This document provides an overview of key concepts in corporate finance including:
- Definitions of finance, business finance, and financial management.
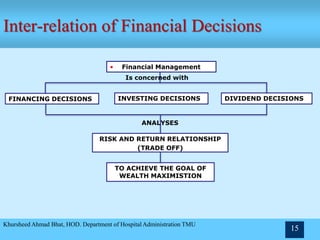
- The objectives of financial management being profit maximization and wealth maximization.
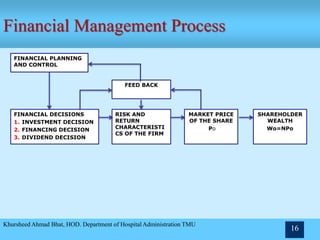
- The scope and importance of financial management in planning, raising funds, investment decisions, and more.
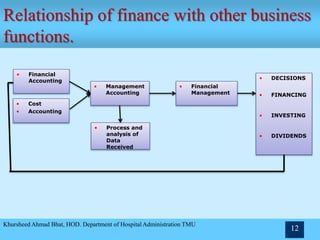
- The relationship between financial management and other business functions like production, accounting, and marketing.
- The roles and functions of a finance manager in areas like financial planning, acquiring and investing funds.