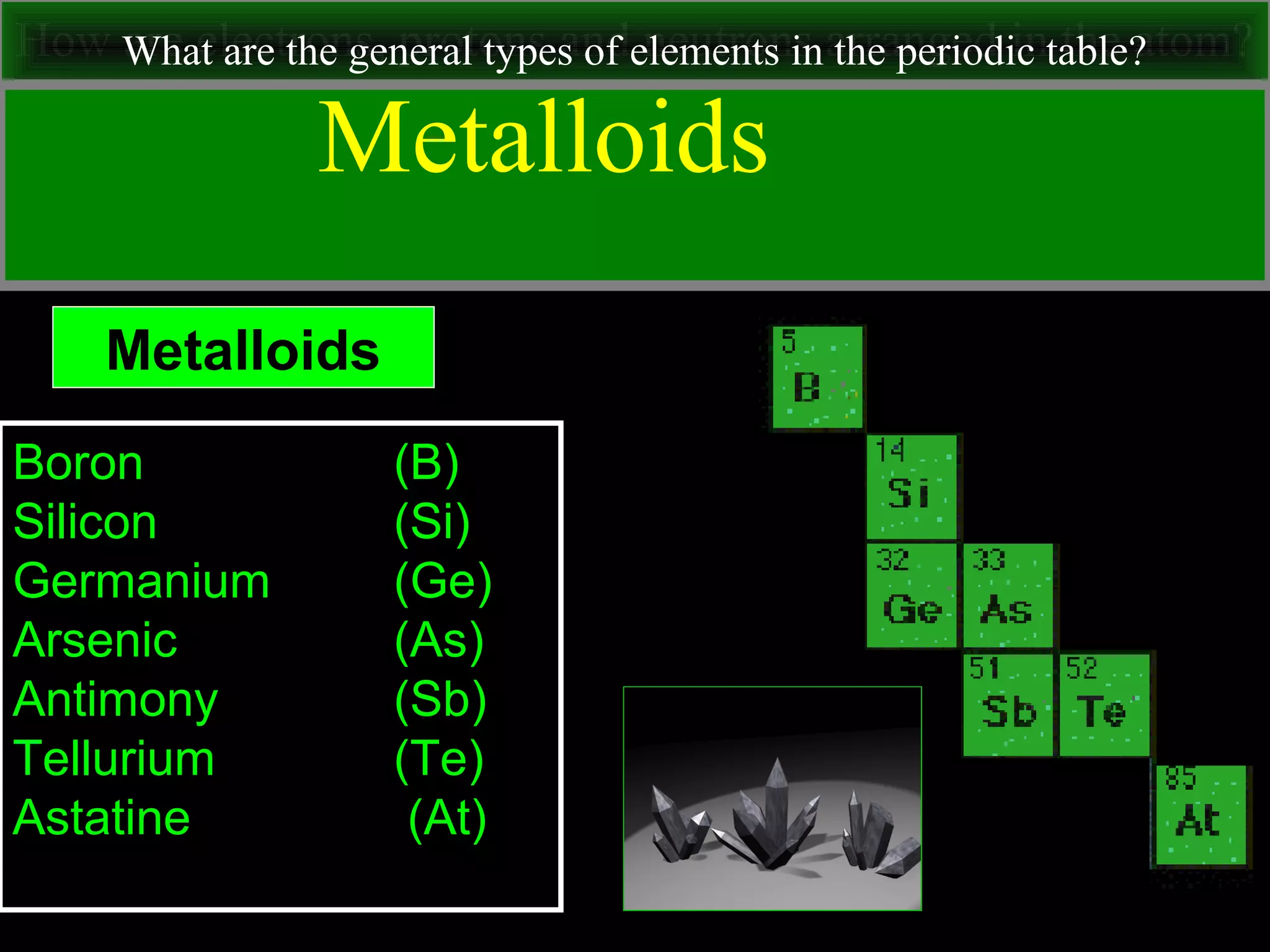
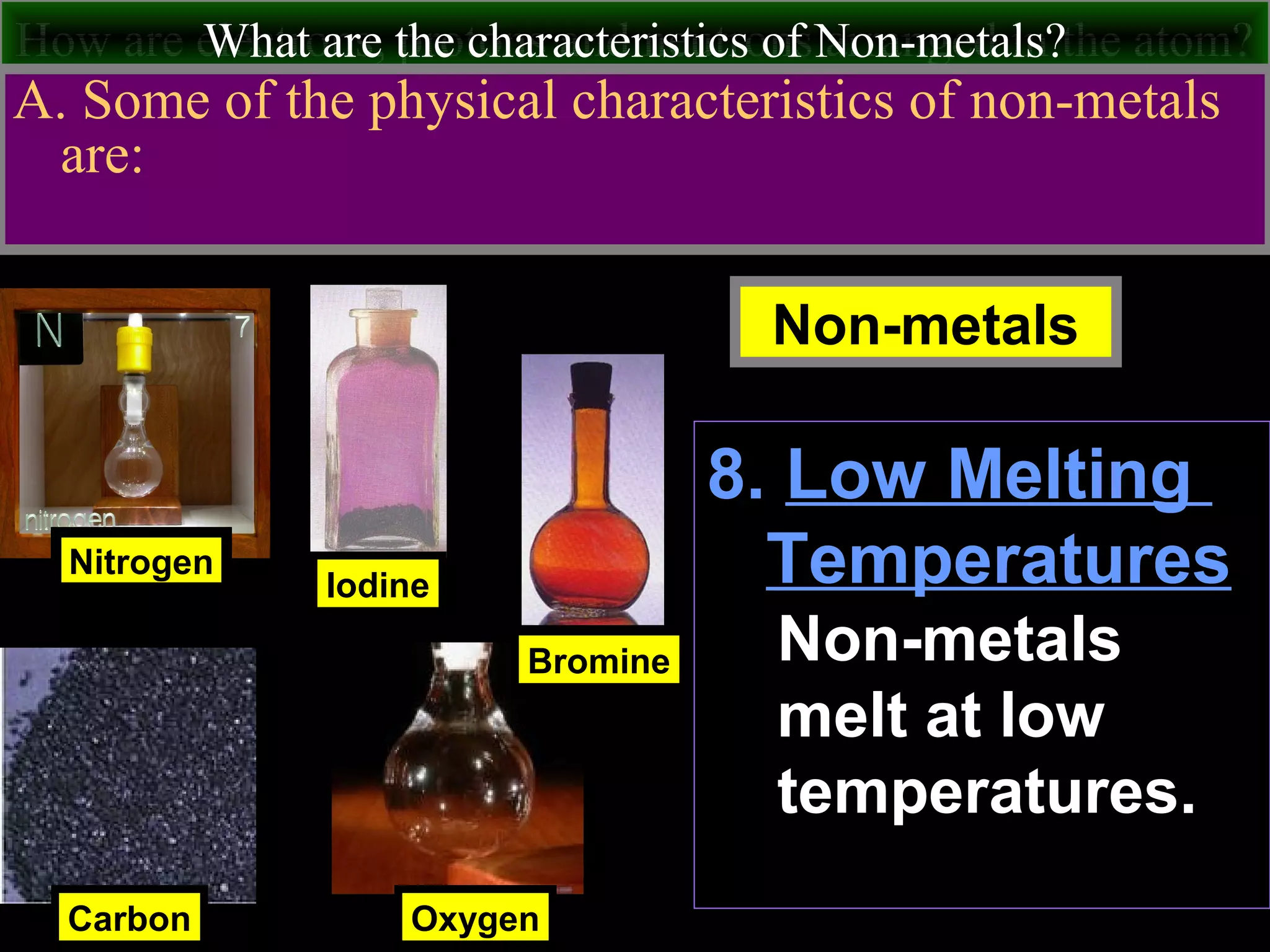
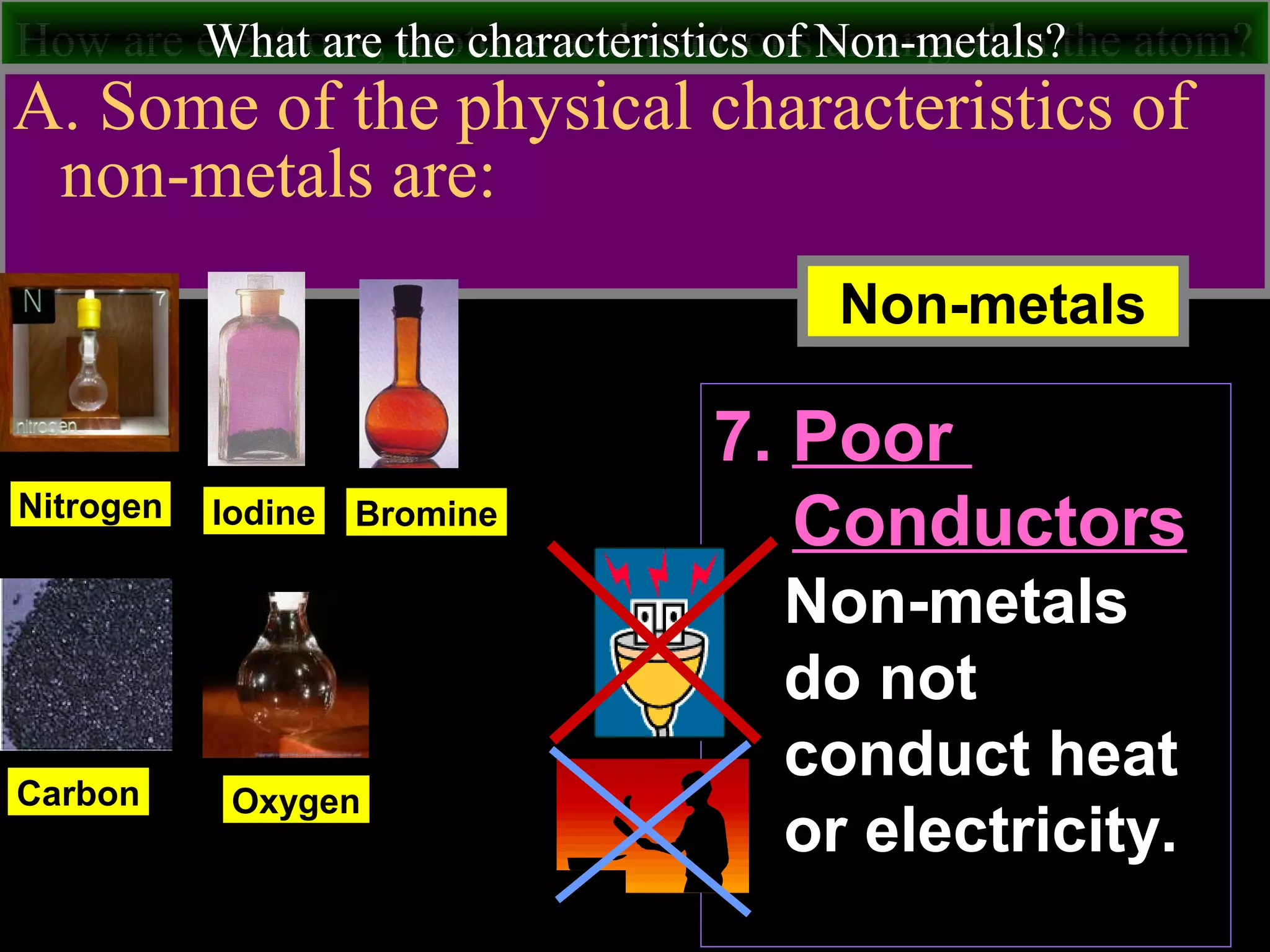
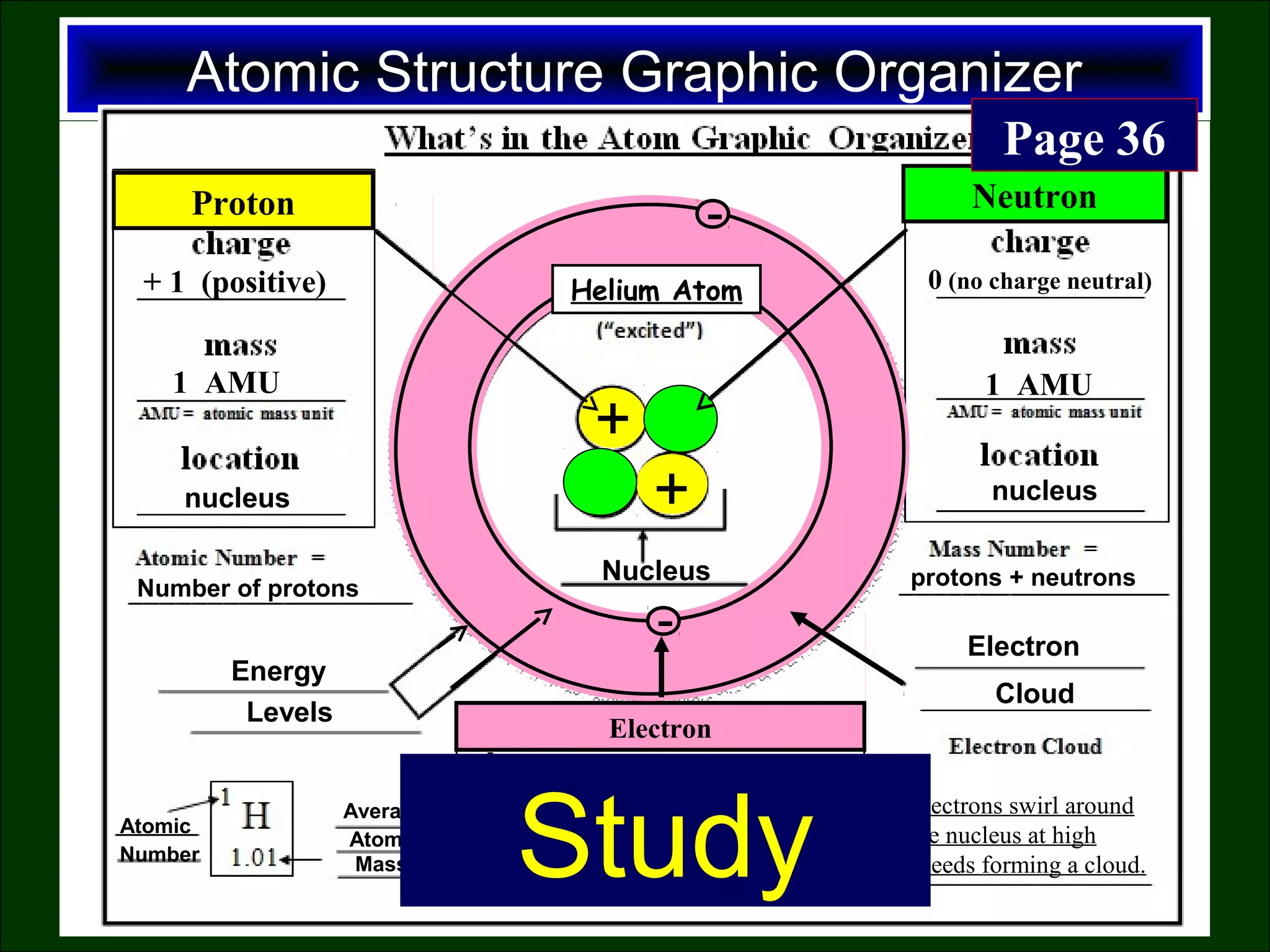
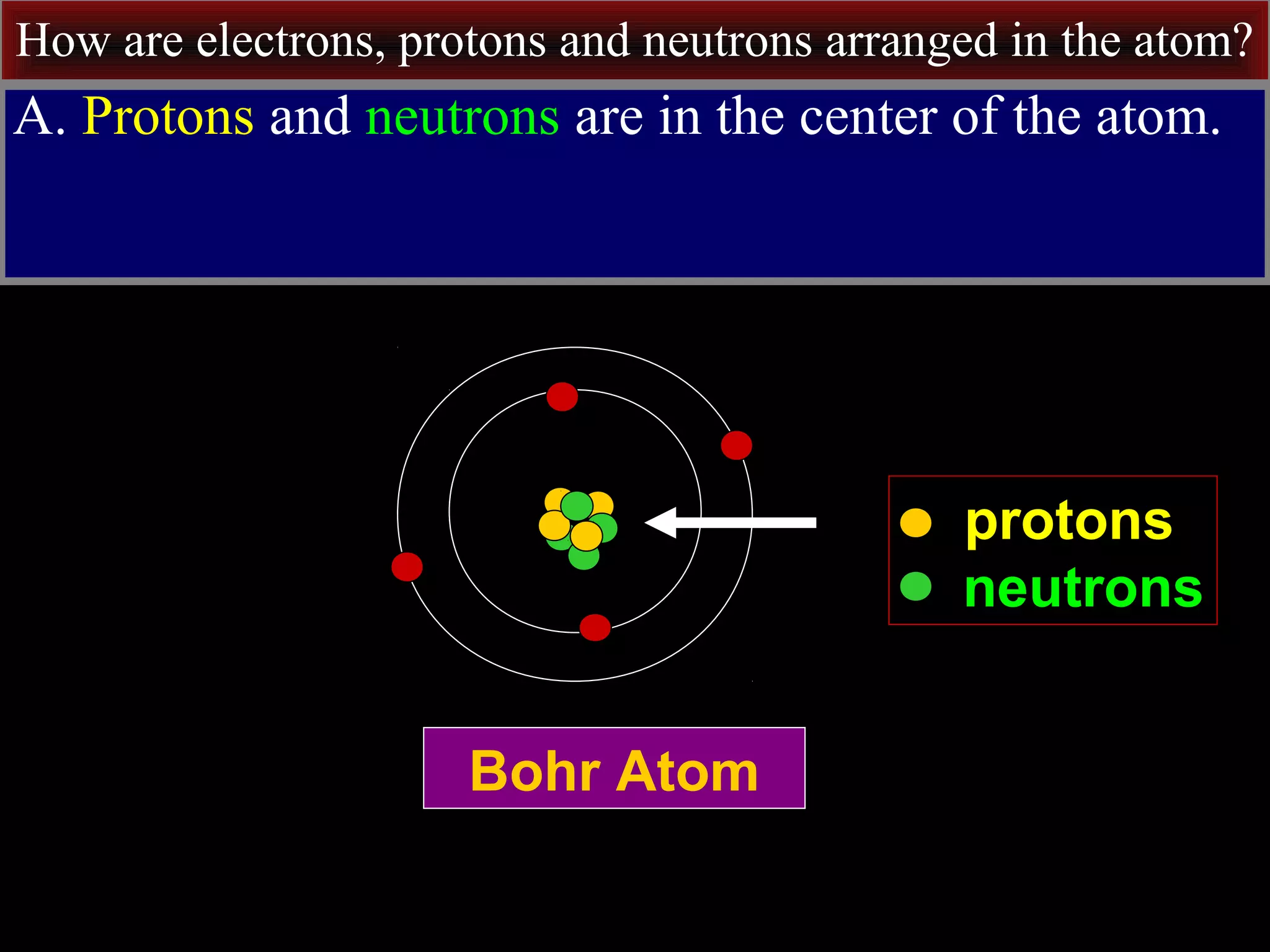
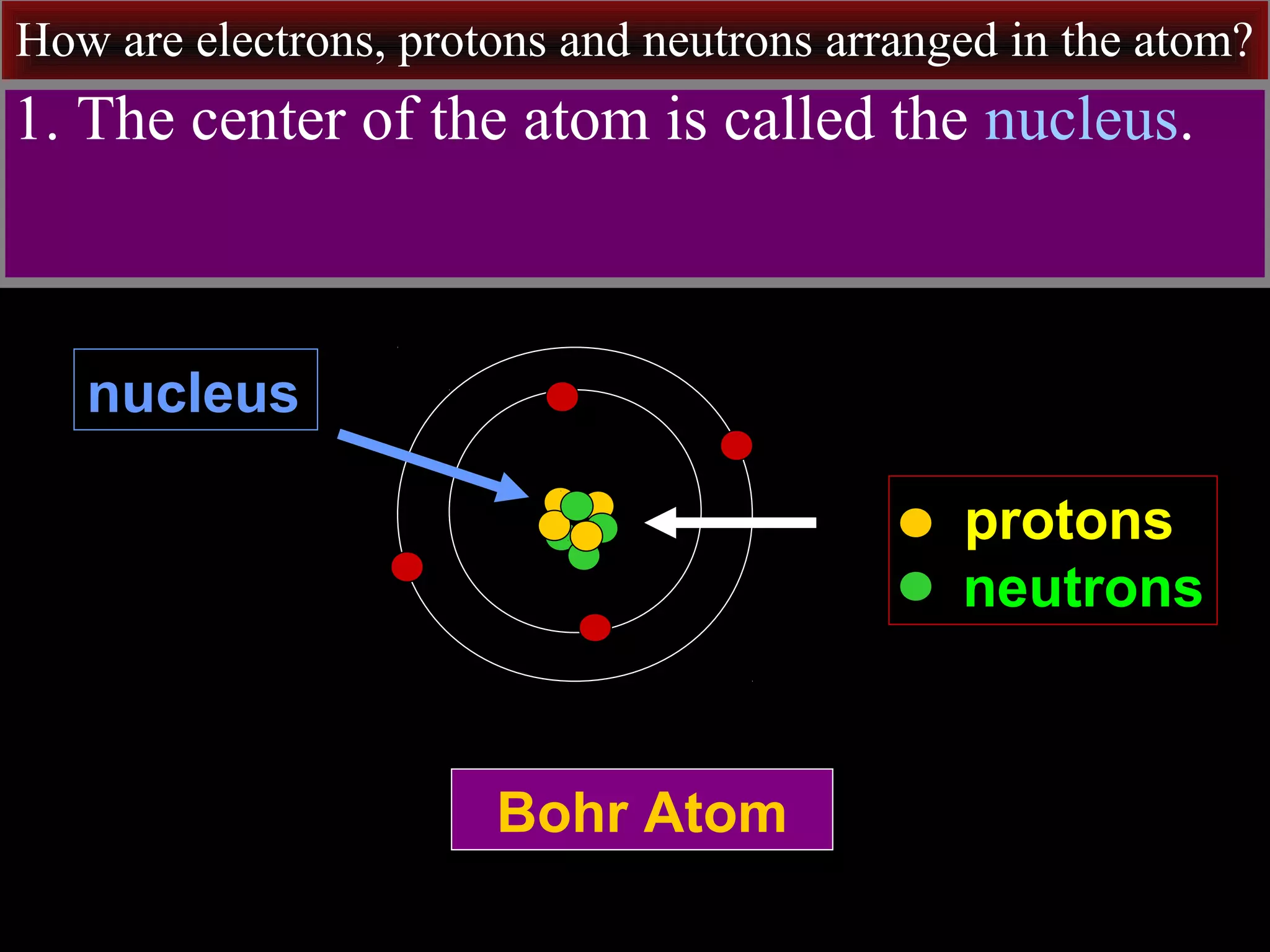
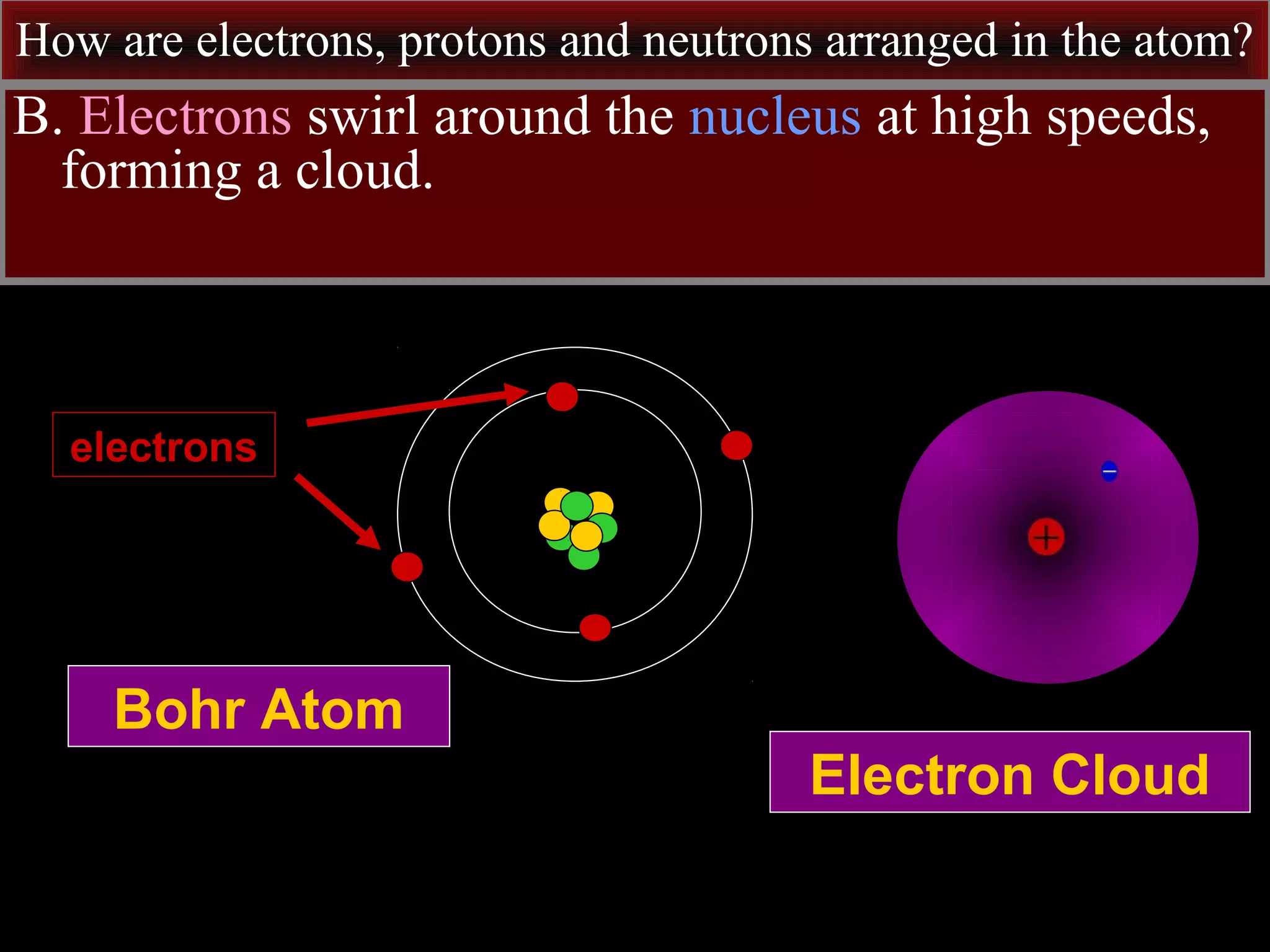
