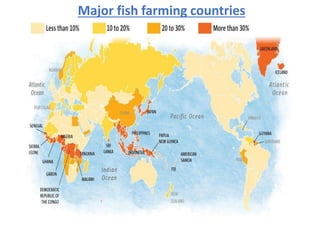
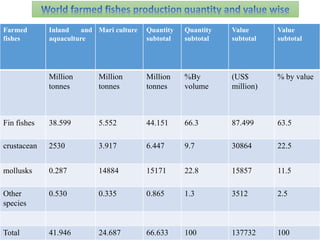
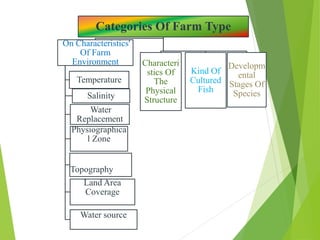
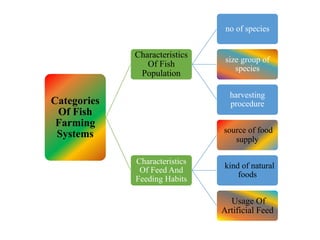
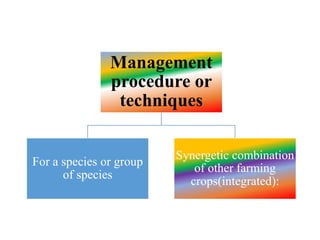
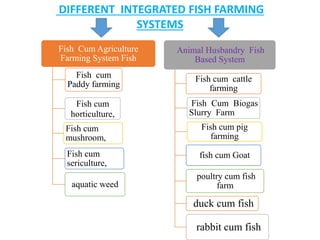
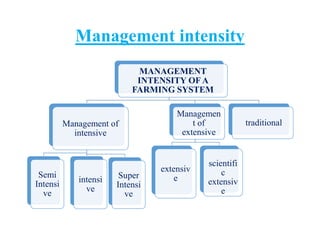
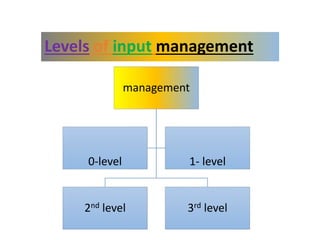
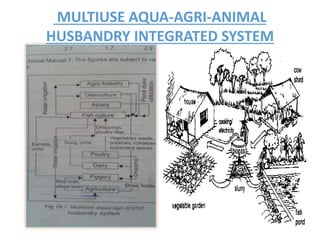
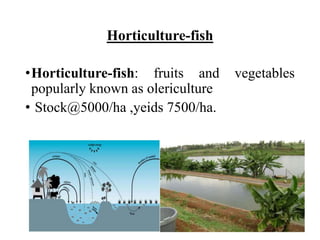
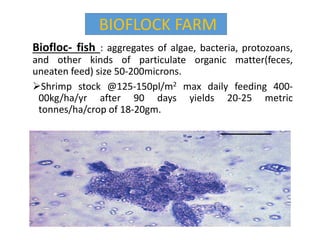
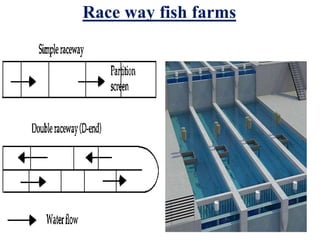
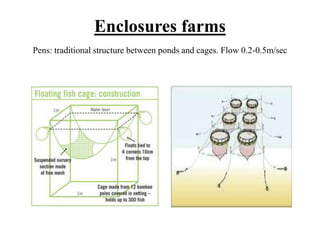
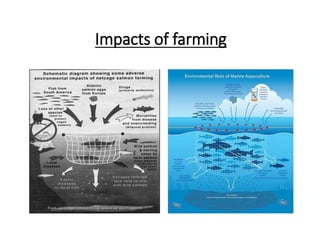
The document discusses the historical development and various systems of fish farming worldwide, starting with ancient practices in Rome and Egypt. It presents data on global fish production in 2012, categorized by species and farming types, highlighting integrated systems and their management intensities. Additionally, it addresses the environmental impacts of fish farming and emphasizes the importance of eco-friendly practices and integrated farming for sustainability.