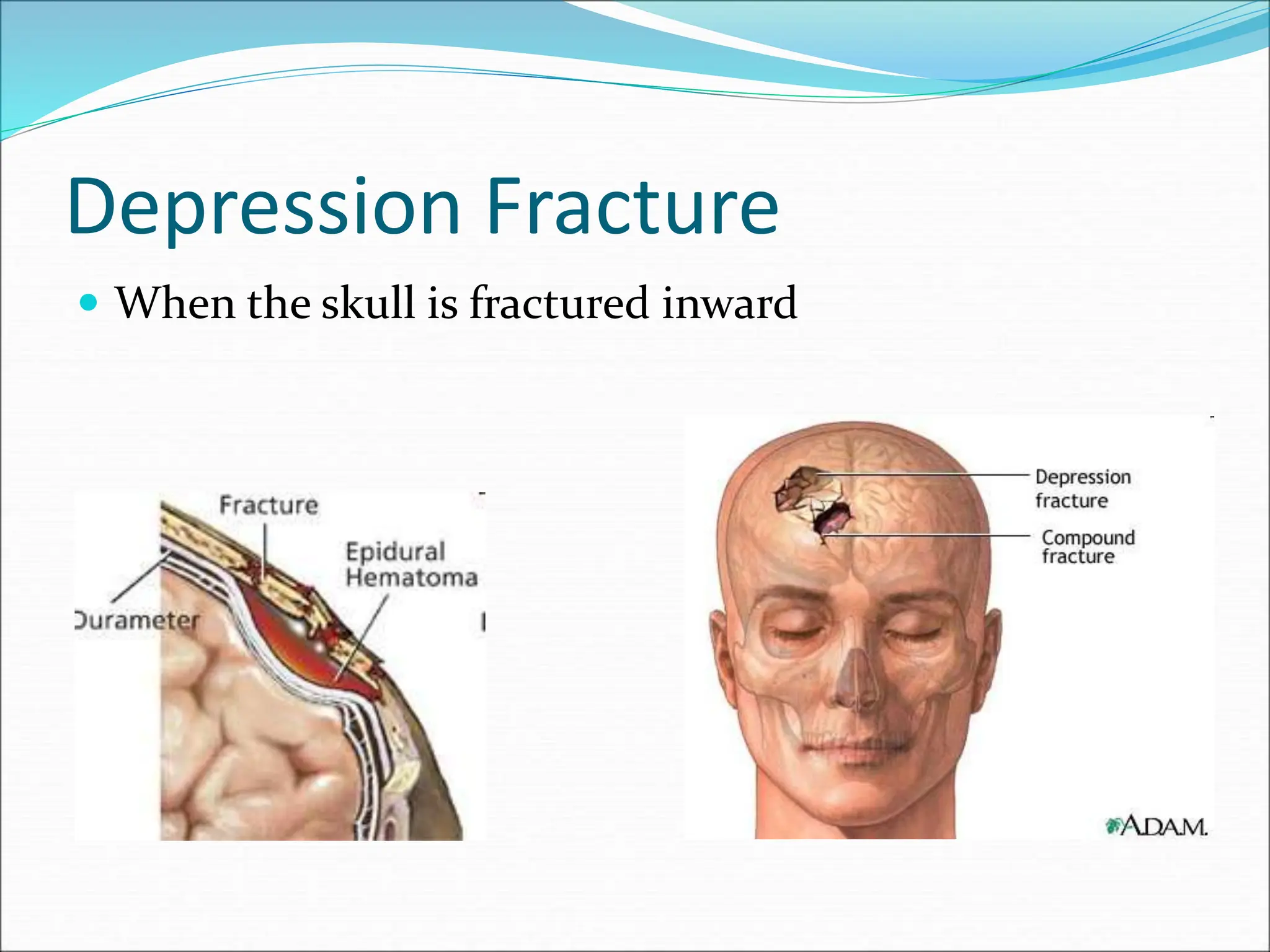
This document discusses different types of fractures, sprains, and dislocations. It defines a fracture as a break or crack in a bone. Fractures are categorized as either closed, where the skin is not broken, or open/compound, where the skin is broken and the bone may be visible. Common types of fractures include hairline, stress, complete, greenstick, comminuted, depression, complicated, transverse, oblique, and spiral. The document also defines sprains as injuries to ligaments and dislocations as bones no longer being in proper contact at a joint. General treatment principles for injuries include resting, immobilizing, applying cold, and elevating the injured area.