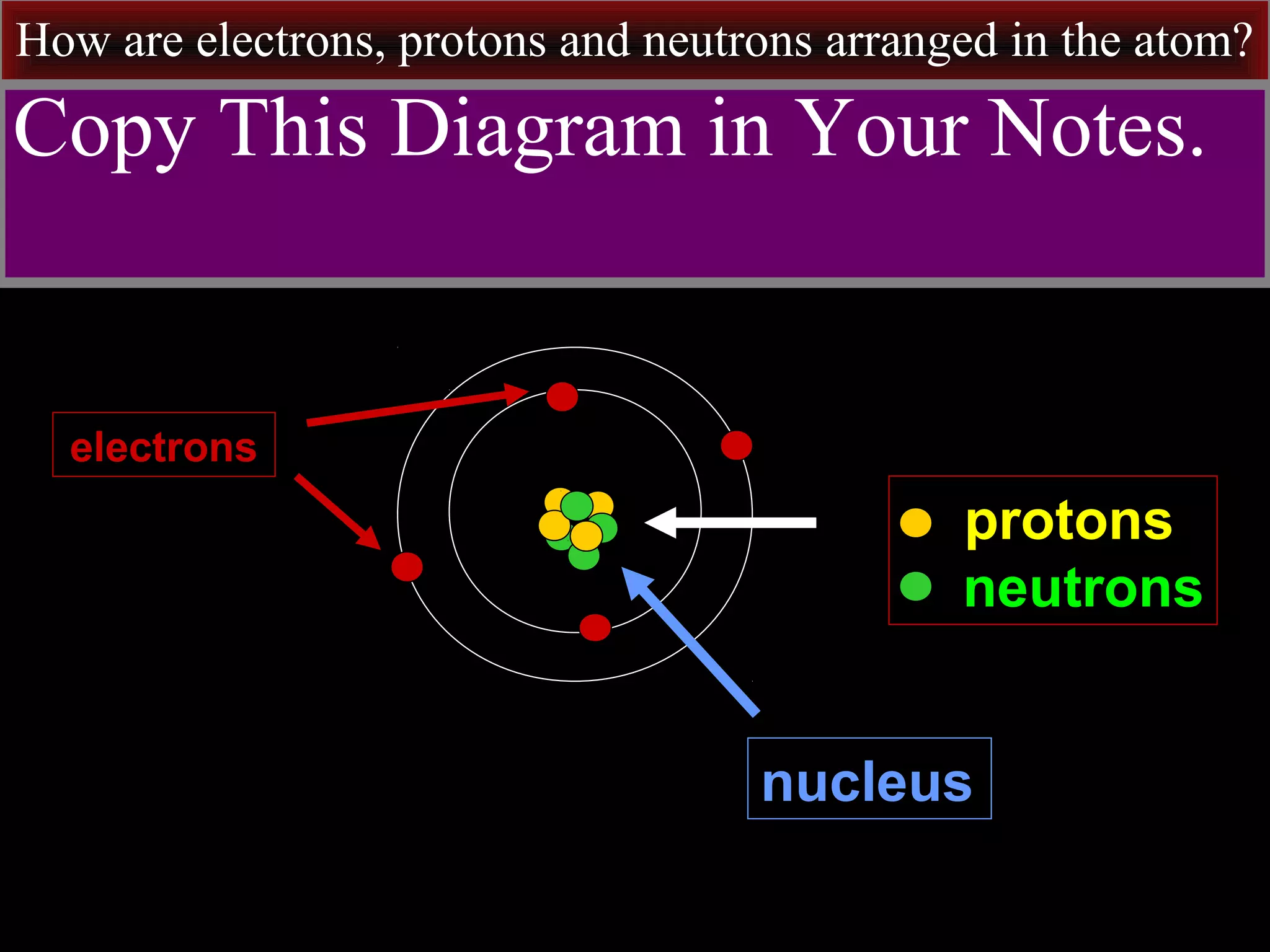
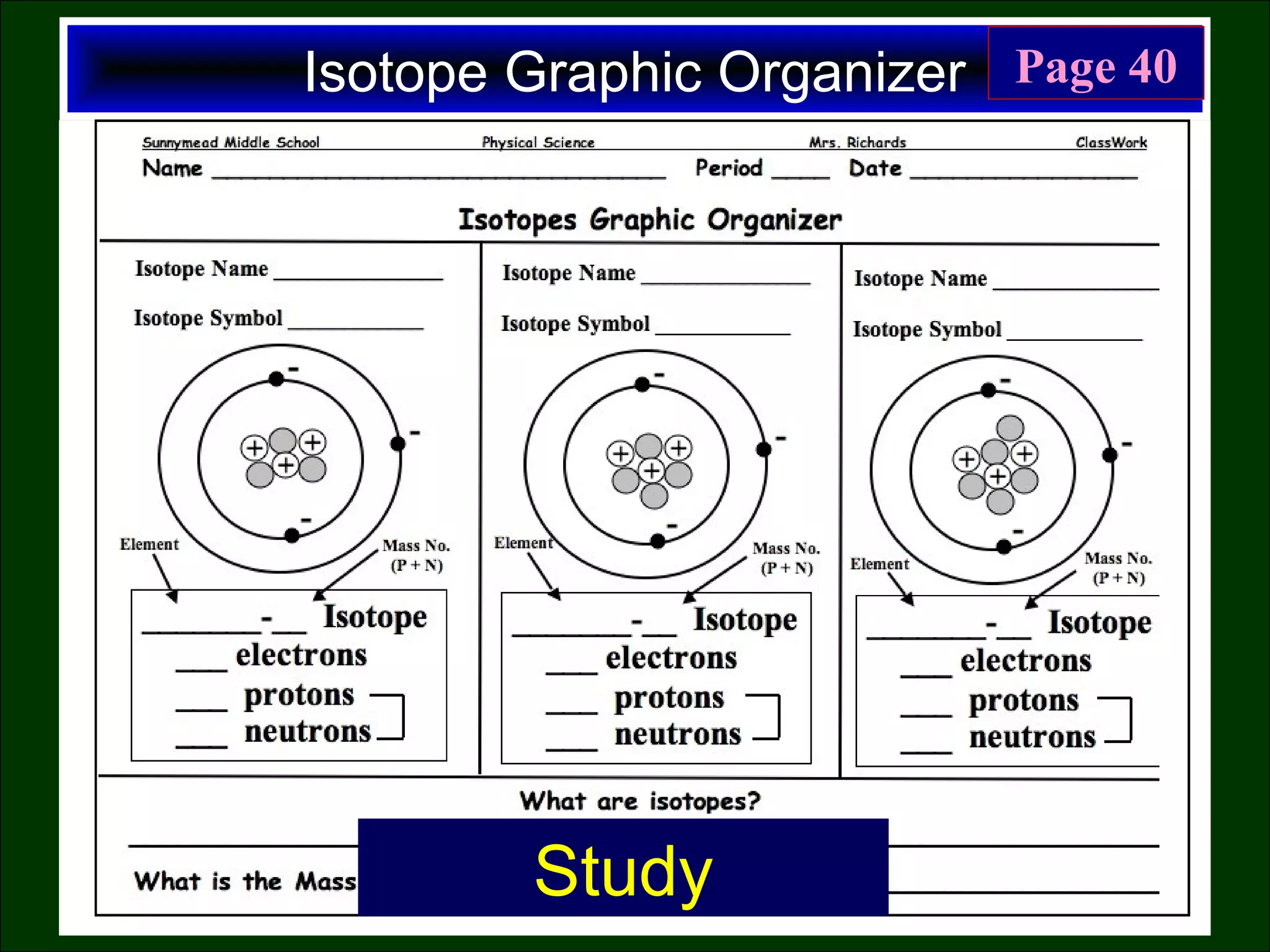
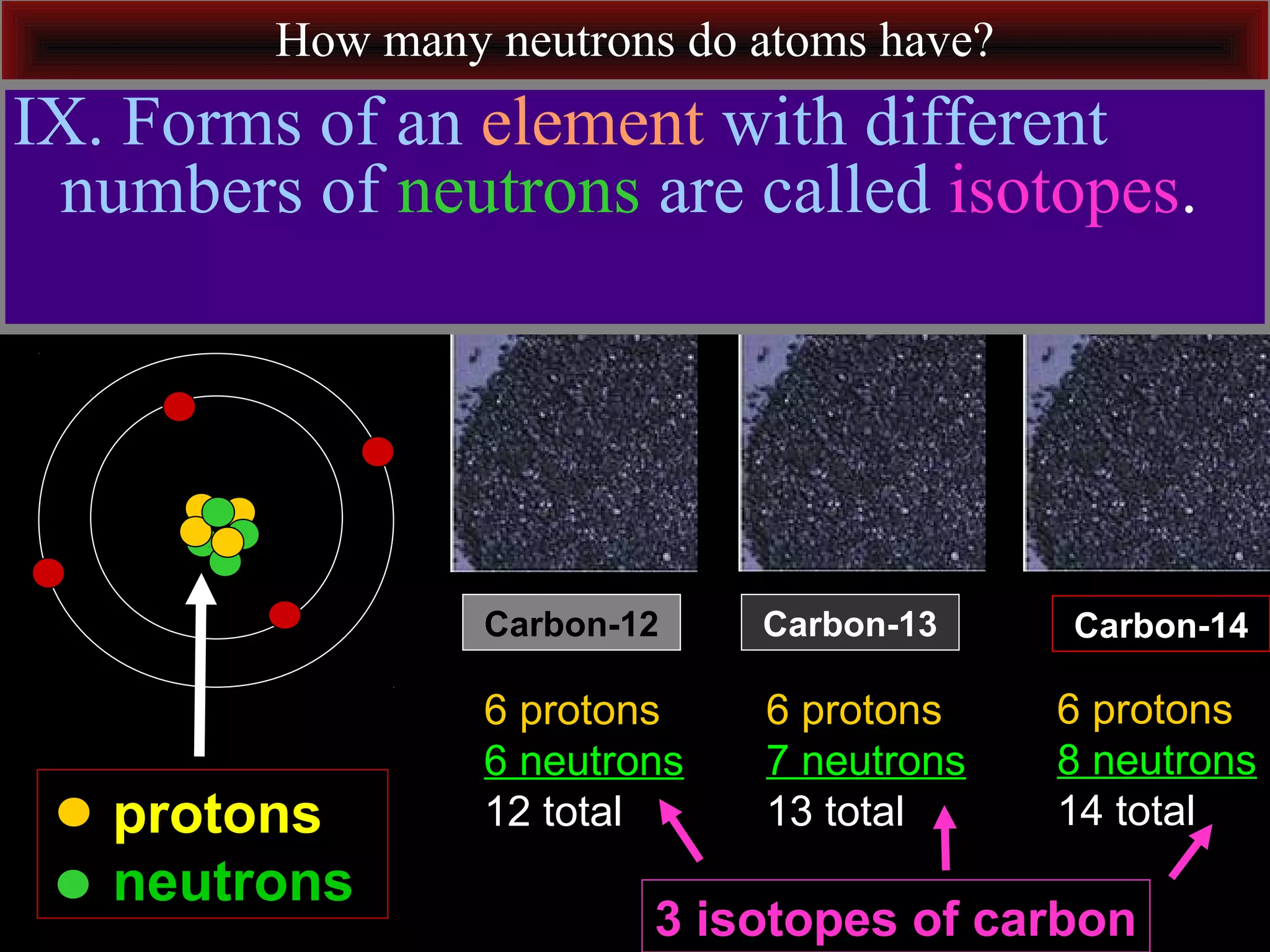
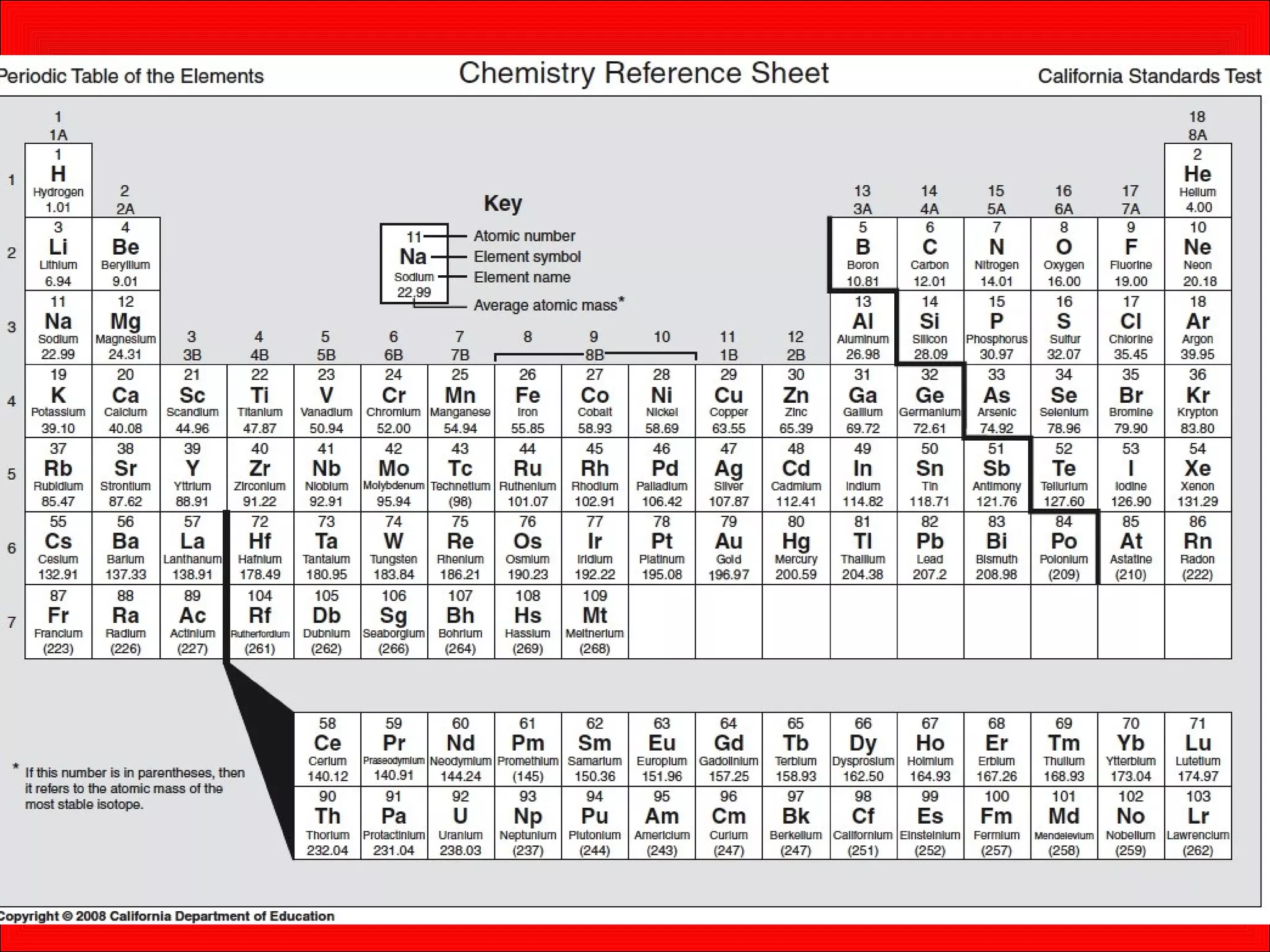
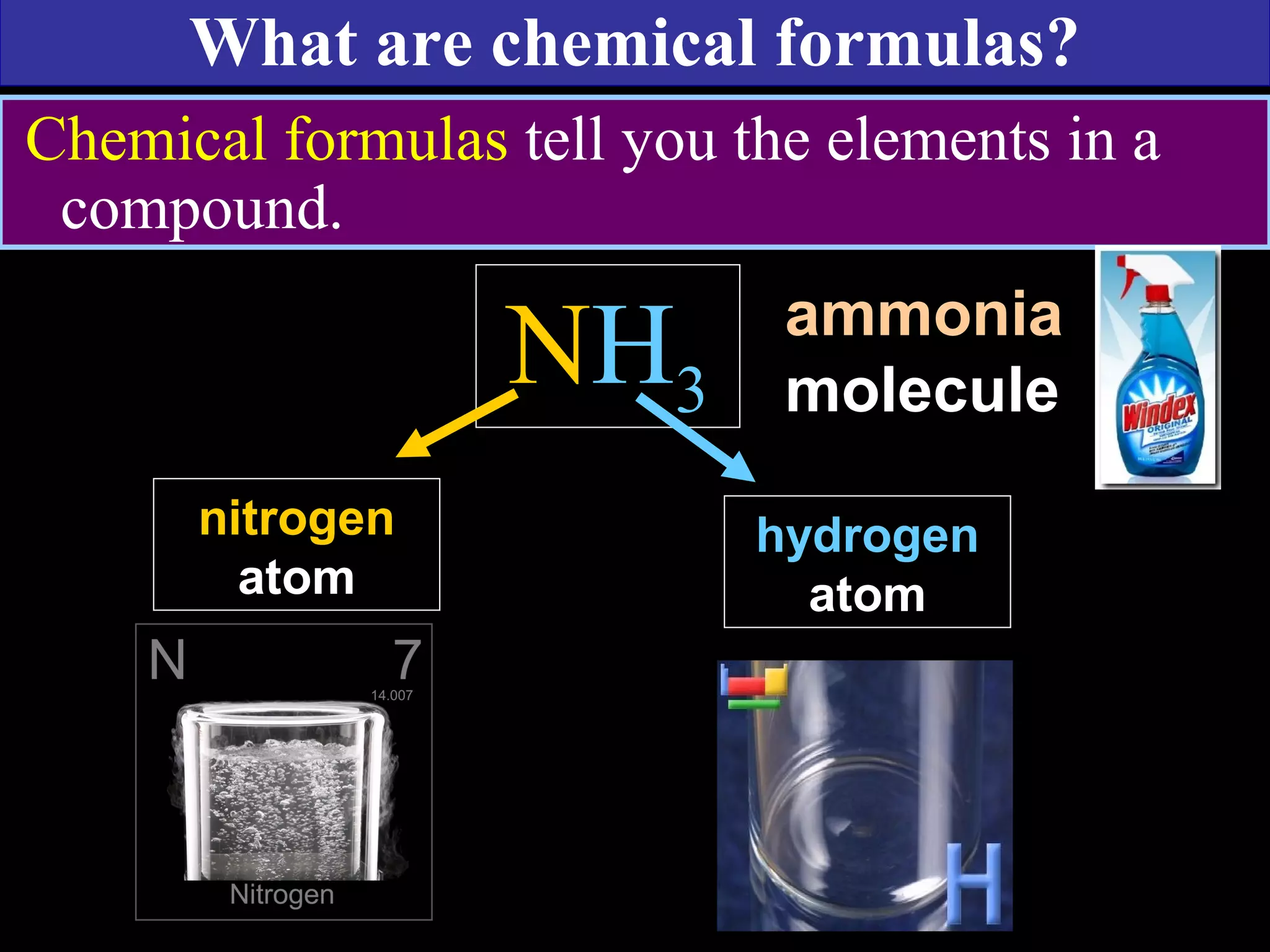
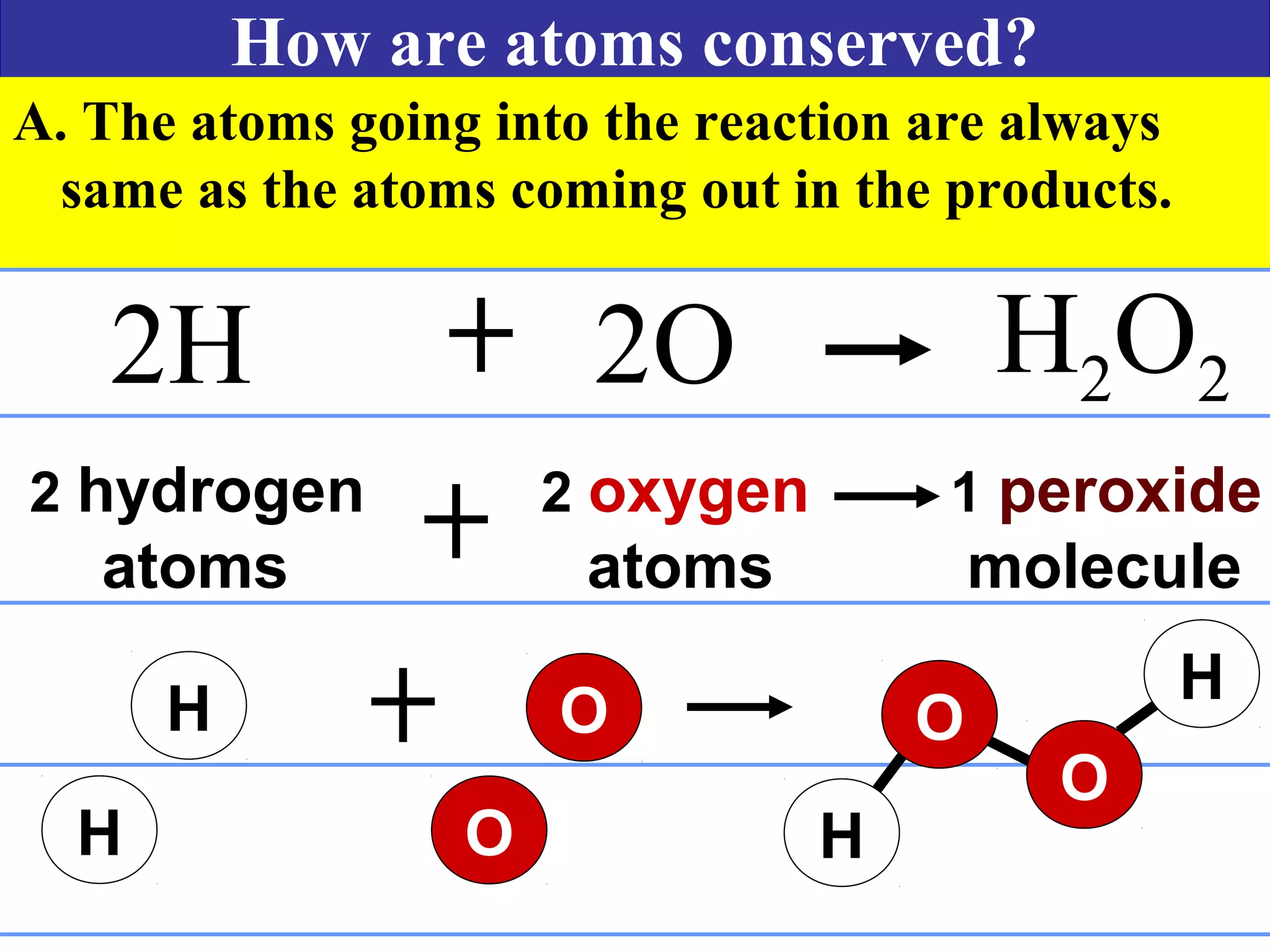
