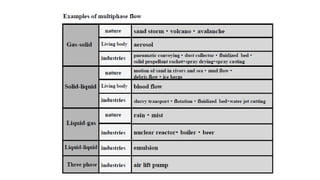
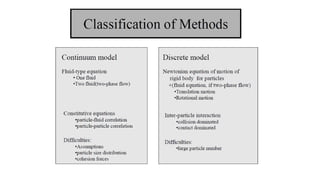
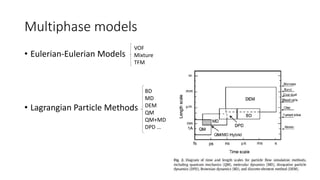
The document provides an overview of multiphase models, focusing on Eulerian-Eulerian and Lagrangian particle methods, particularly the Two-Fluid Model (TFM) and the mixture model. It explains the mathematical foundations and applications of these models in modeling interactions between multiple phases, including liquids, gases, and solids. The mixture model is presented as a simplified alternative to the full multiphase model, suitable for various applications like sedimentation and particle-laden flows.