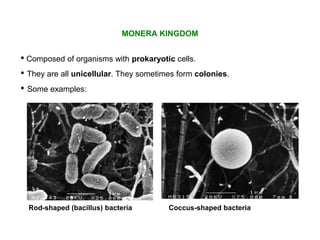
The document discusses the five kingdoms used to classify living things: Monera, Protoctista, Fungi, Plants, and Animals. Monera contains prokaryotic organisms like bacteria. Protoctista contains eukaryotic unicellular or multicellular organisms without tissues, like algae and amoebas. Fungi are eukaryotic decomposers like molds and mushrooms. Plants are eukaryotic autotrophs with tissues and organs like trees and ferns. Animals are eukaryotic heterotrophs with tissues, organs, and often systems like squirrels and jellyfish.