This document provides information on the Carangidae family of fish, including:
1) Carangids are a large family of marine fish found worldwide, with over 146 species across 32 genera. They are found in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans.
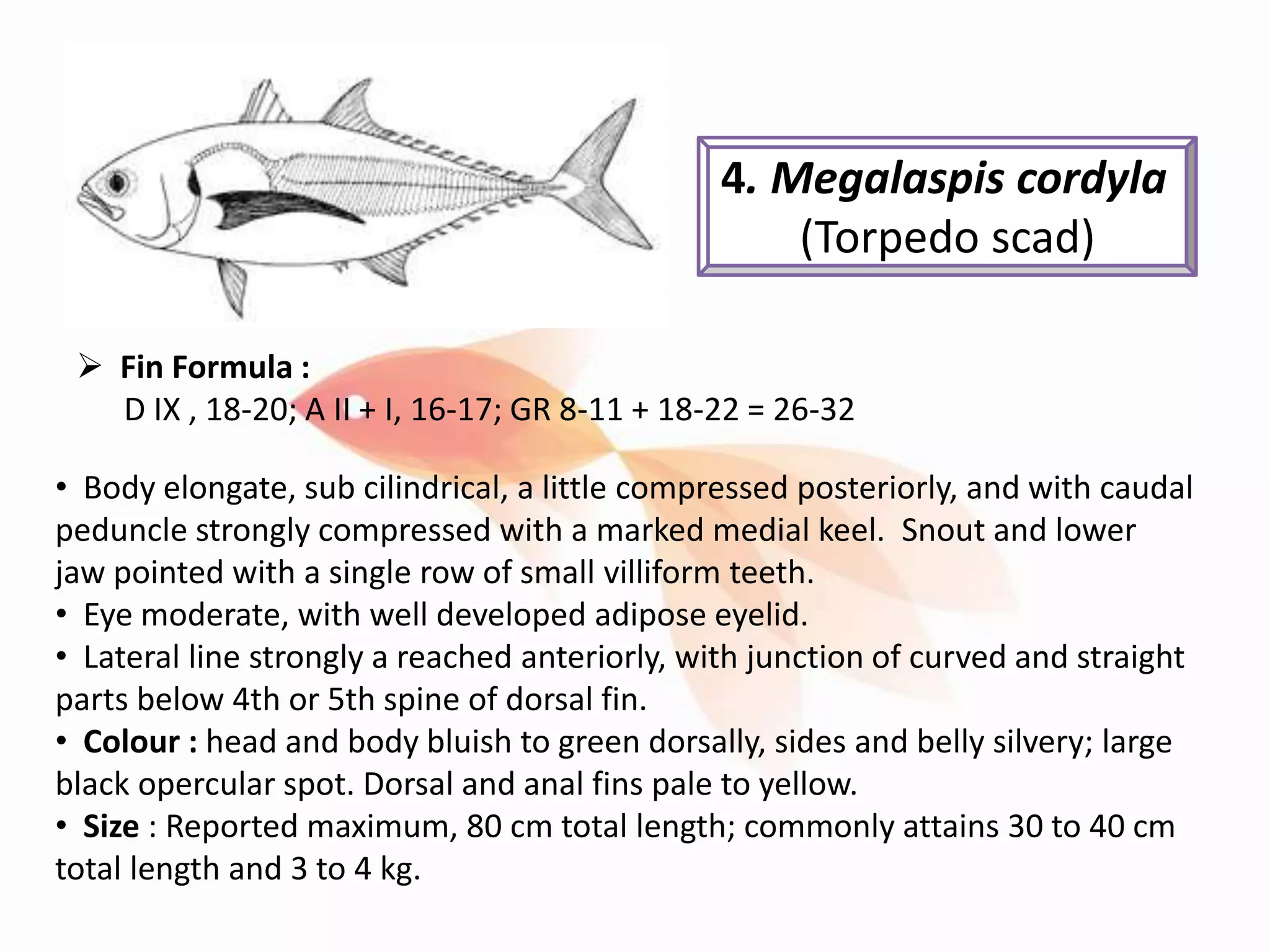
2) Four commercially important species from the Indian subcontinent are described: Alepes djedaba (shrimp scad), Scomberoides tol (needlescaled queenfish), Alectis indicus (Indian threadfish), and Megalaspis cordyla (torpedo scad).
3) Key identifying characteristics and features of the Carangidae family are outlined, along with fin formulas and size information for the four