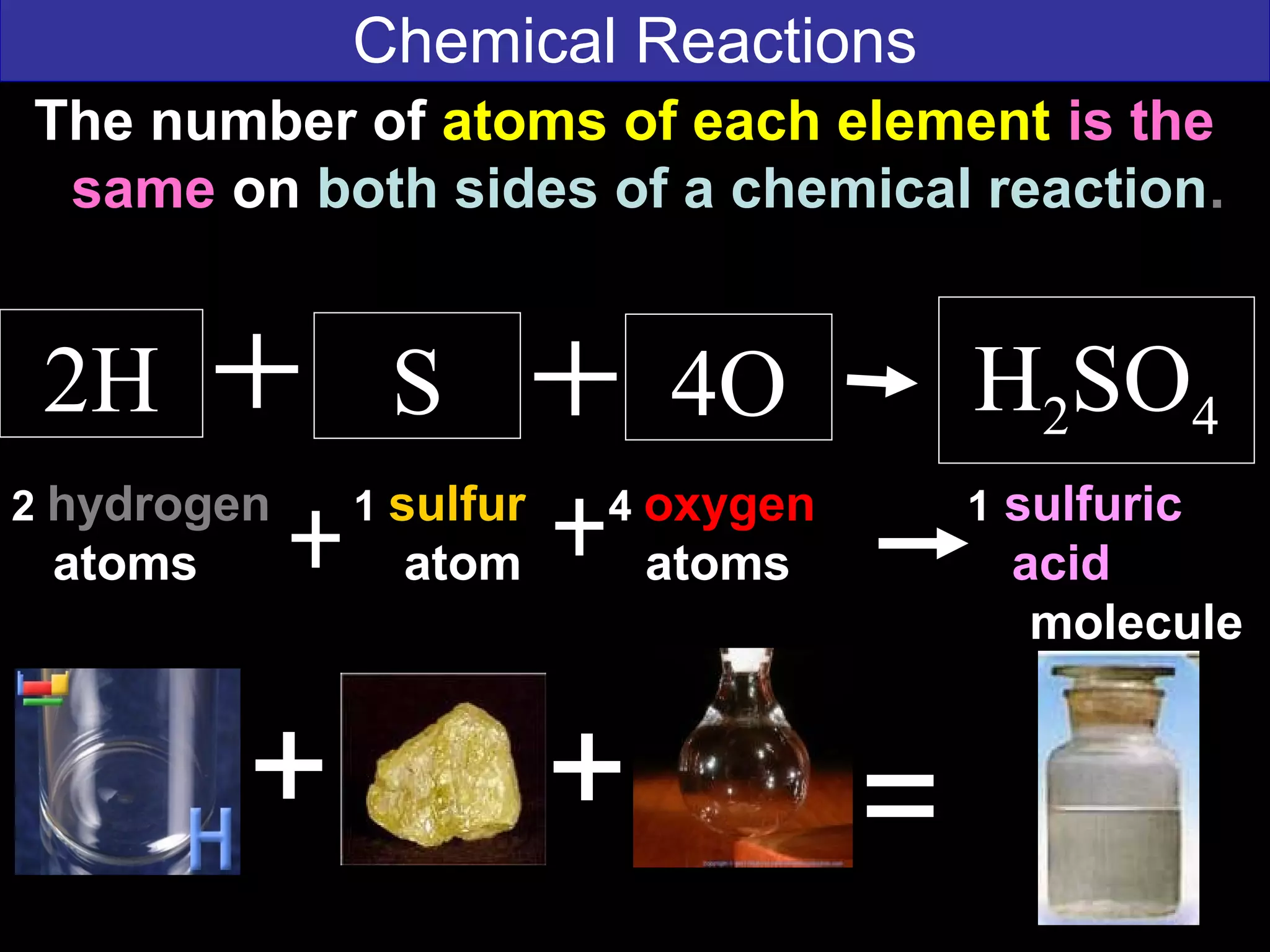
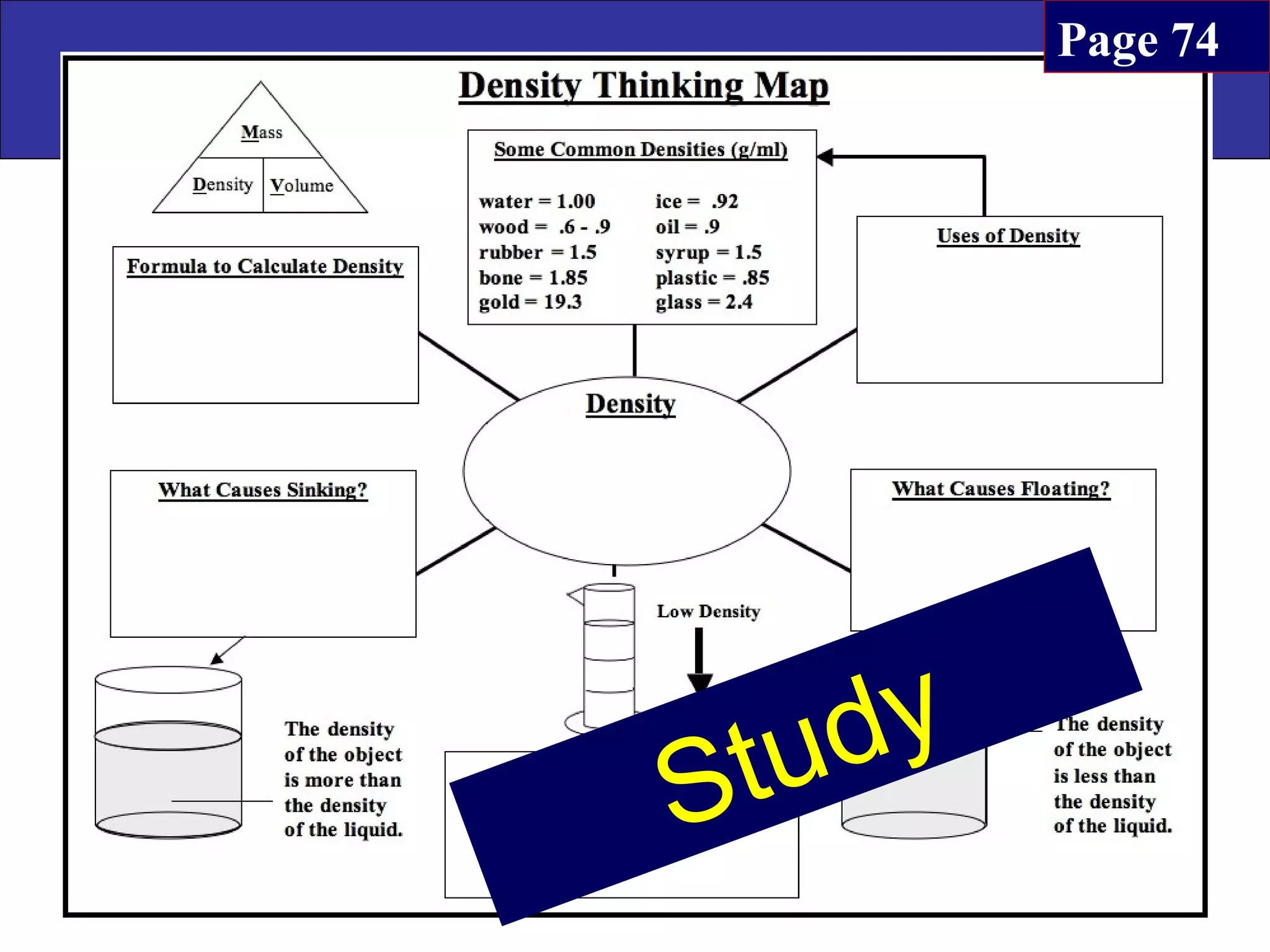
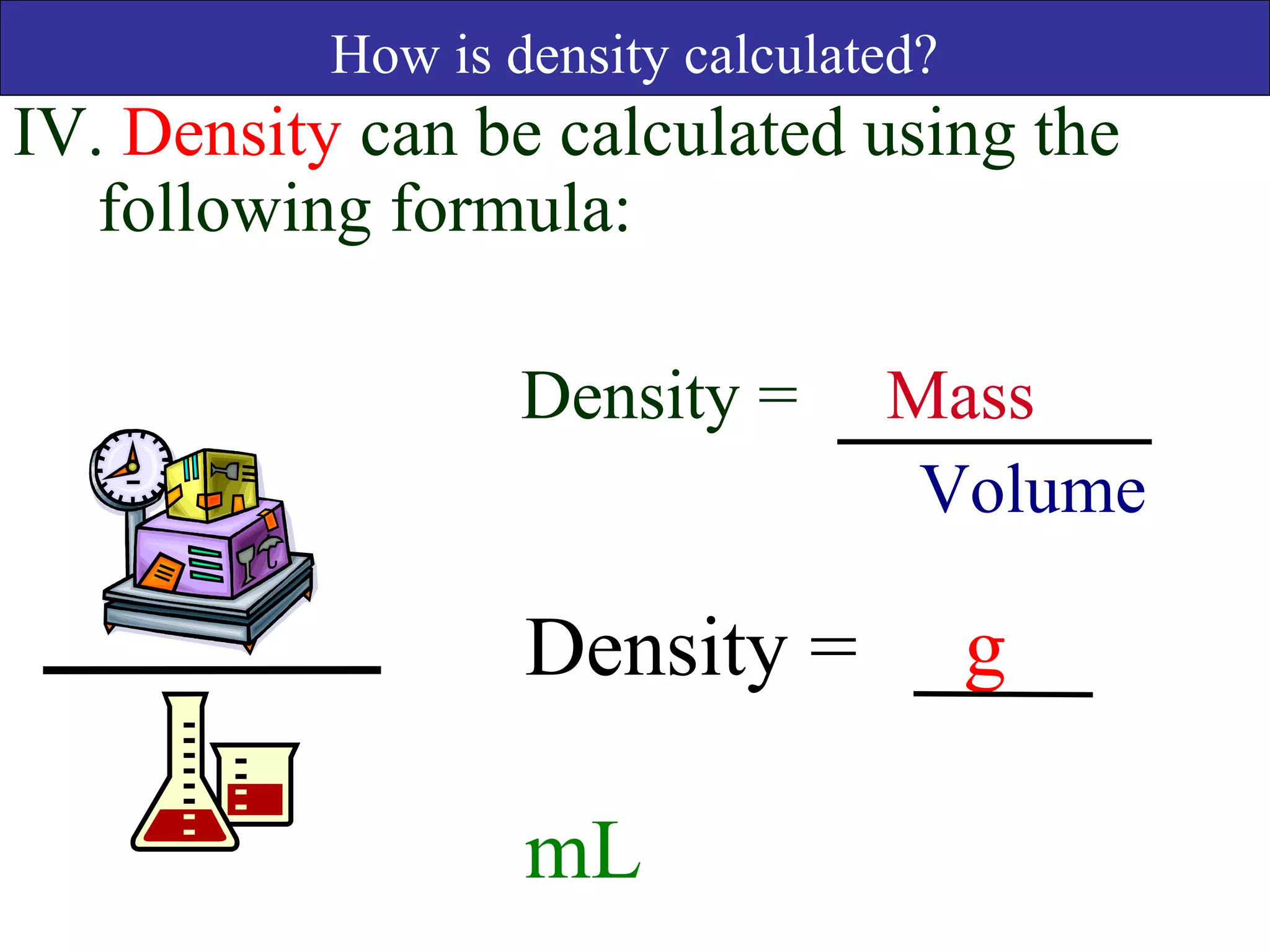
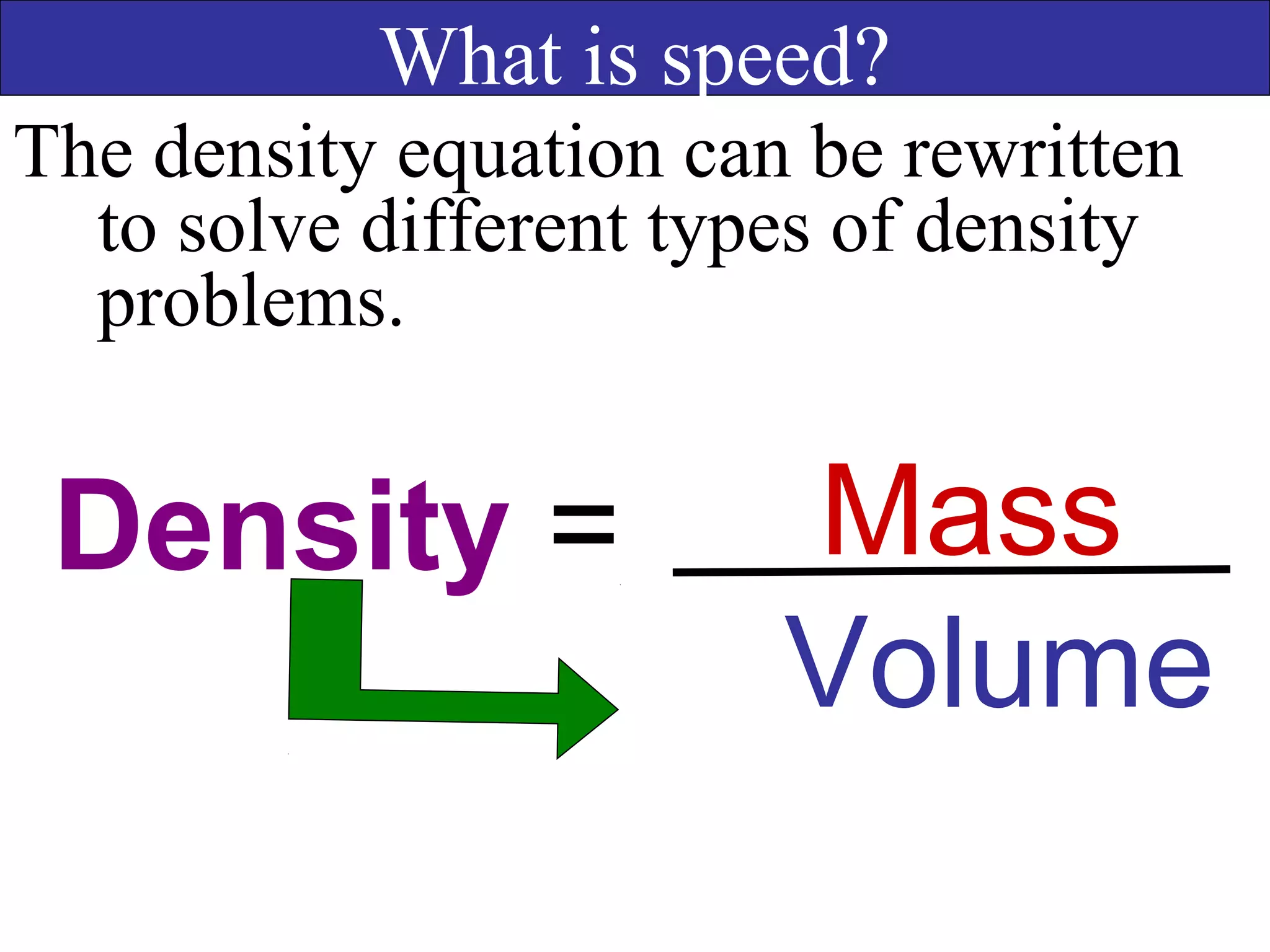
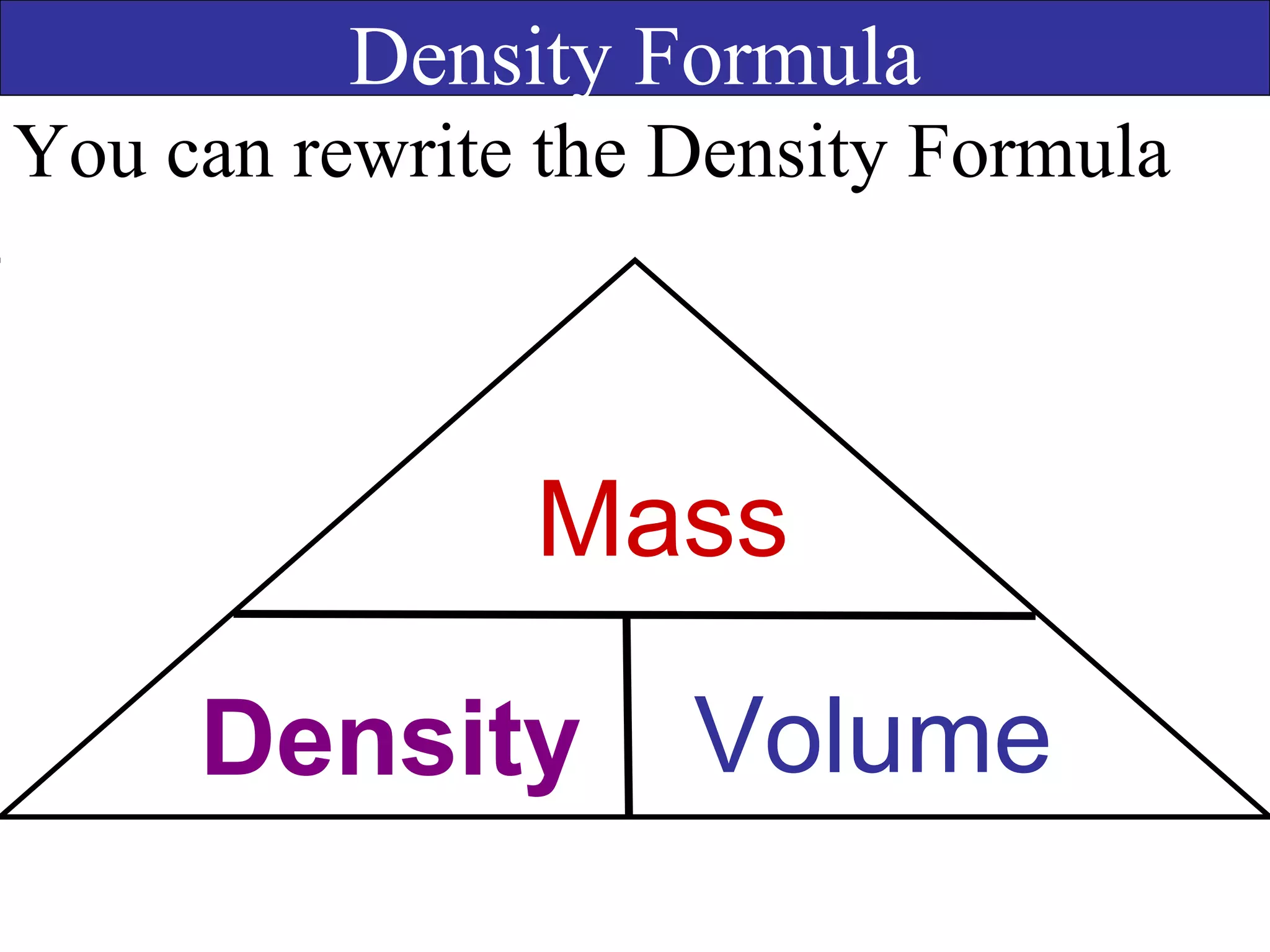
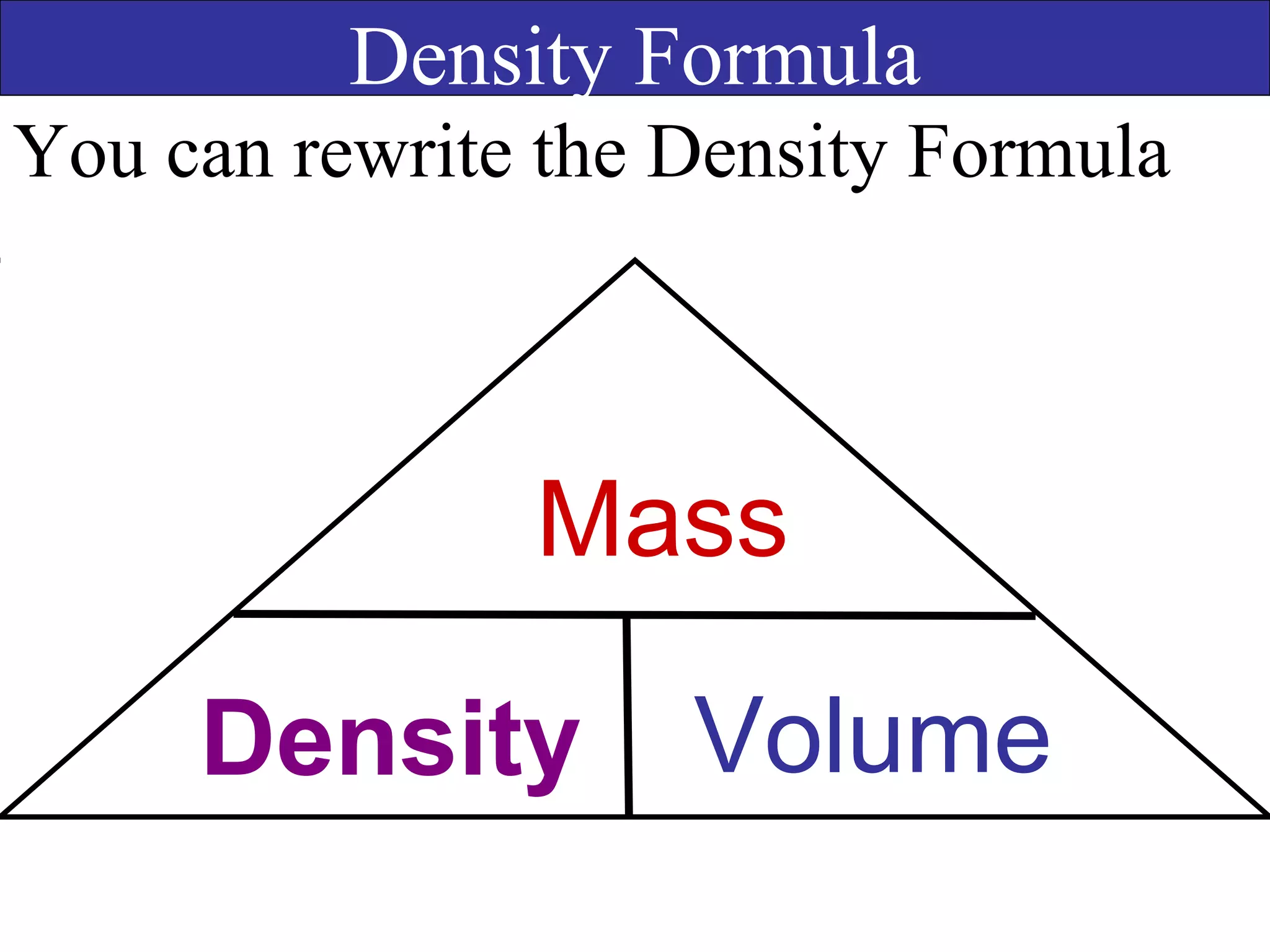
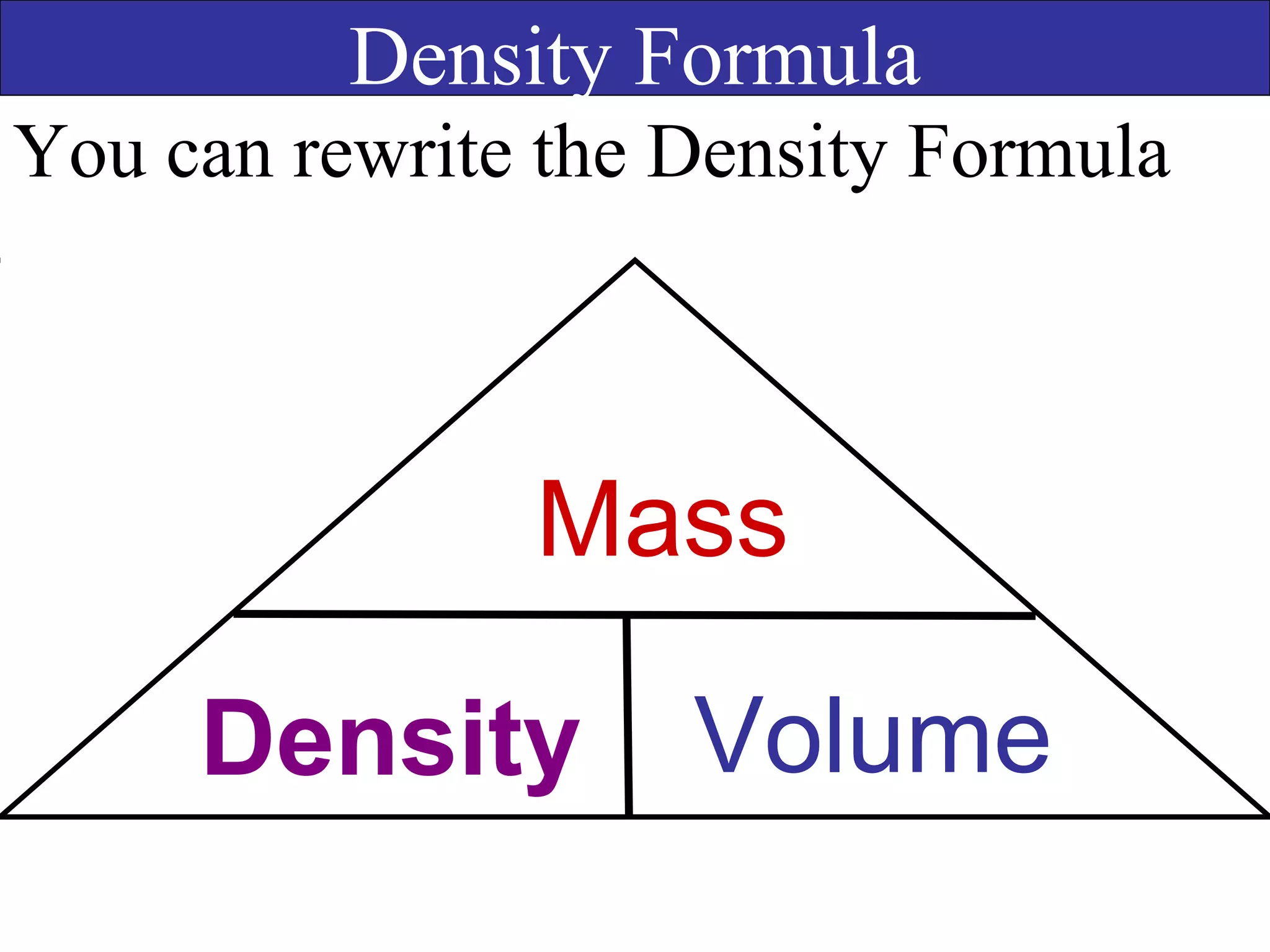
