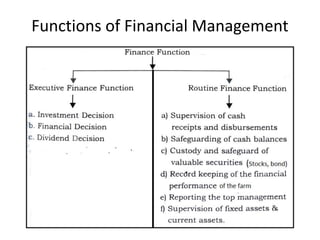
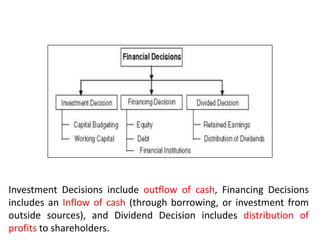
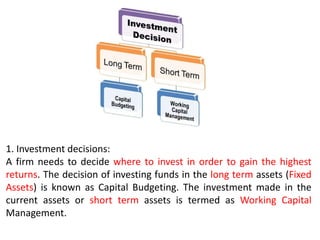
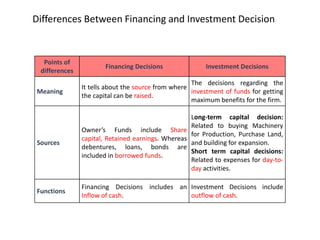
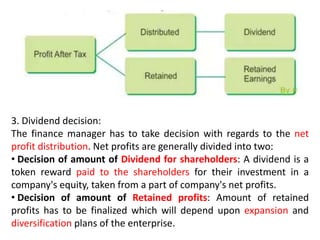
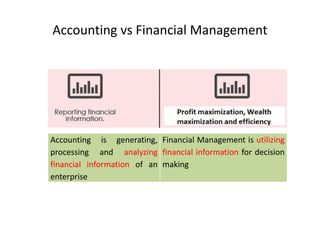
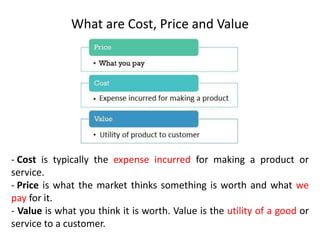
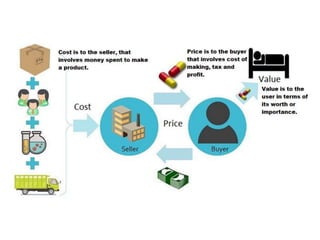
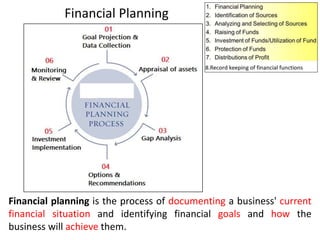
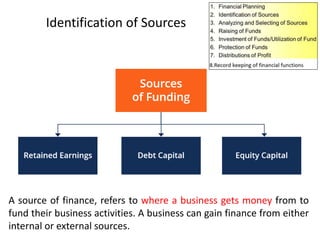
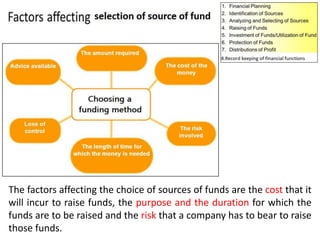
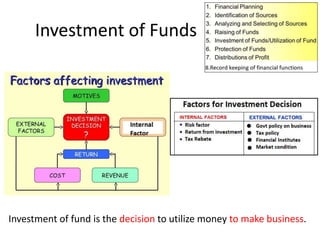
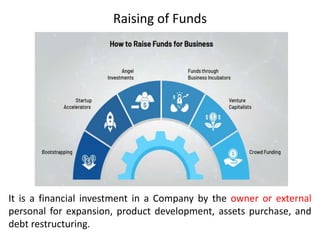
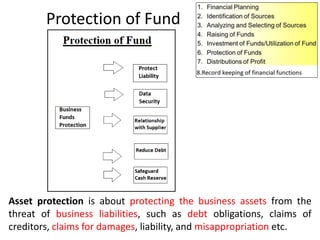
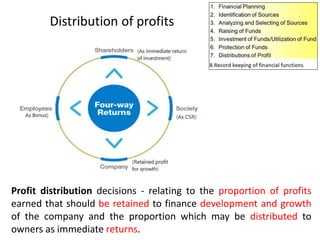
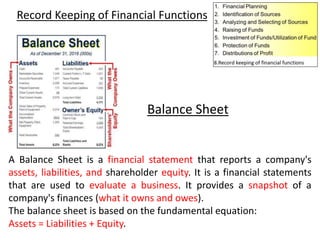
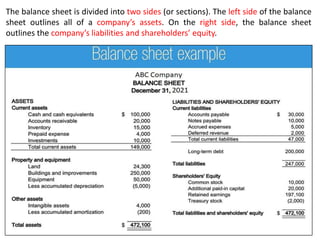
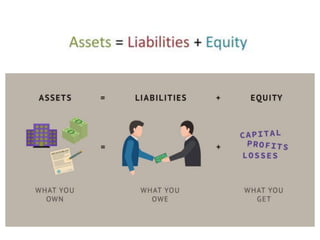
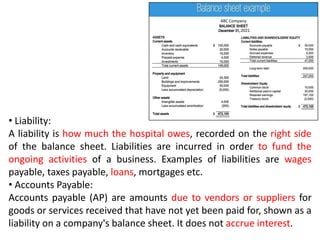
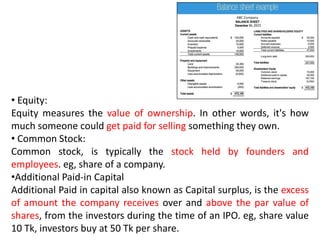
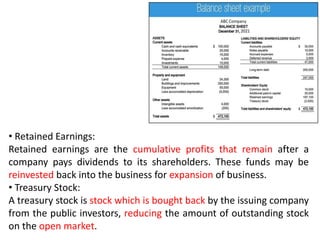
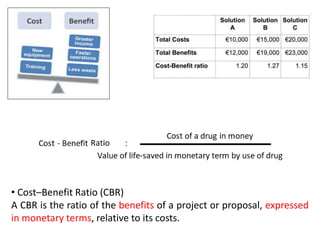
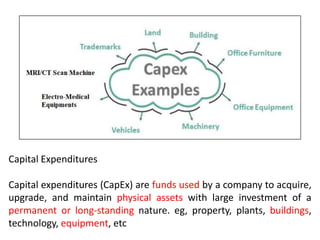
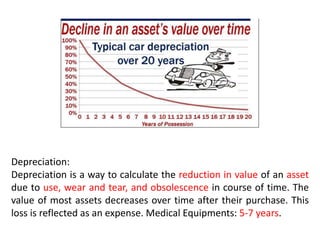
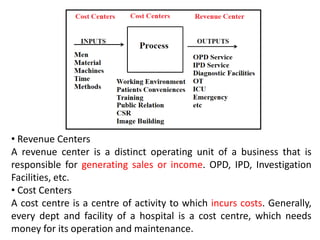
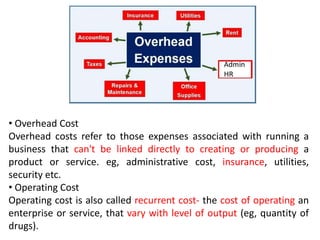
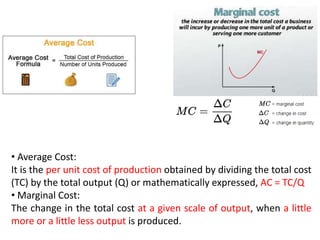
