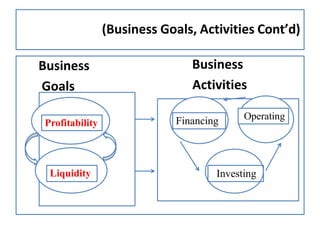
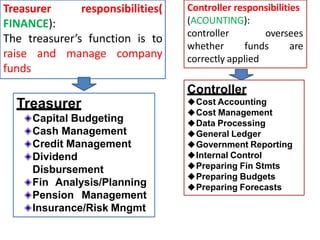
This document provides an overview of financial management. It defines key terms like accounting, financial management, and their various roles. It describes the goals of financial management as maximizing profits and shareholder wealth. It also outlines the major activities of businesses including financing, operating, and investing activities. Finally, it discusses the major areas of financial decision making for firms, including investment decisions, financing decisions, asset management, liquidity decisions, and dividend decisions.