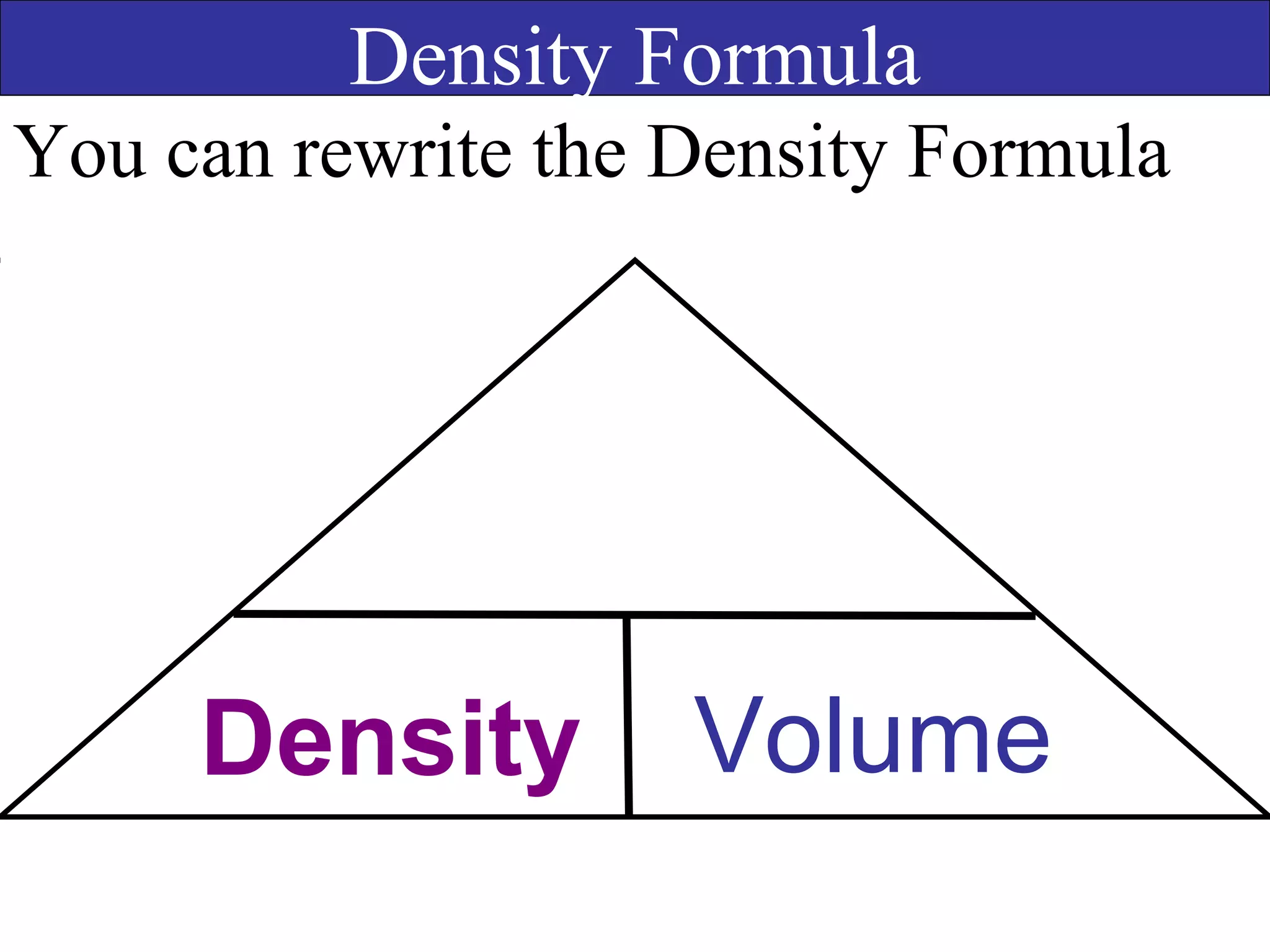
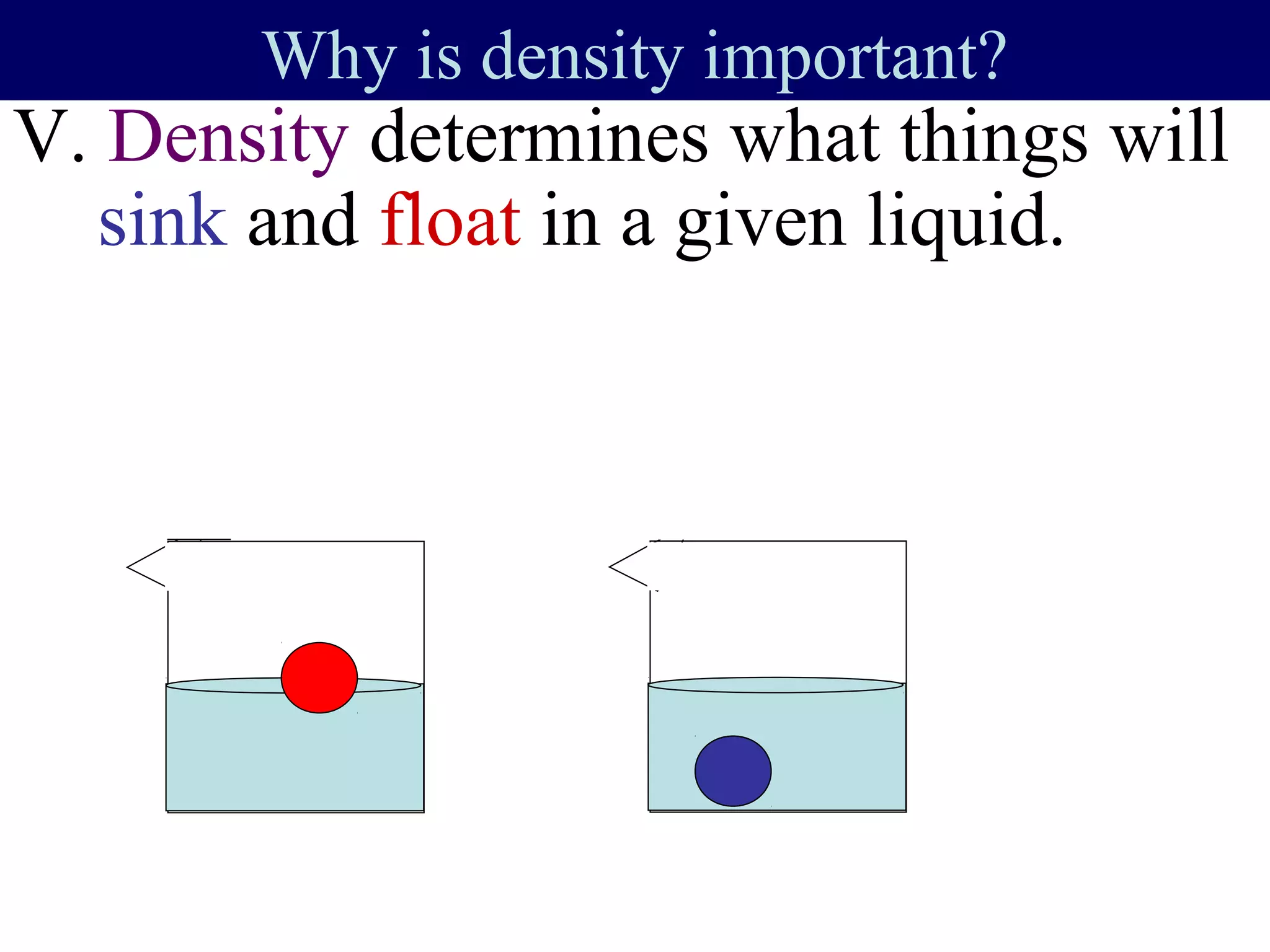
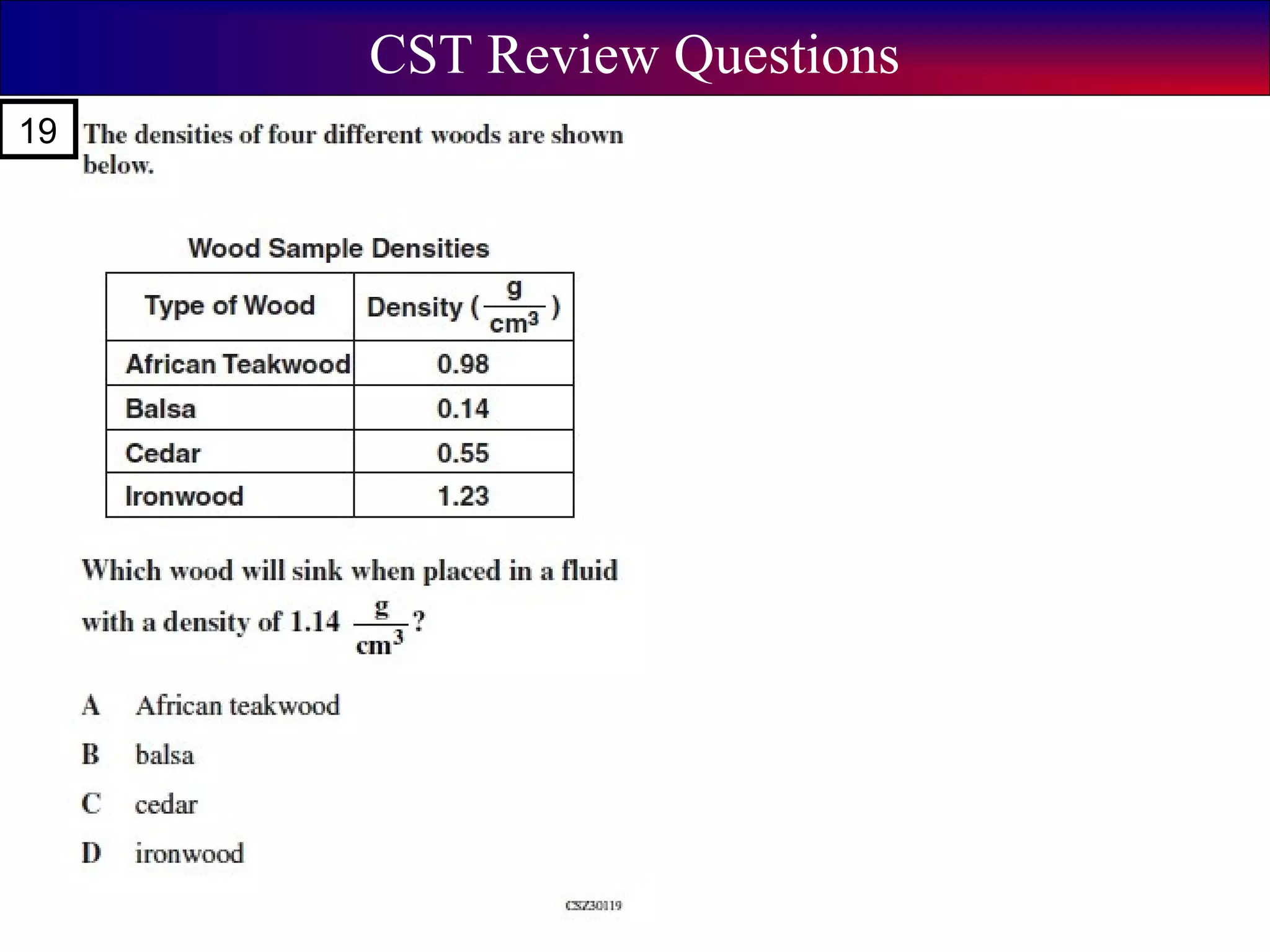
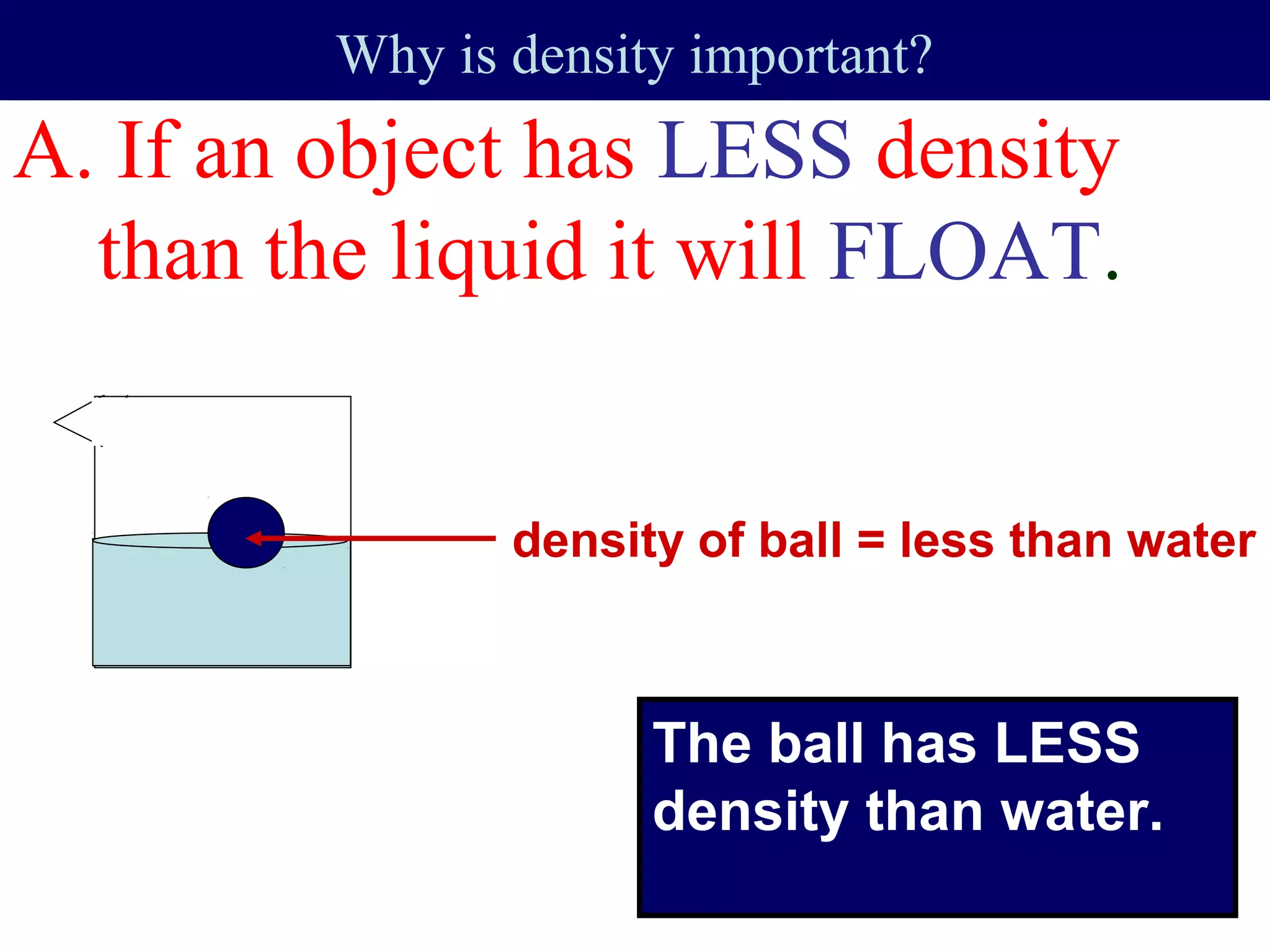
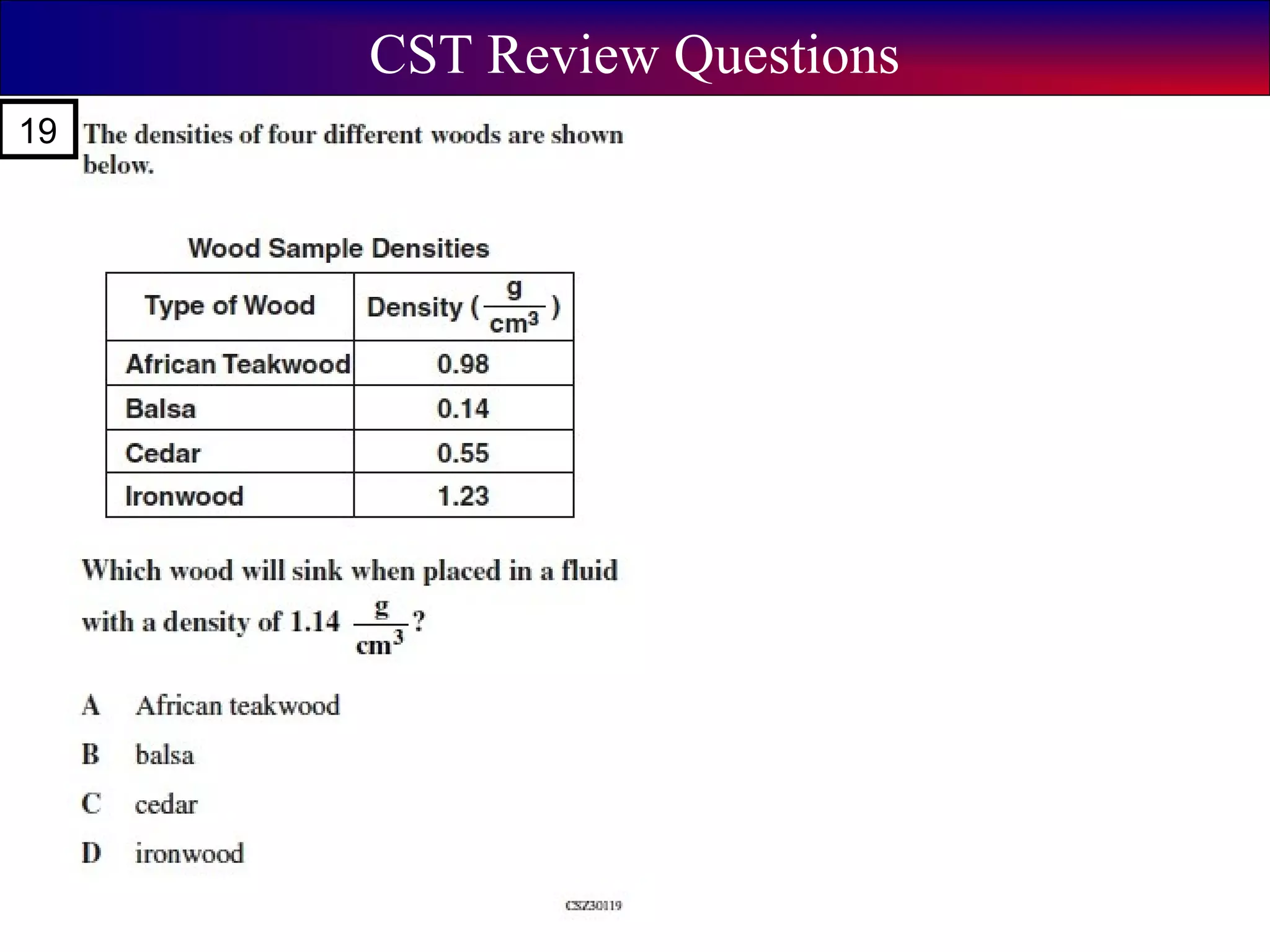
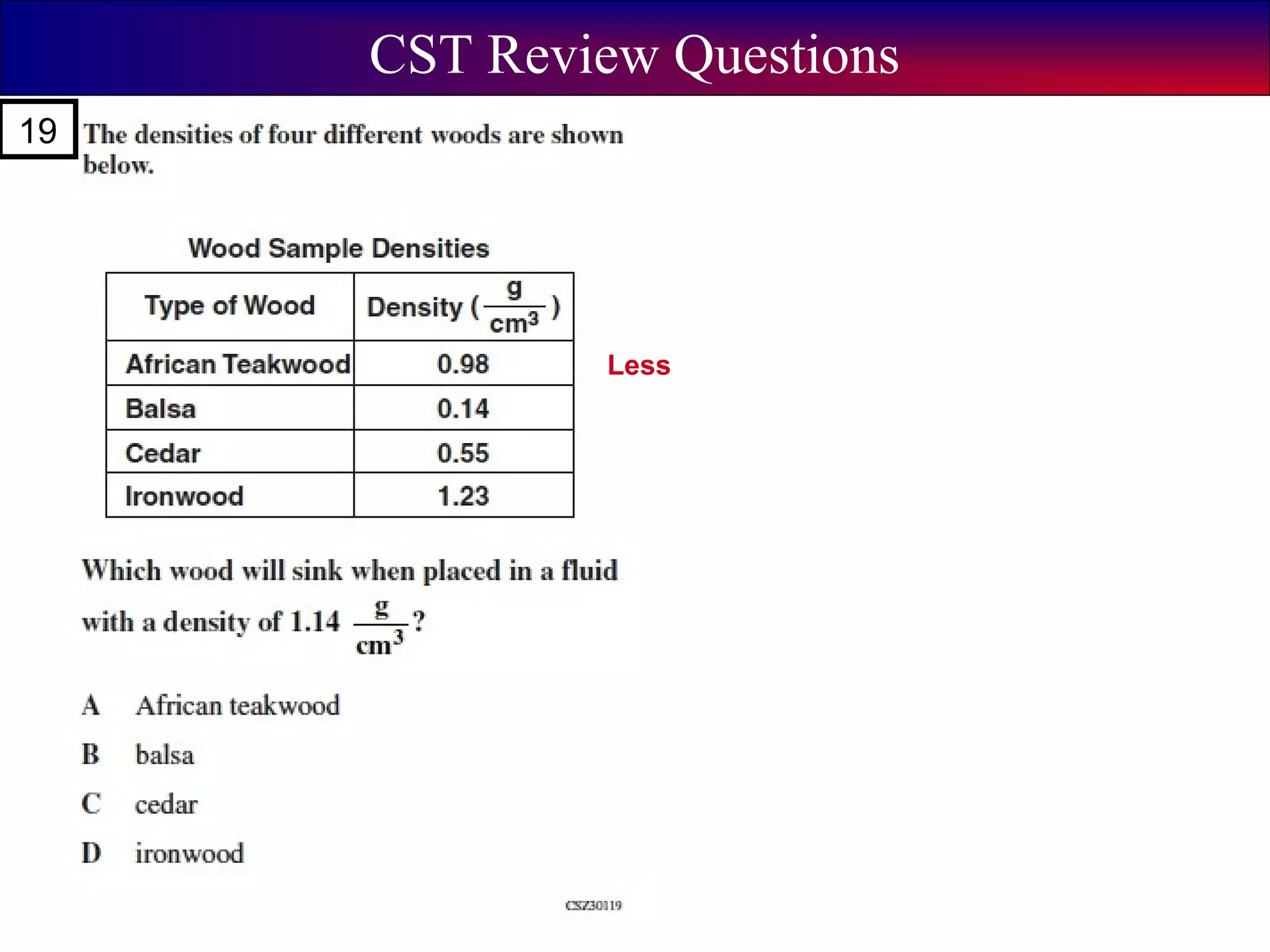
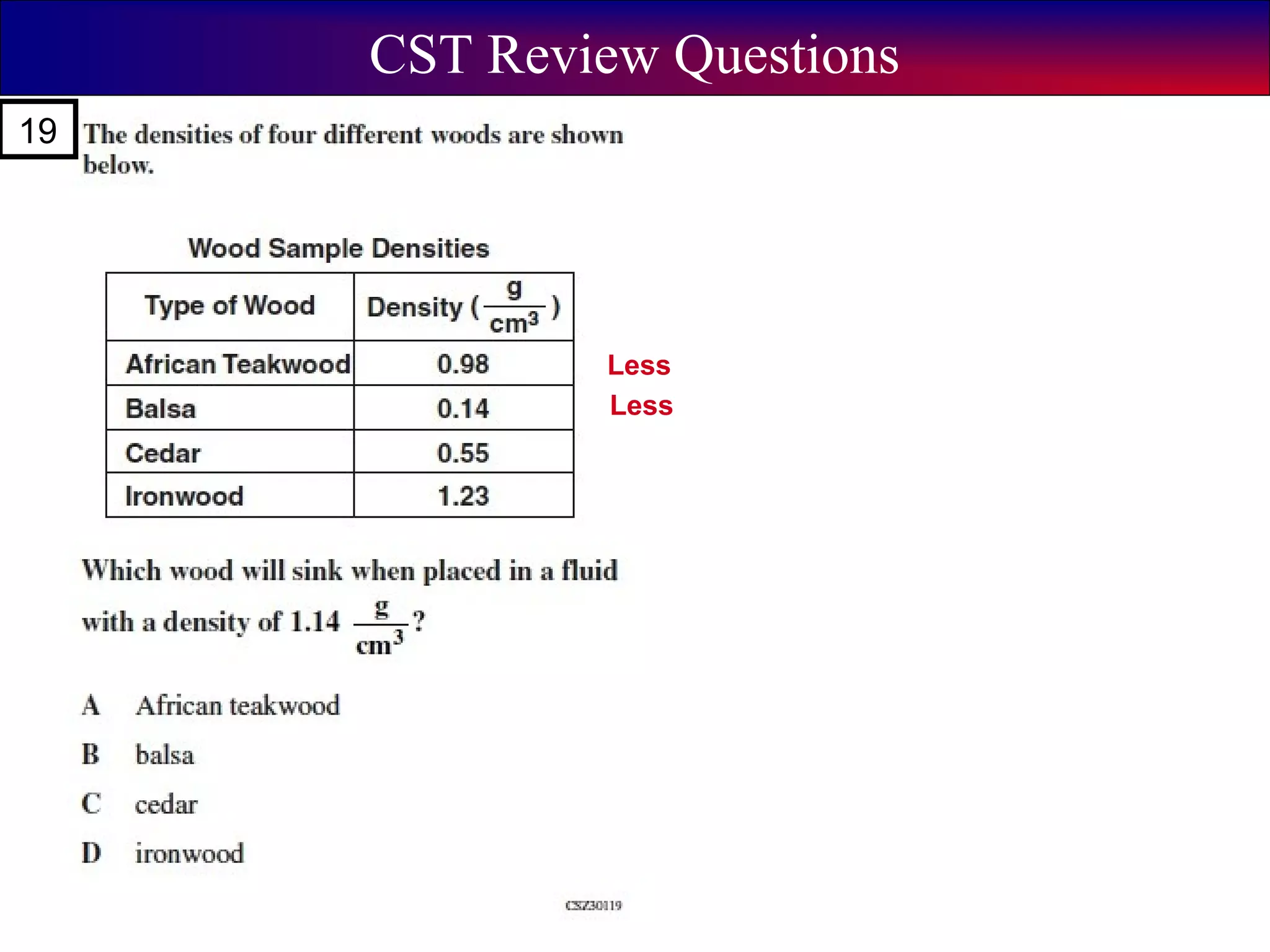
