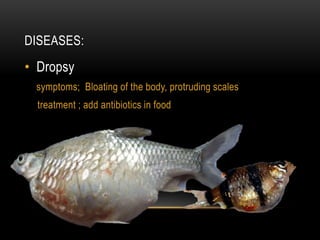
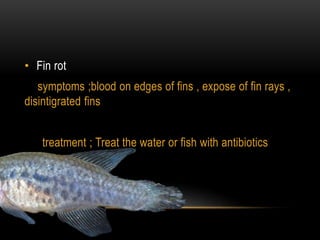
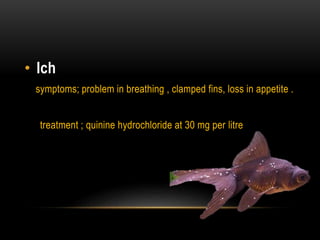
Fish farming involves raising fish commercially for food. There are three main types of fish farming: extensive, semi-intensive, and intensive. Extensive relies on natural food sources while intensive is totally dependent on supplementary feed. Common fish farming methods include ponds and cages. Major farmed species include carp, trout, milkfish, and tilapia. Starting a fish farm involves site selection, species selection, construction, ecosystem development, introduction of fish, feeding, maintenance, harvest, and breeding. Breeding can be done naturally or manually by injecting hormones and hand-spawning. Common diseases include dropsy, fin rot, and ich.