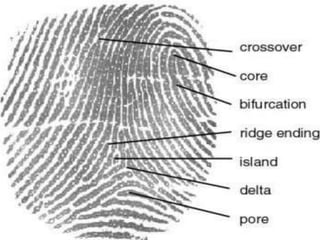
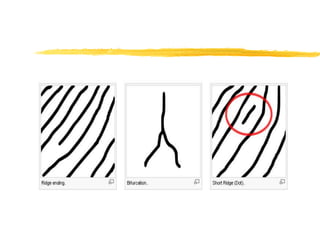
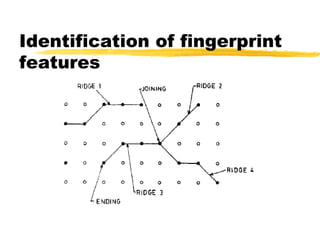
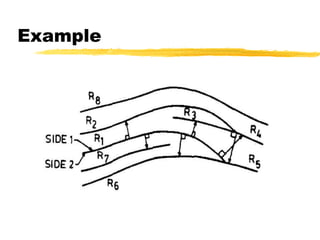
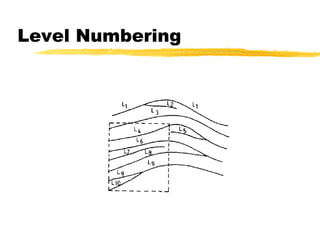
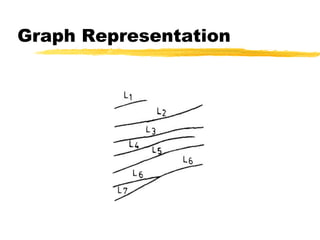
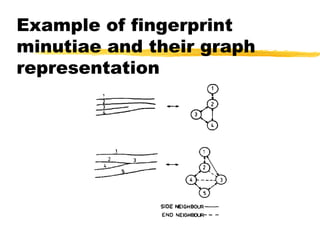
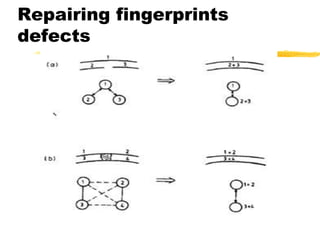
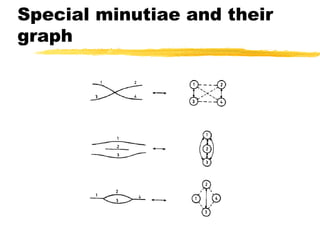
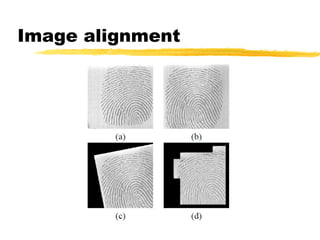
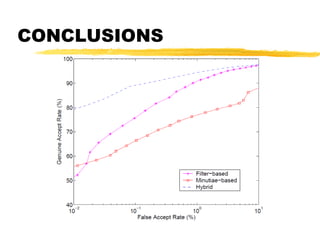
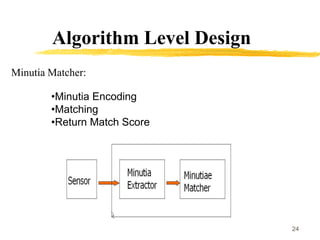
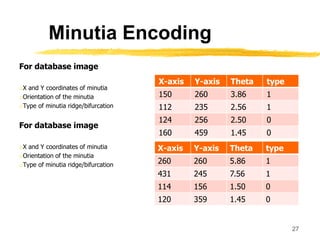
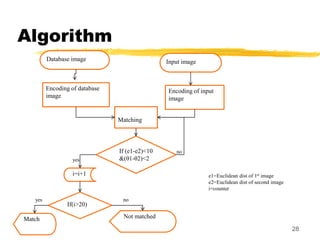
This document discusses different methods for fingerprint encoding and matching. It describes representing fingerprints as graphs based on ridge and minutiae features. Neighbor relationships between ridges are defined. Fingerprints are encoded by extracting minutiae points and recording their x-y coordinates, orientations, and types. Fingerprint matching involves calculating the Euclidean distance between corresponding minutiae points in the input and template fingerprints and determining a match if the distance is below a threshold. A hybrid approach is also presented that combines minutiae-based matching with texture-based matching using Gabor filters.