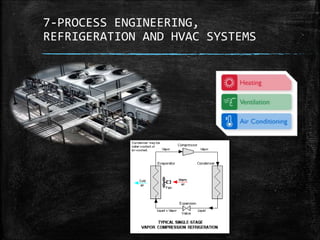
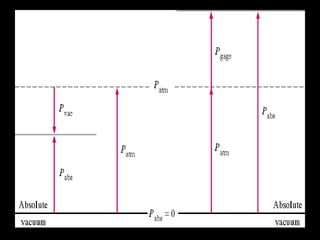
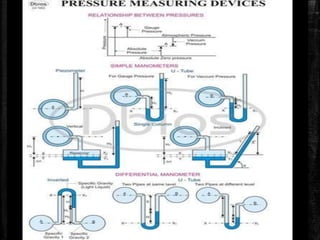
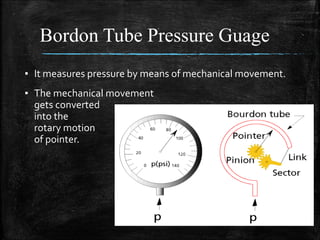
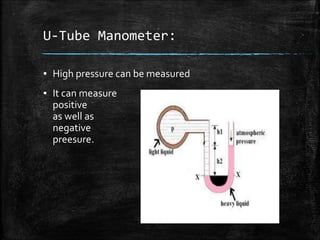
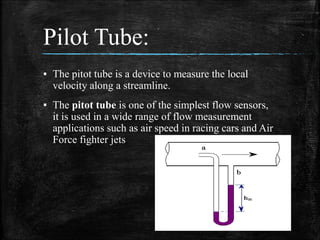
This document provides an overview of fluid mechanics for chemical engineers. It defines a fluid as a substance that can flow or deform continuously under stress, and discusses ideal and real fluids. Fluid mechanics is described as the study of fluids and forces on them, with wide applications including engineering, geophysics, and biology. Some key applications of fluid mechanics mentioned are in meteorology, forecasting natural disasters, aerospace, automobiles, turbomachines, hydraulics, renewable energy systems, and process engineering. The document also defines pressure, and describes several common devices used to measure pressure, such as manometers, Bourdon tube gauges, and the pitot tube.