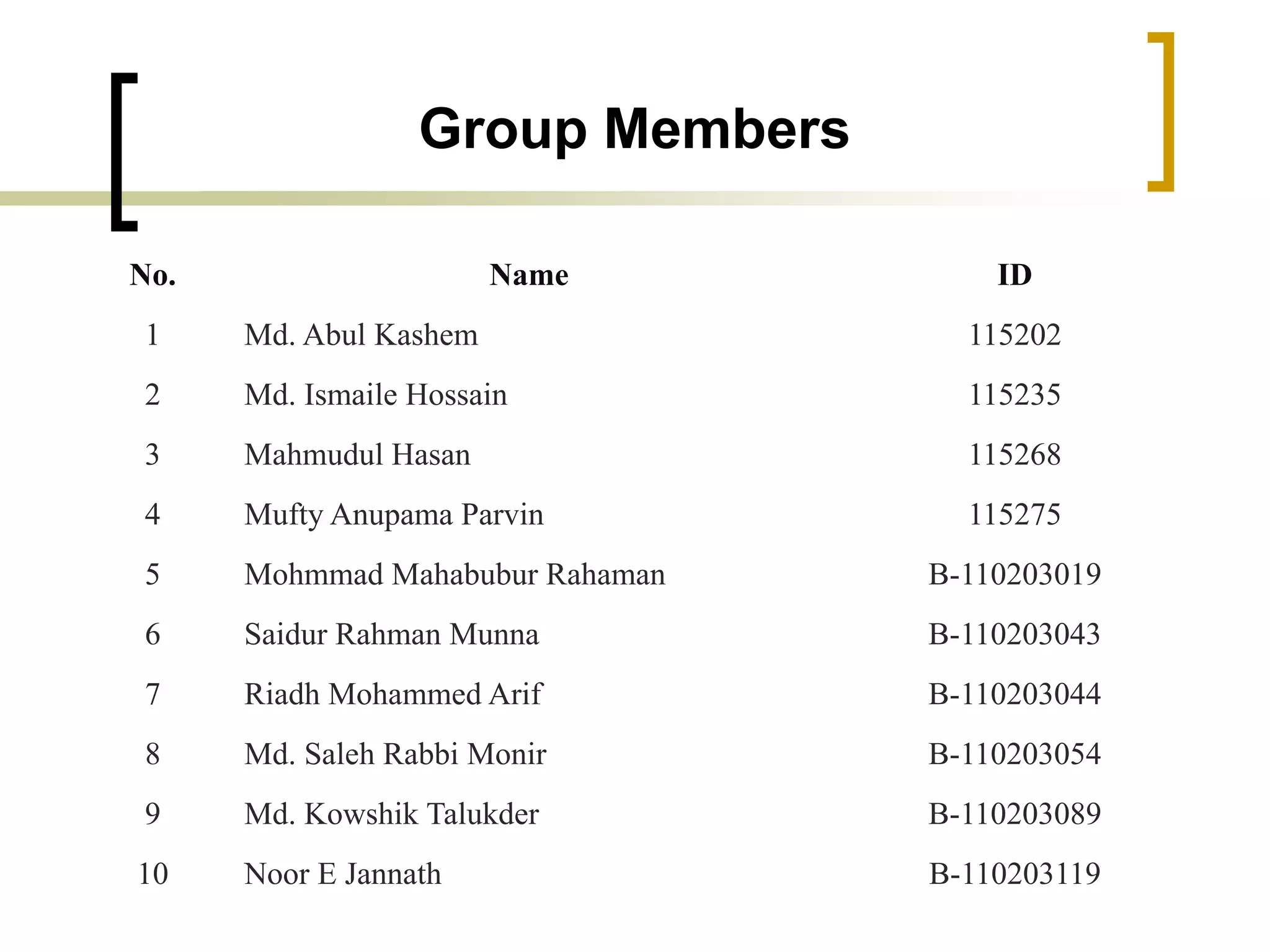
