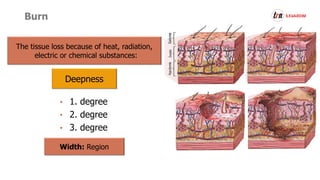
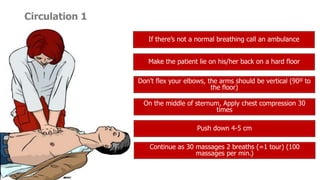
The document provides information about first aid seminar including the ABCs of first aid, evaluating an emergency situation, common medical emergencies like seizures and chest pain, injuries like bleeding and fractures, and performing CPR. Key steps in first aid include assessing for dangers, checking the victim's response, opening the airway, checking breathing and circulation, treating based on condition found, and calling for emergency help. Proper first aid can help save lives until emergency responders arrive.