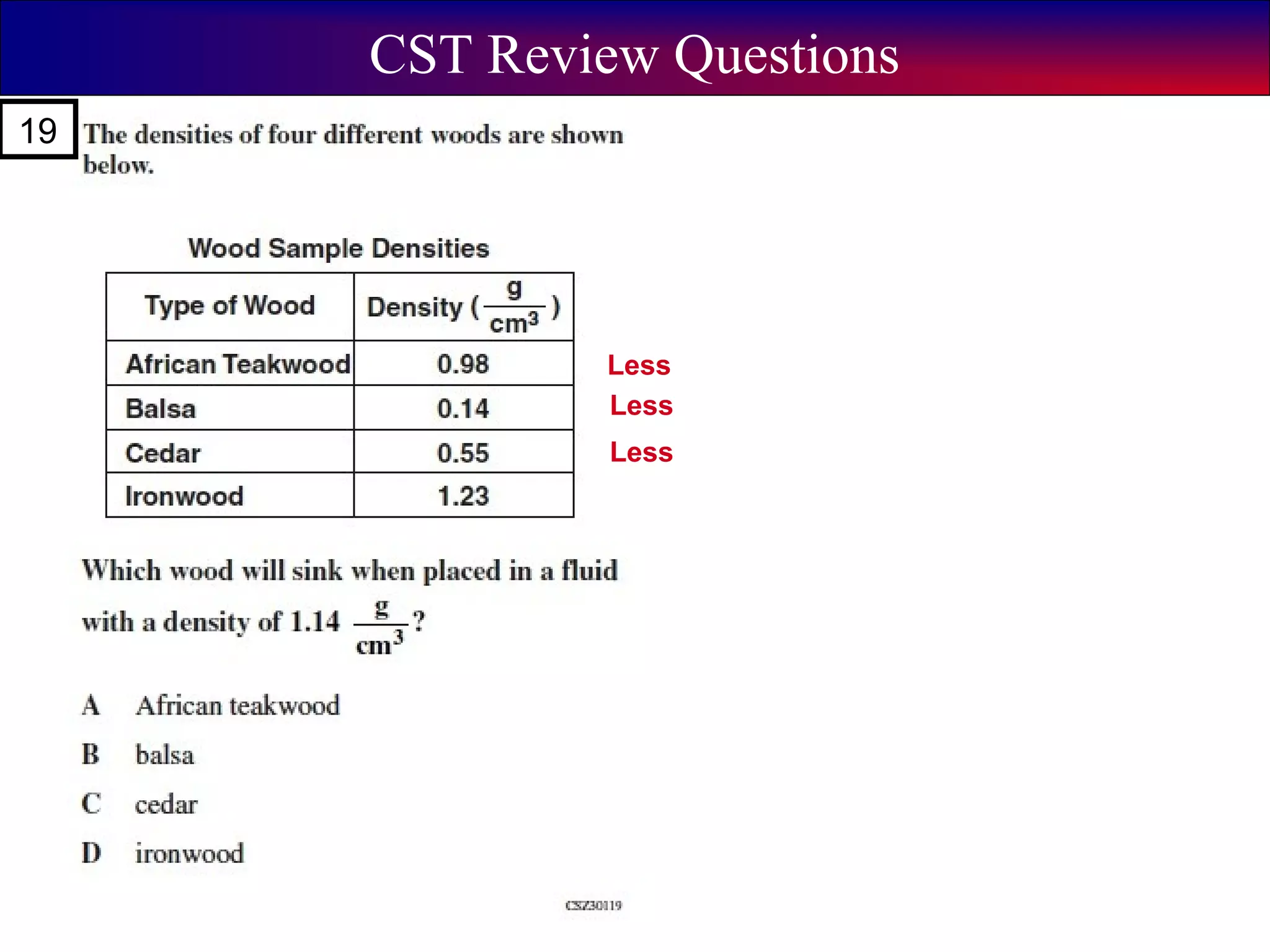
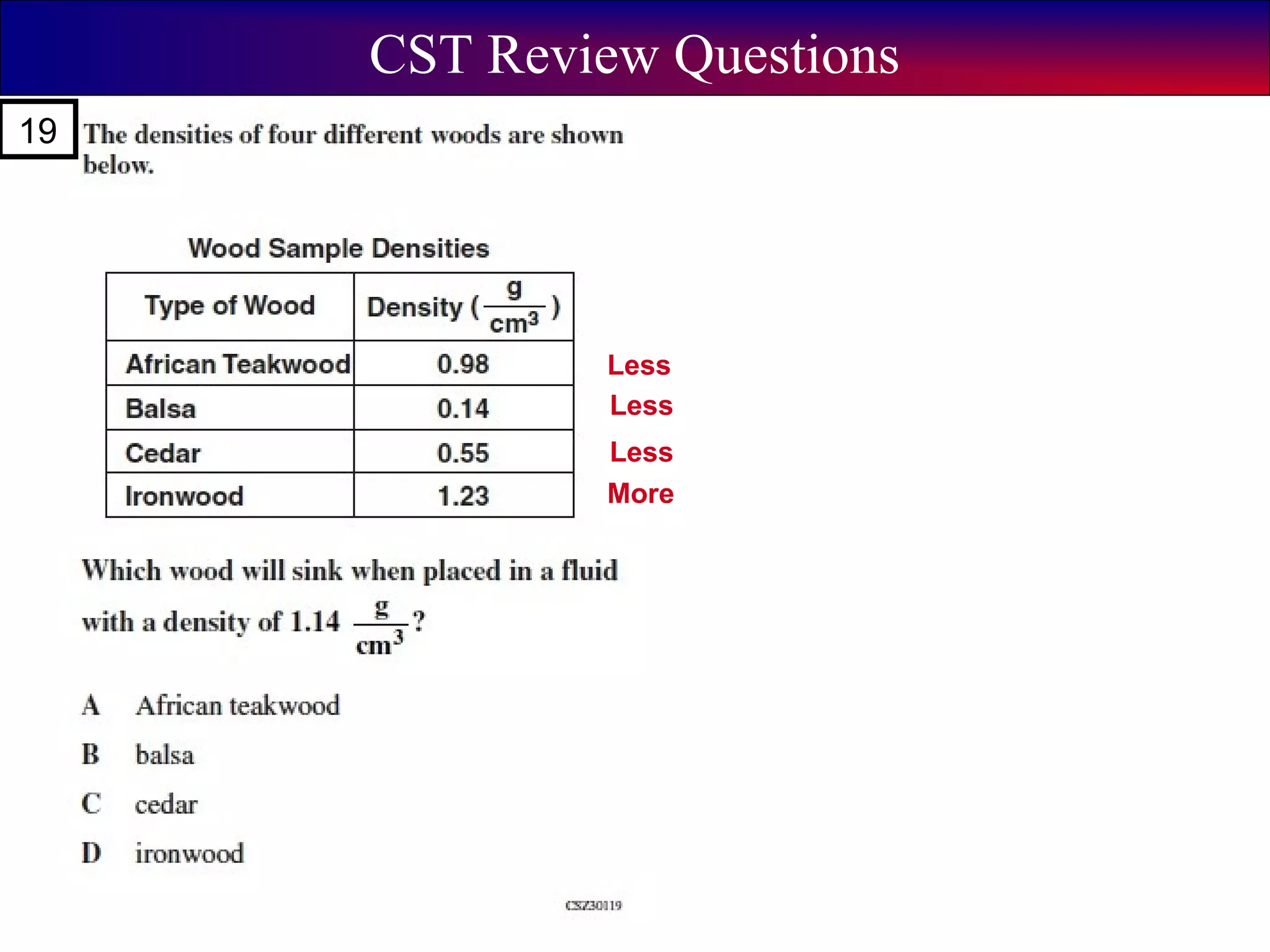
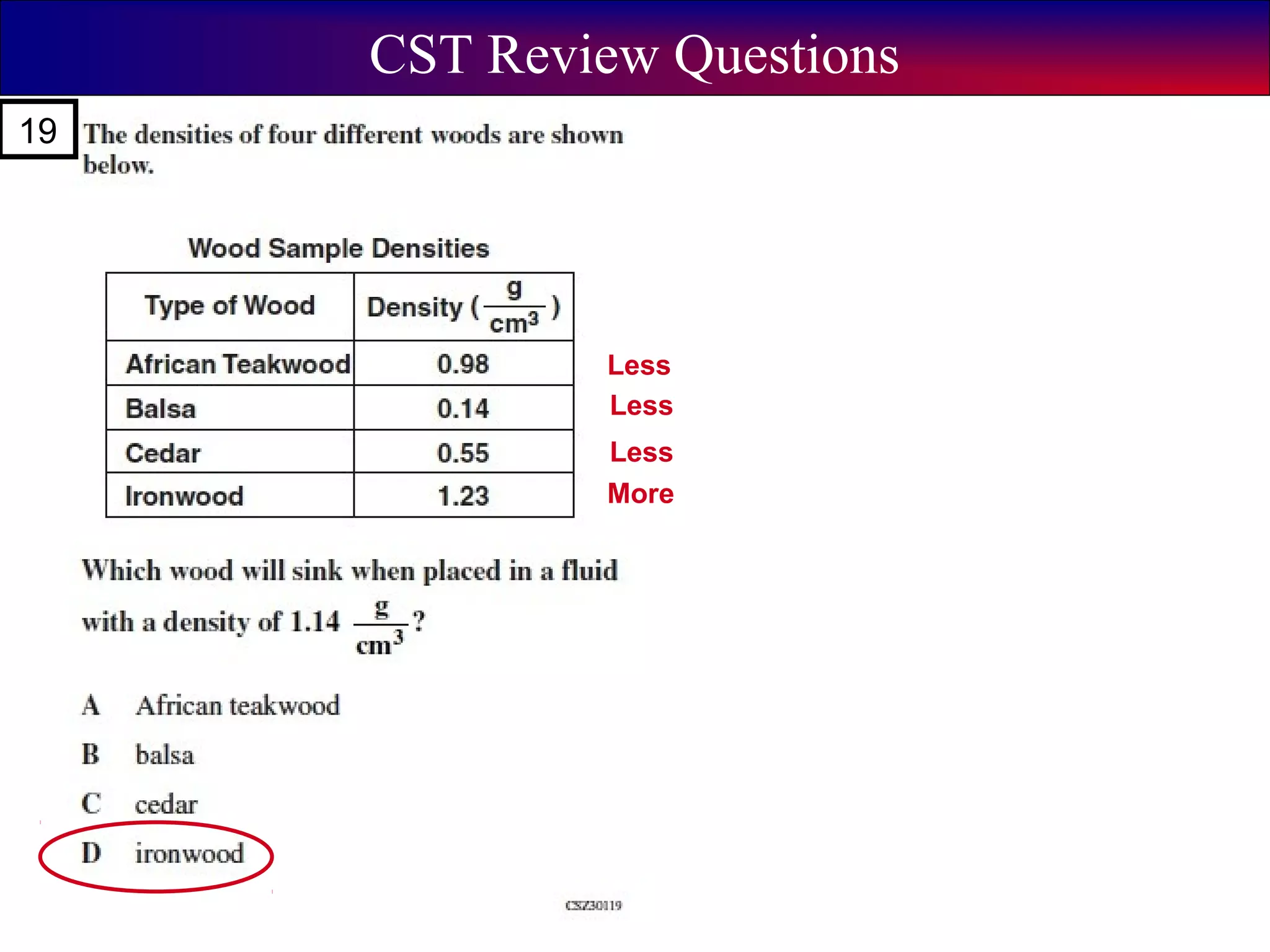
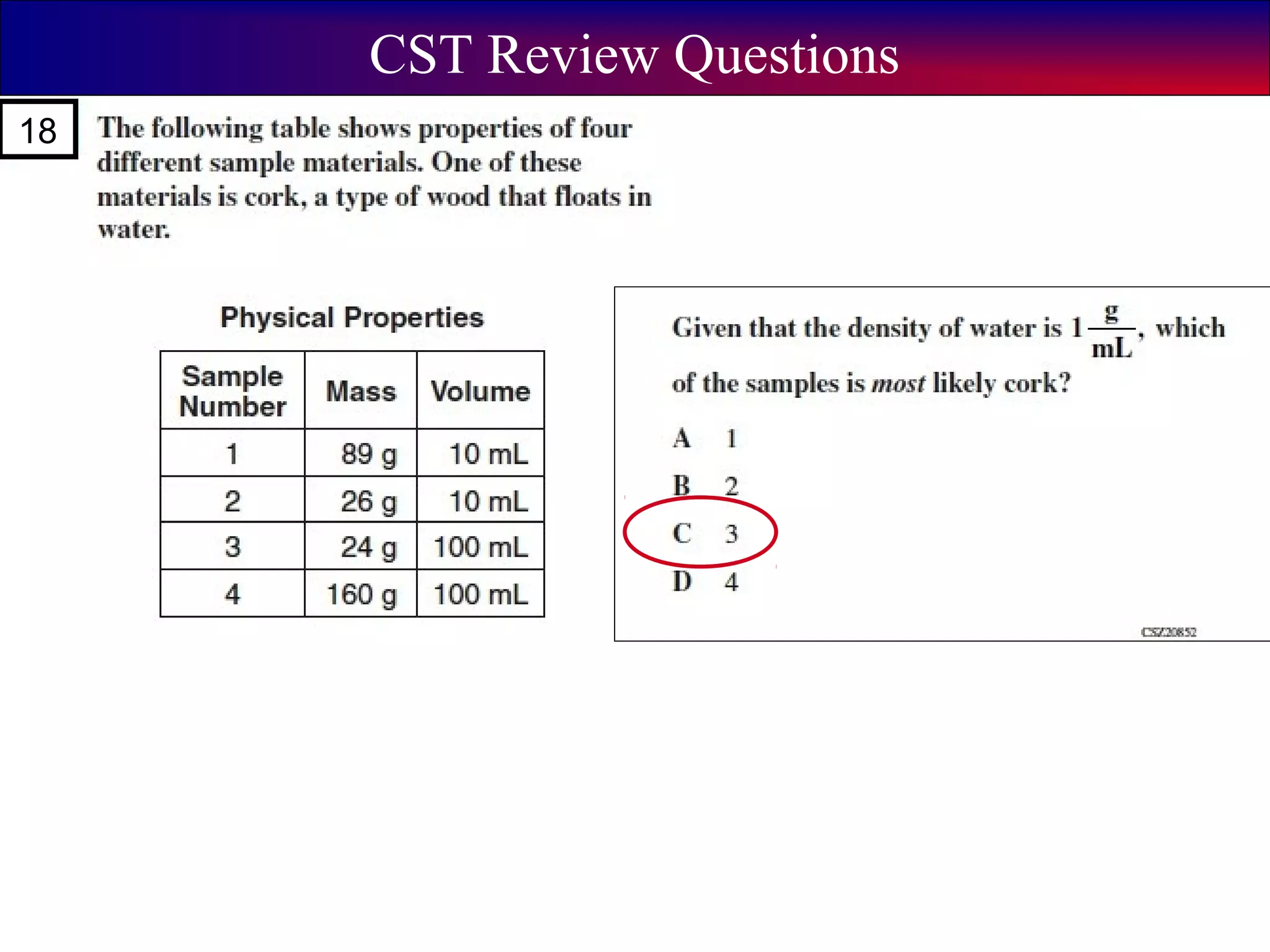
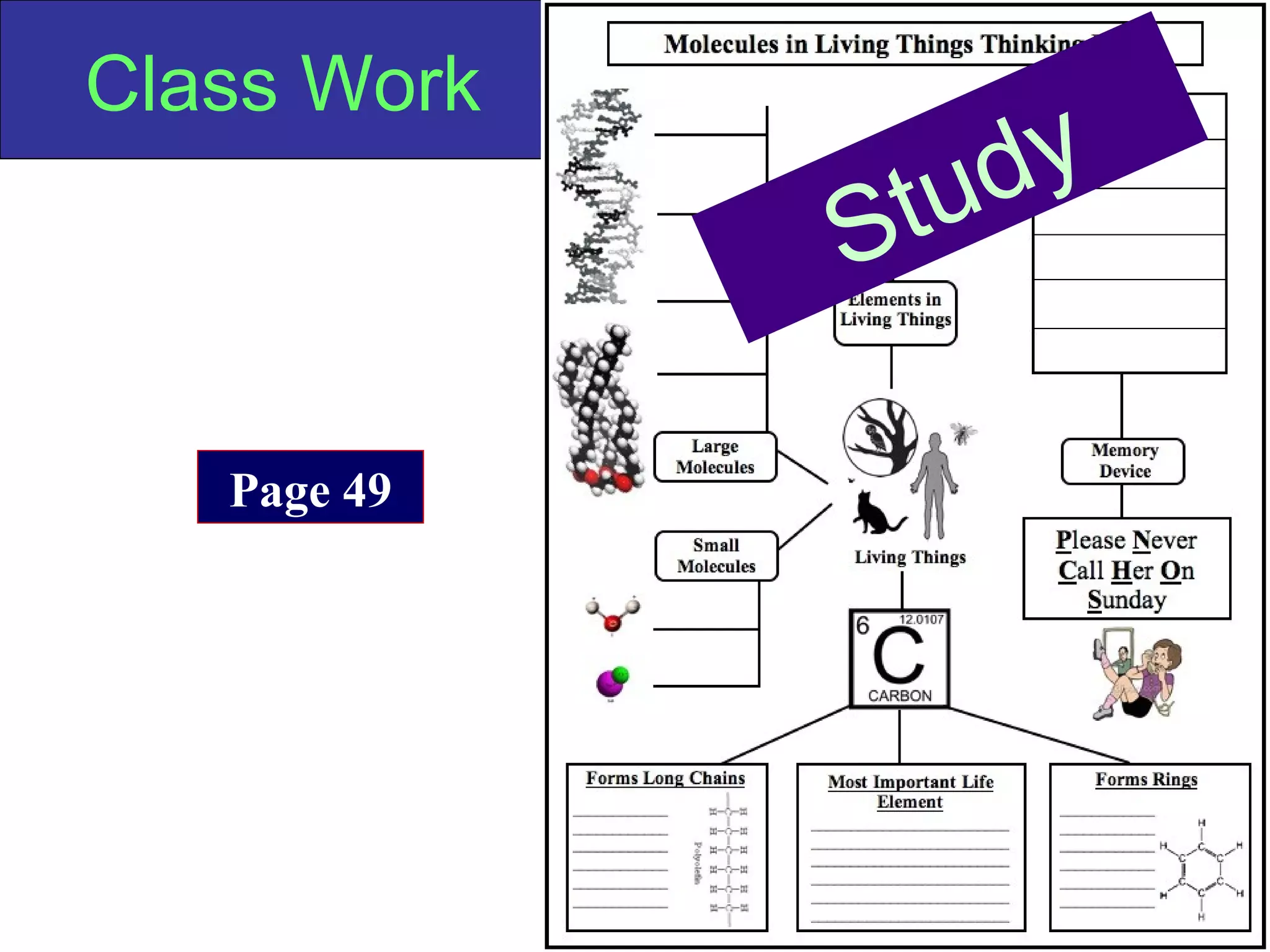
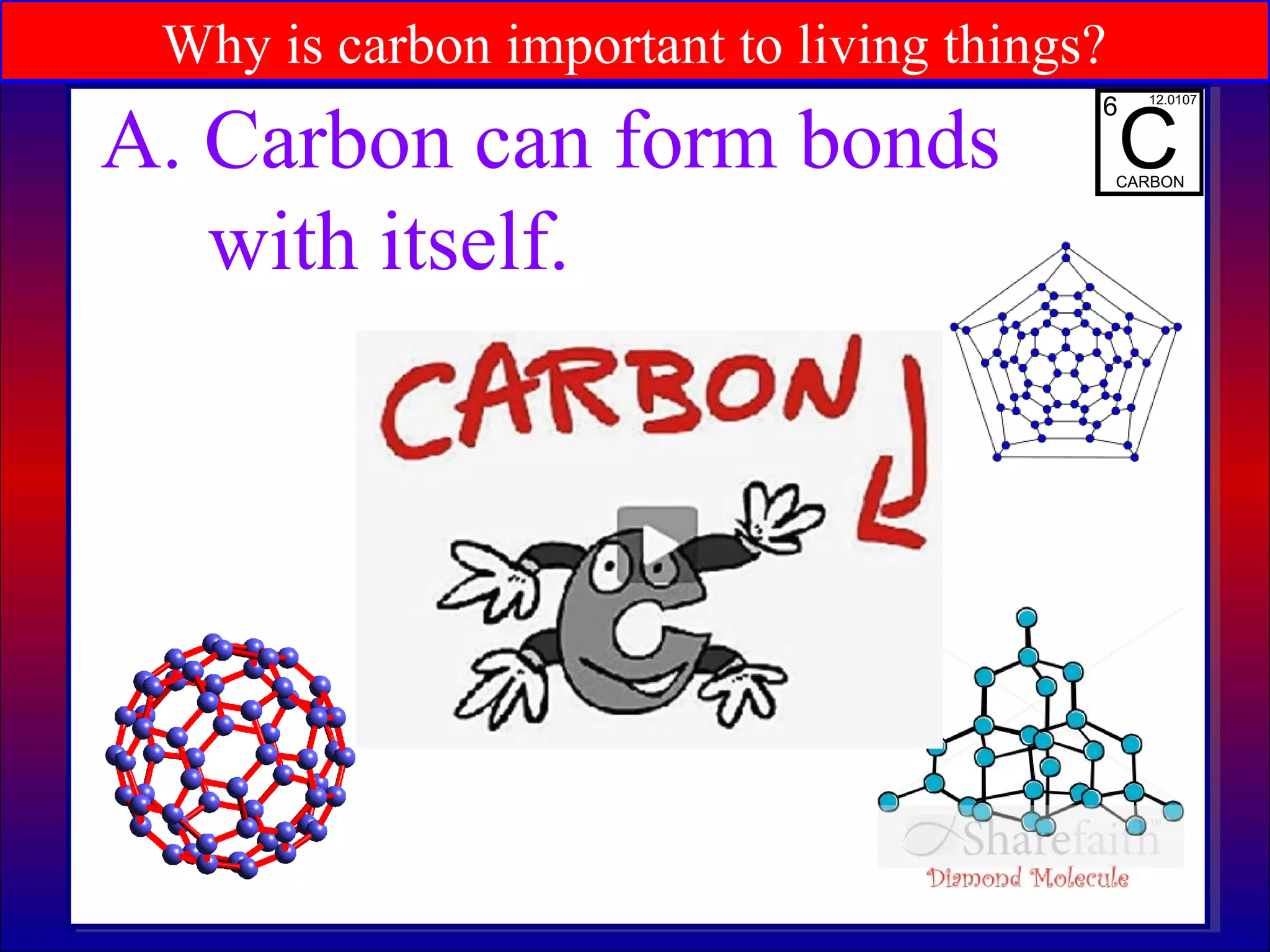
