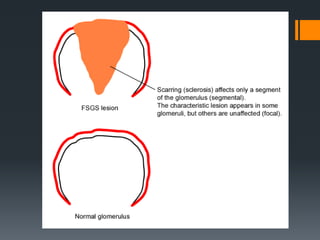
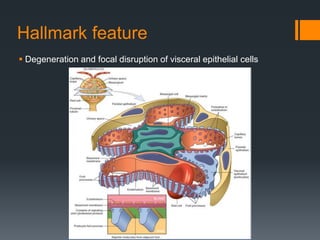
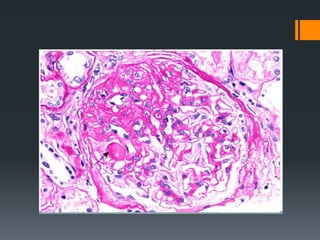
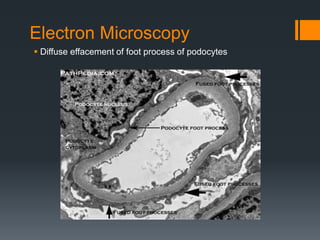
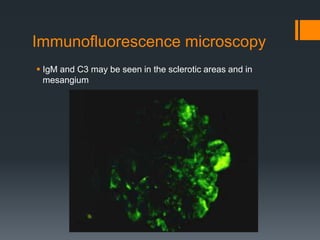
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSG) is a kidney disorder characterized by scarring of a portion of the glomeruli. It is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome. FSG can be idiopathic or secondary to conditions like HIV, sickle cell anemia, or drug abuse. On microscopy, FSG shows sclerosis, hyalinosis, and diffuse effacement of podocyte foot processes. It causes non-selective proteinuria, reduced kidney function, and hypertension. A variant called collapsing glomerulopathy is seen in HIV patients and has a poorer prognosis. While treatment options are limited, children generally have a better outlook than adults.