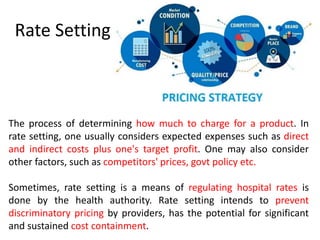
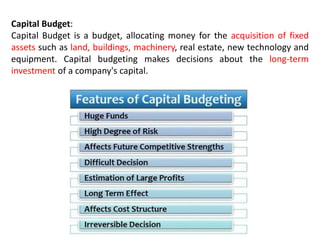
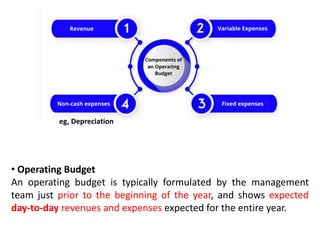
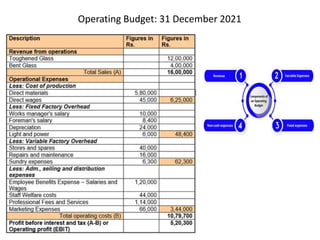
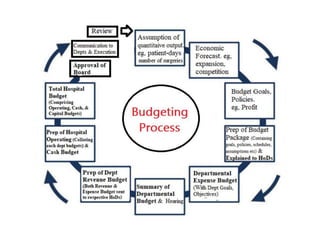
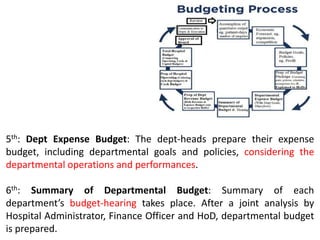
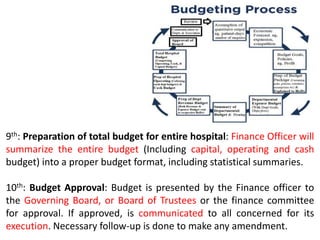
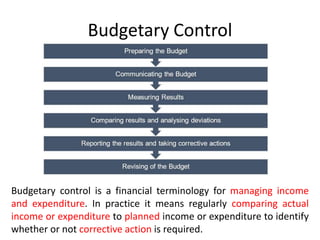
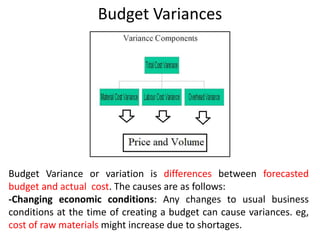
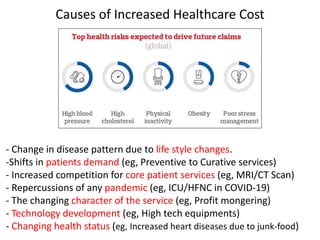
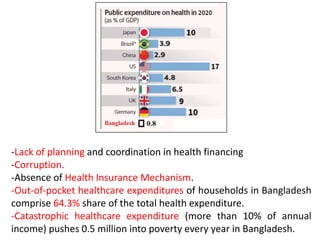
The document discusses financial management in hospitals. It defines financial management and outlines its key objectives such as profit maximization, wealth maximization, and cash flow maintenance. It also discusses the functions of financial management including investment decisions, financing decisions, and dividend decisions. Investment decisions involve the outflow of funds while financing decisions involve the inflow of funds. The responsibilities of a finance manager are also outlined, including financial planning, identifying funding sources, investing funds, raising funds, protecting funds, distributing profits, and keeping financial records.