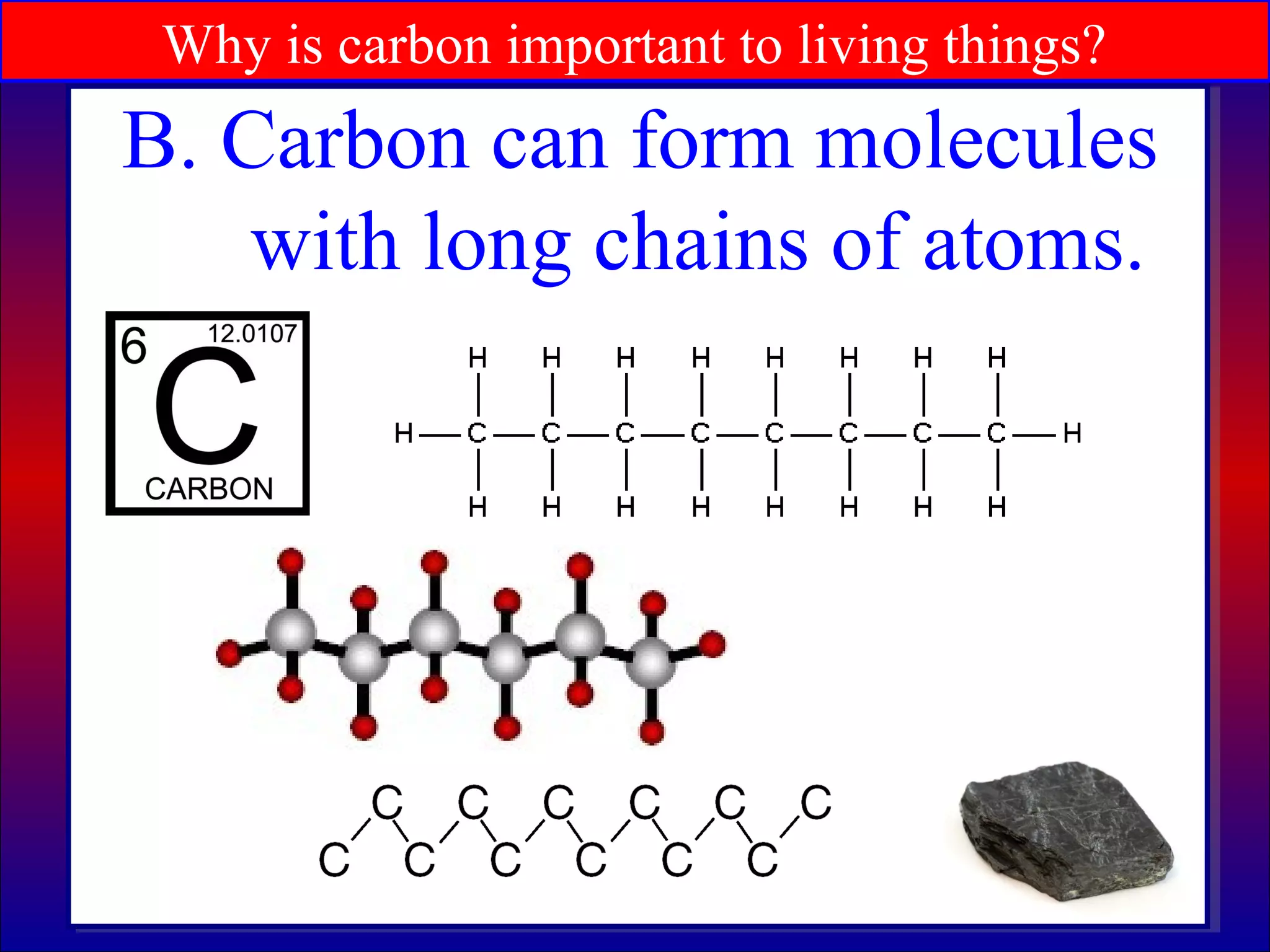
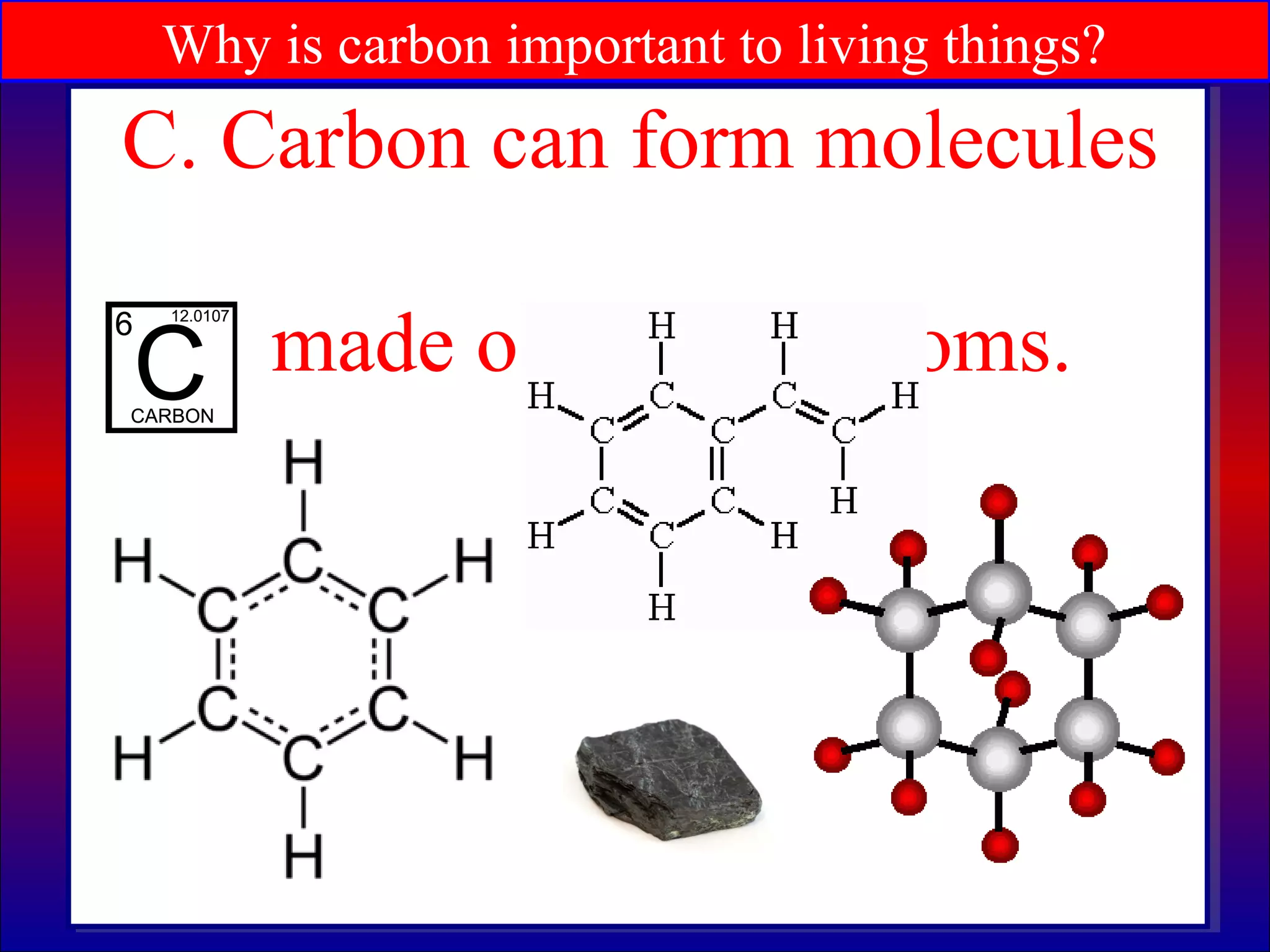
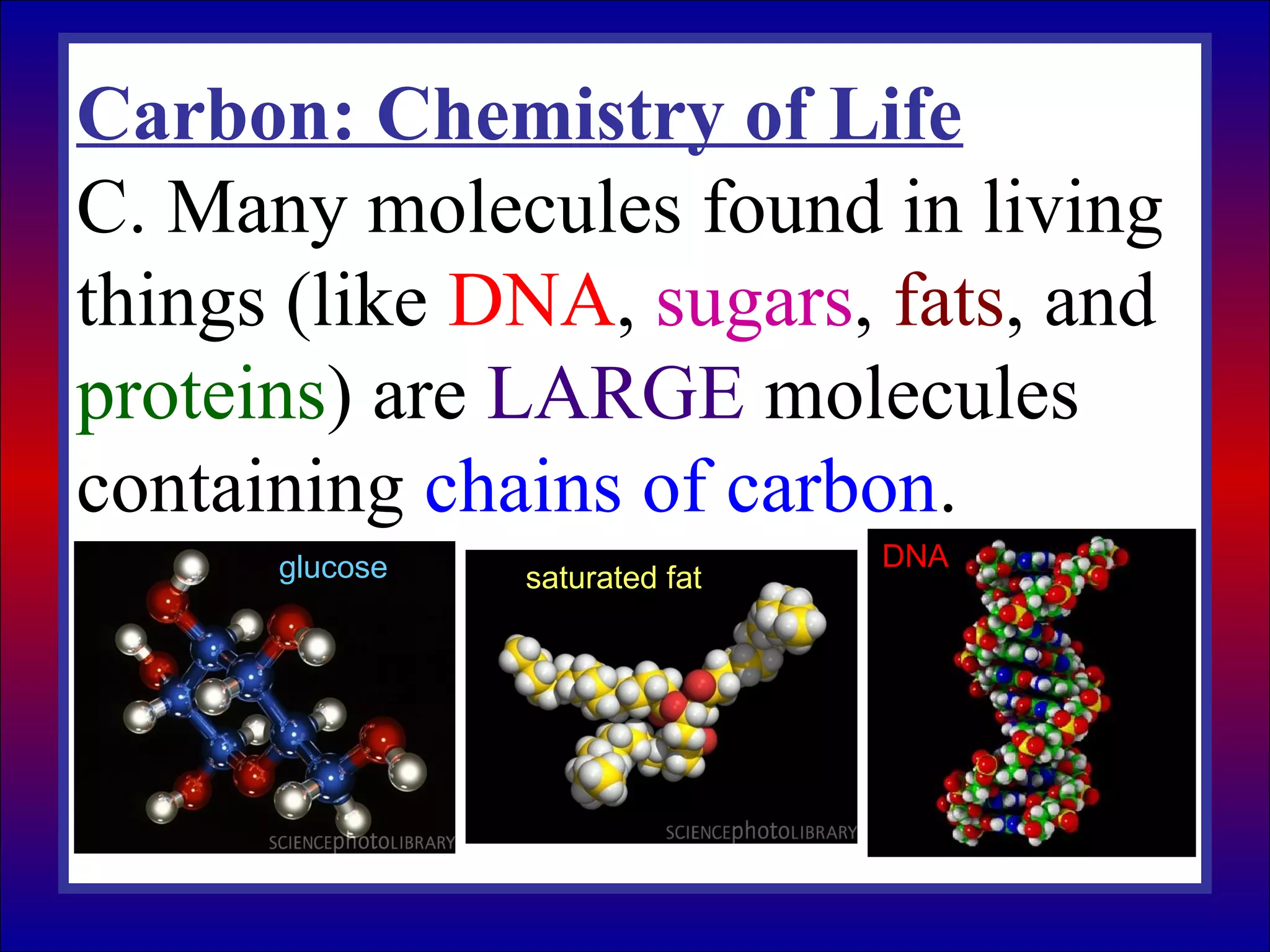
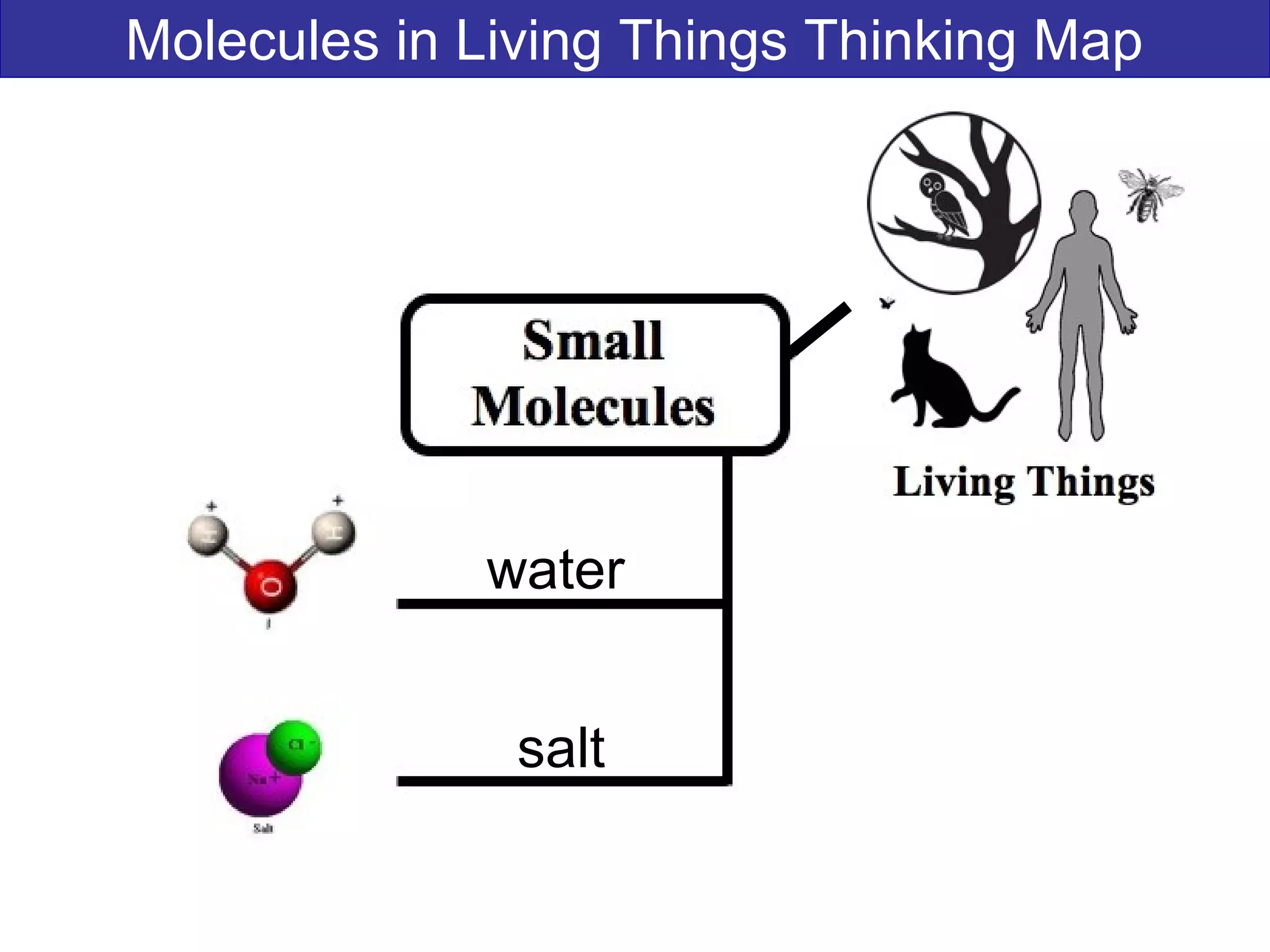
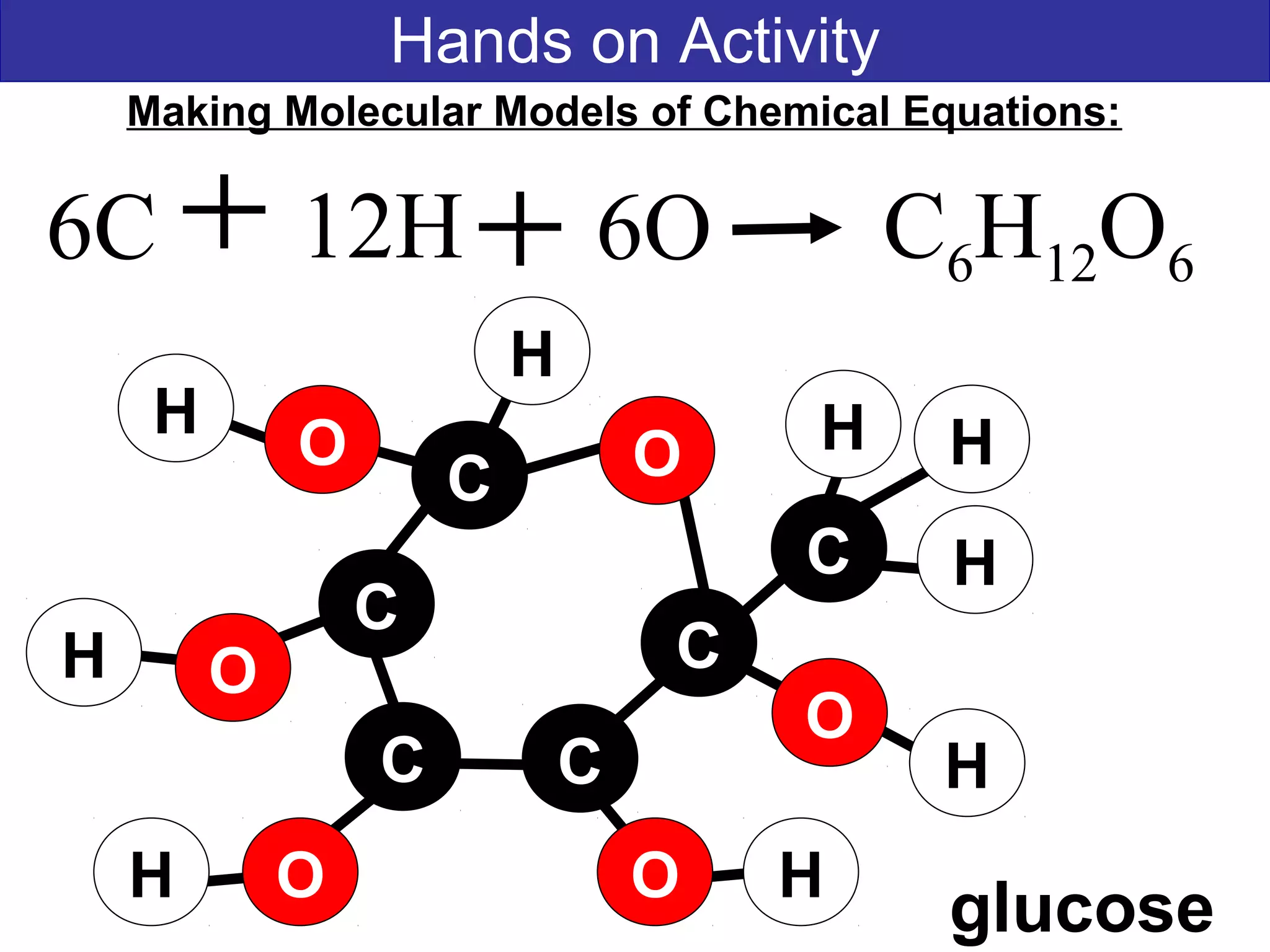
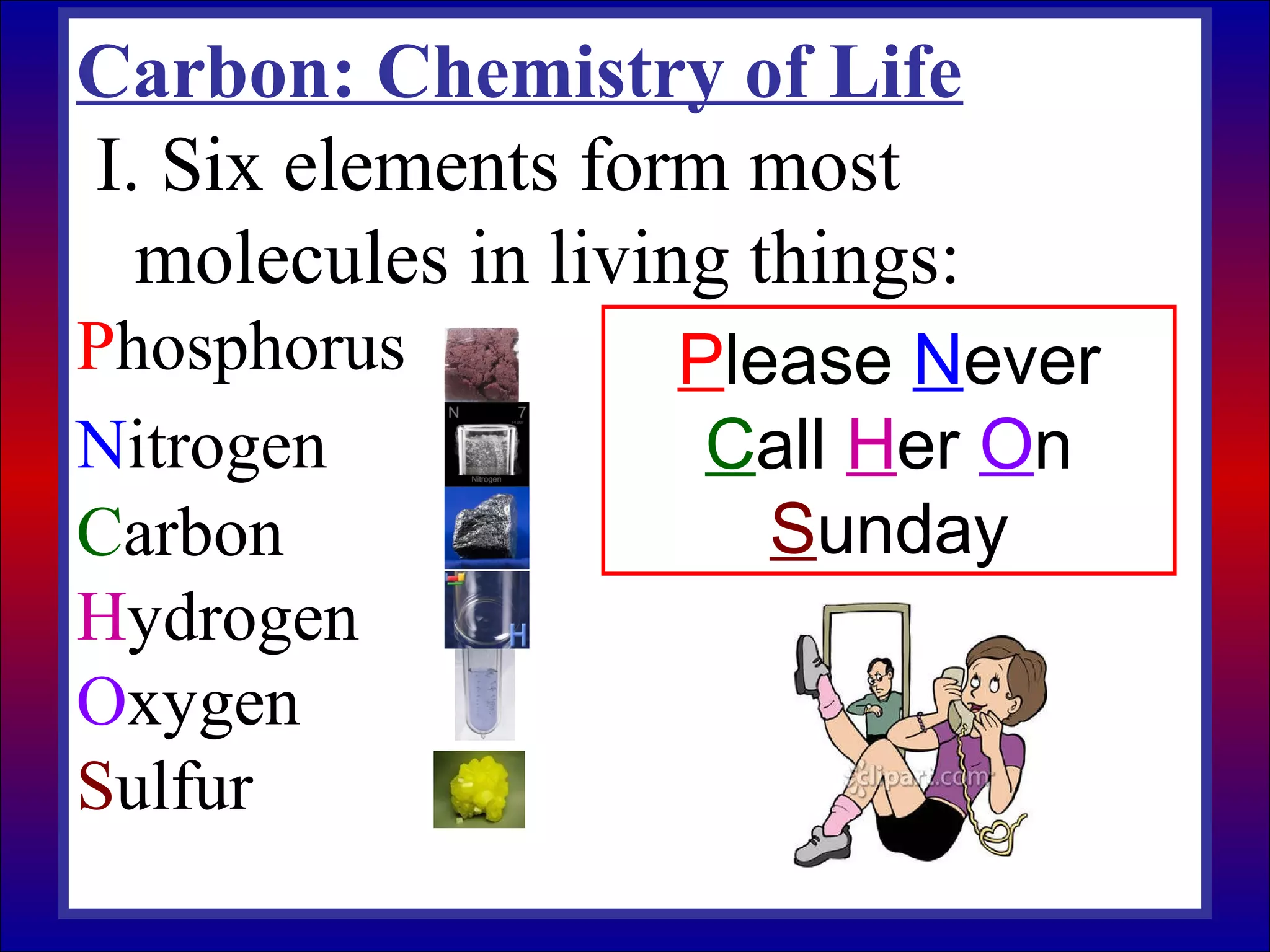
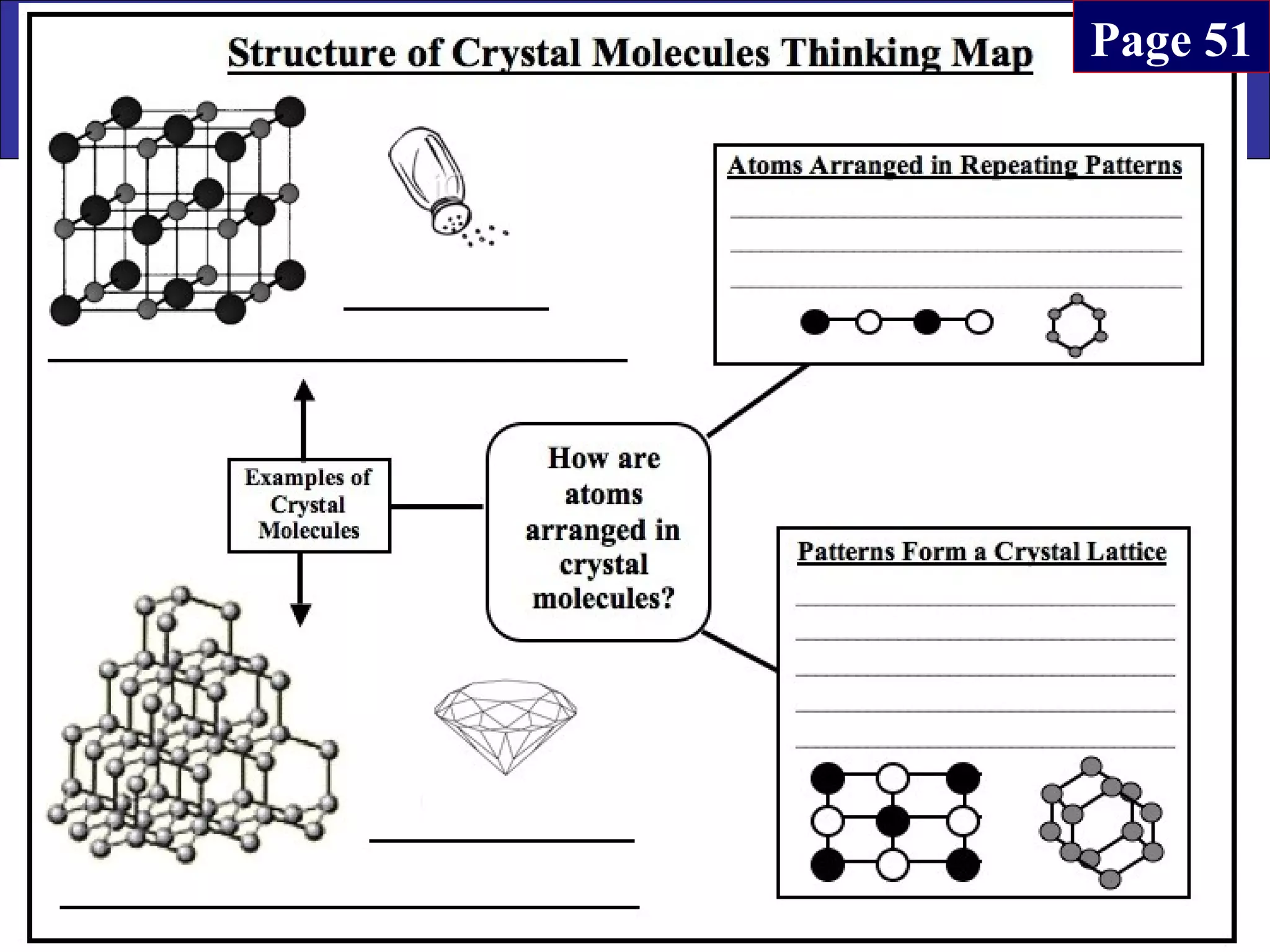
