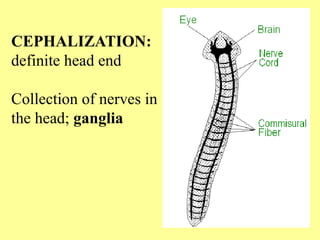
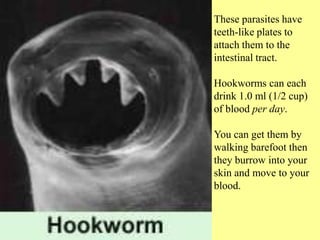
Flatworms and cnidarians share some basic characteristics like having simple tissue organization but differ in key aspects like flatworms having bilateral symmetry and a digestive system while cnidarians do not. Some flatworms like tapeworms are parasitic and can infect humans, causing illnesses if meat or water is ingested that contains the parasite larvae. Roundworms also infect many humans and include parasites like hookworms that burrow into the skin and travel to the bloodstream, feeding on blood.