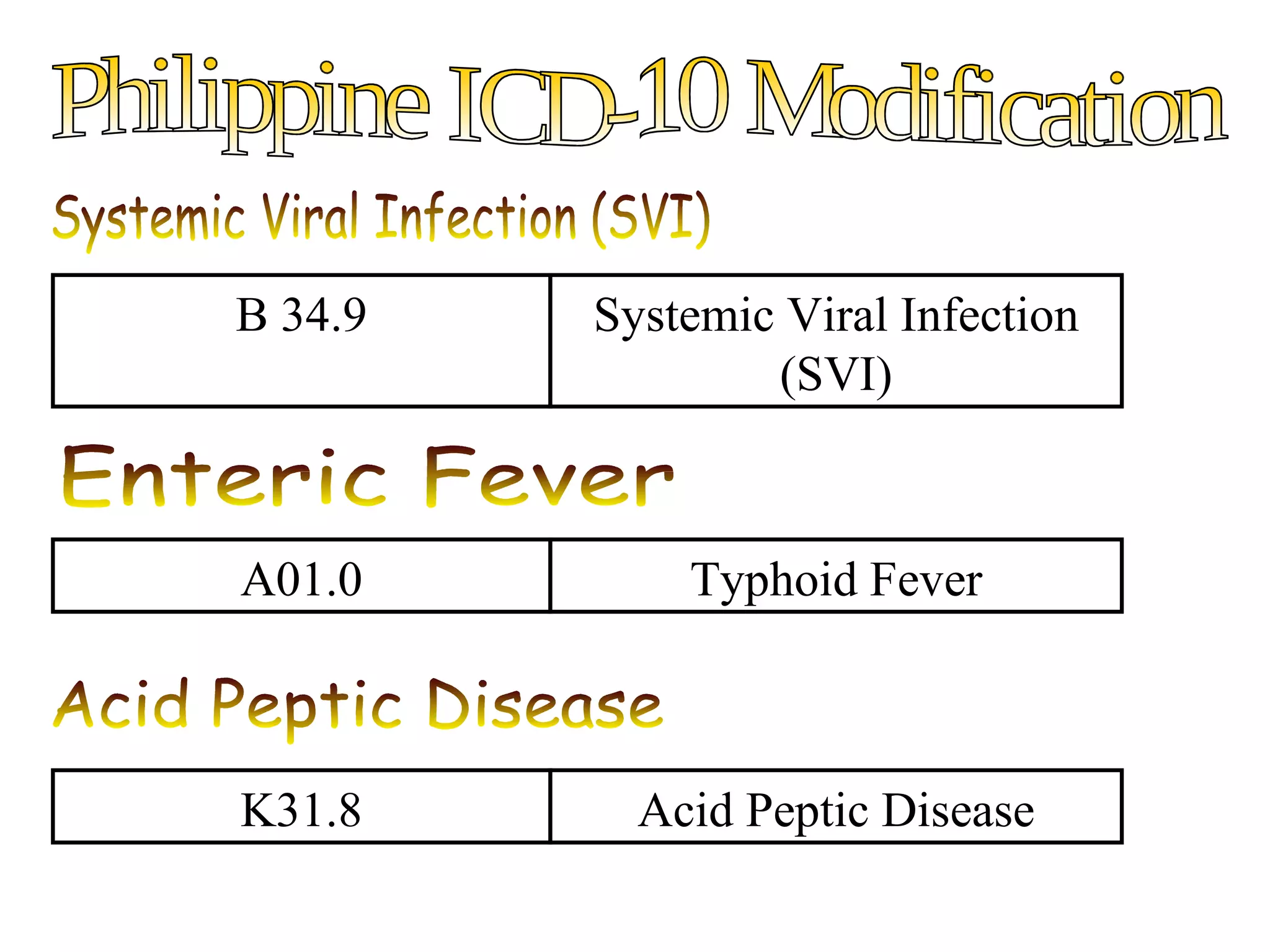
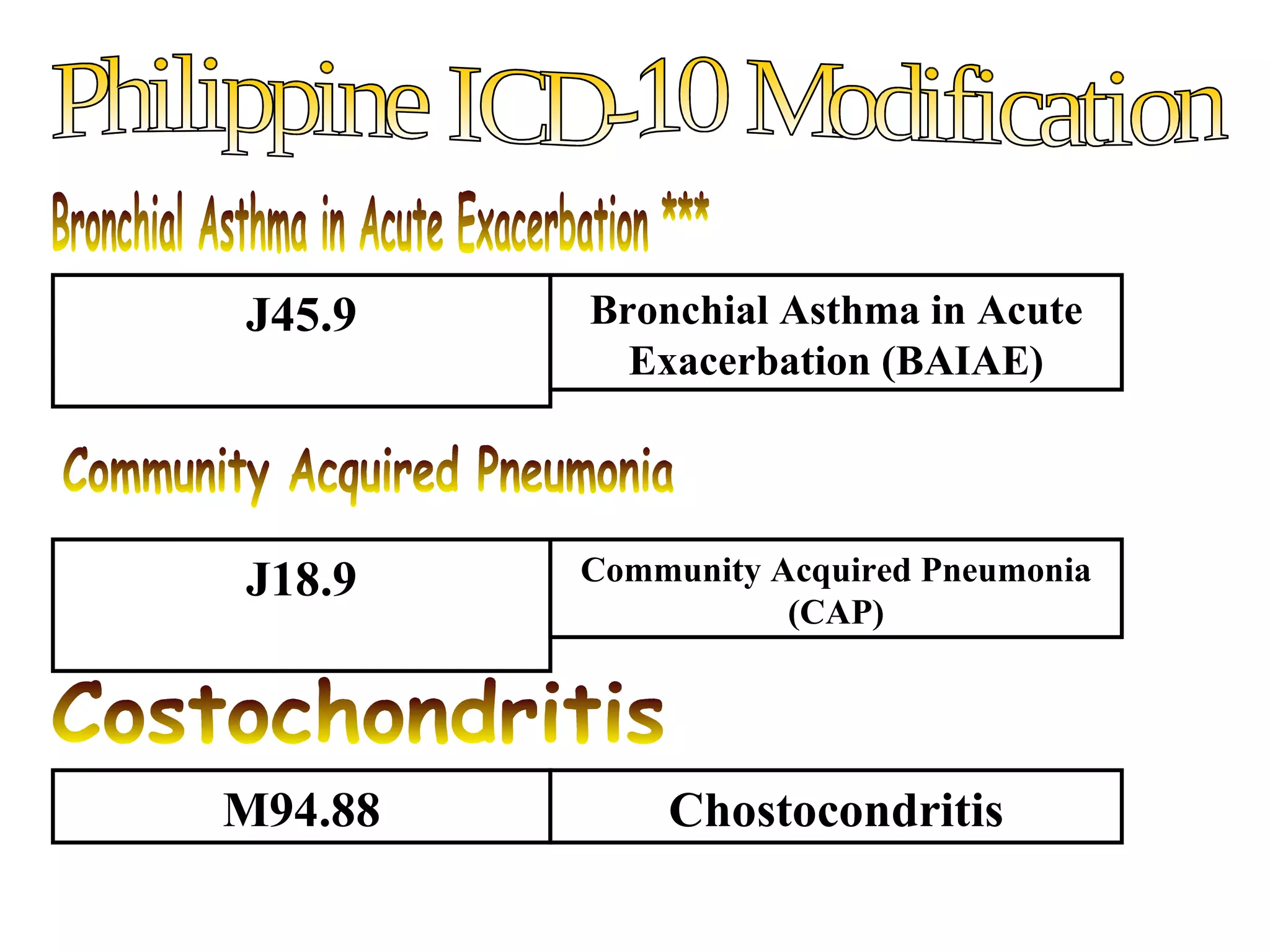
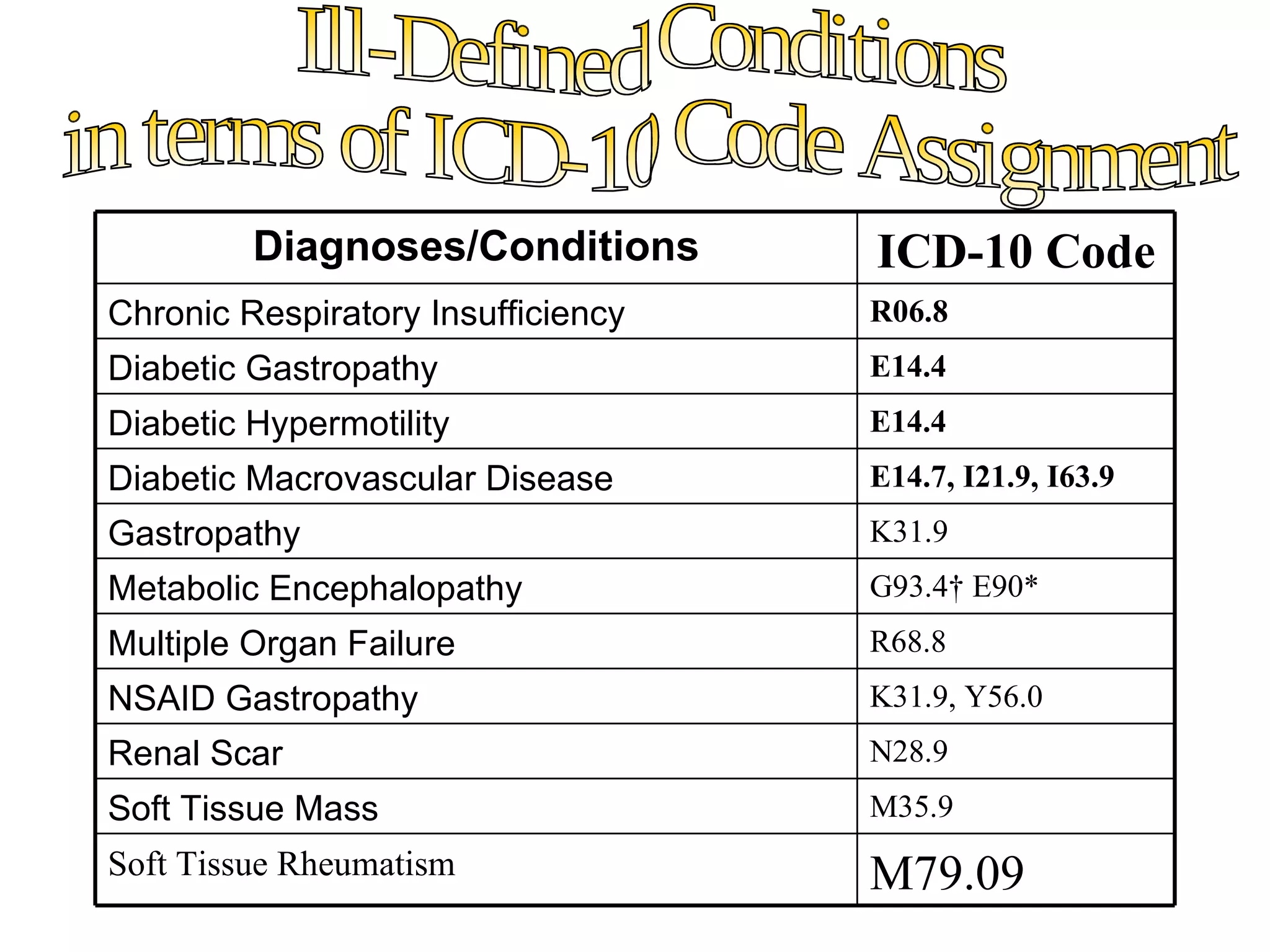
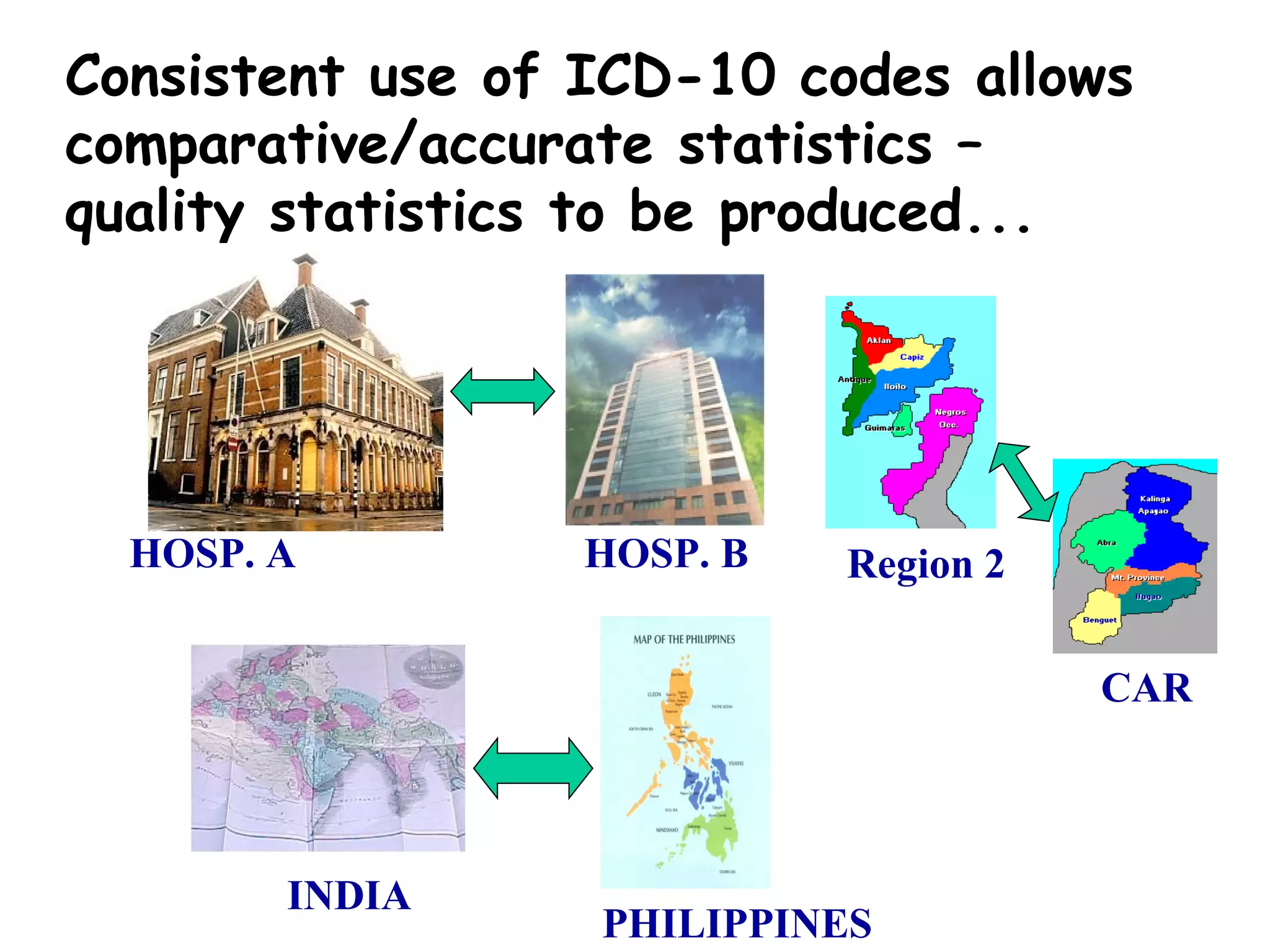
The ICD-10 is a systematic coding system developed by the World Health Organization for classifying diseases and health conditions into categories for statistical analysis and reporting, and it has been revised over 100 years. The ICD-10 code structure is alphanumeric and used internationally to classify morbidity and mortality data for purposes like epidemiology, health services planning, and medical care management. Proper use of ICD-10 codes allows for consistent and accurate health statistics to be produced and compared across hospitals, regions, and countries.






















![ICD-10 CODE CONDITIONS
Z20.1 Pulmonary Tuberculosis [PTB]
Class 1,2
A15.0 Pulmonary Tuberculosis [PTB]
Class 3 by sputum confirmation
A16.2 Pulmonary Tuberculosis [PTB]
Pulmonary Tuberculosis [PTB]
Class 2,3,5 by x-ray confirmation
Z03.0 Pulmonary Tuberculosis [PTB]
Class 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icdupdt-120531190319-phpapp02/75/Icd-updt-28-2048.jpg)