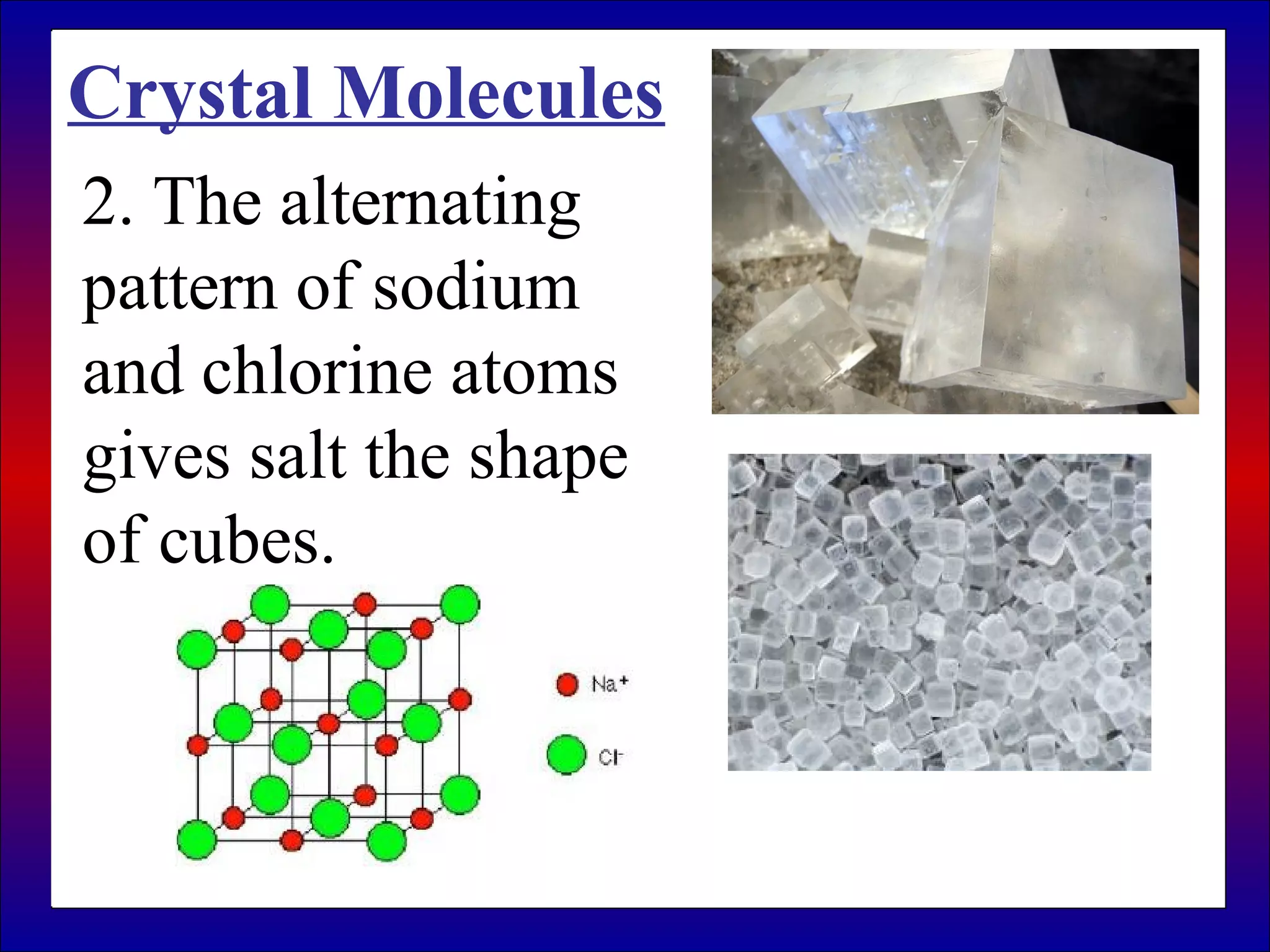
This document contains information about acids and bases, the periodic table, atomic structure, and the properties of metals, non-metals and metalloids. It includes review questions, diagrams, and definitions. Key points covered are: how substances can be classified as acids, bases or neutral; the general types of elements in the periodic table including metals, non-metals and metalloids; the characteristics of metals such as conductivity; and how electrons, protons and neutrons are arranged in the atom.