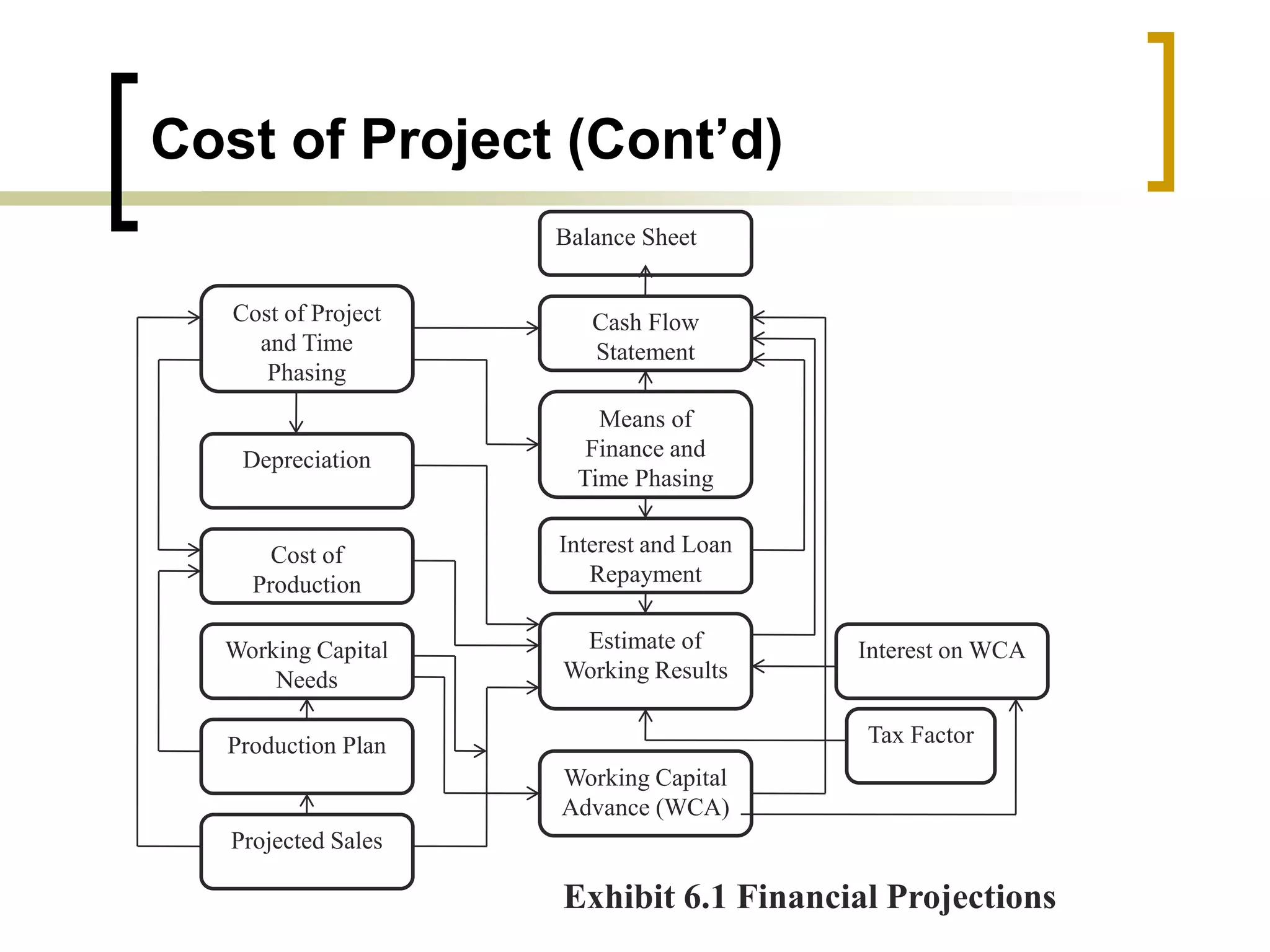
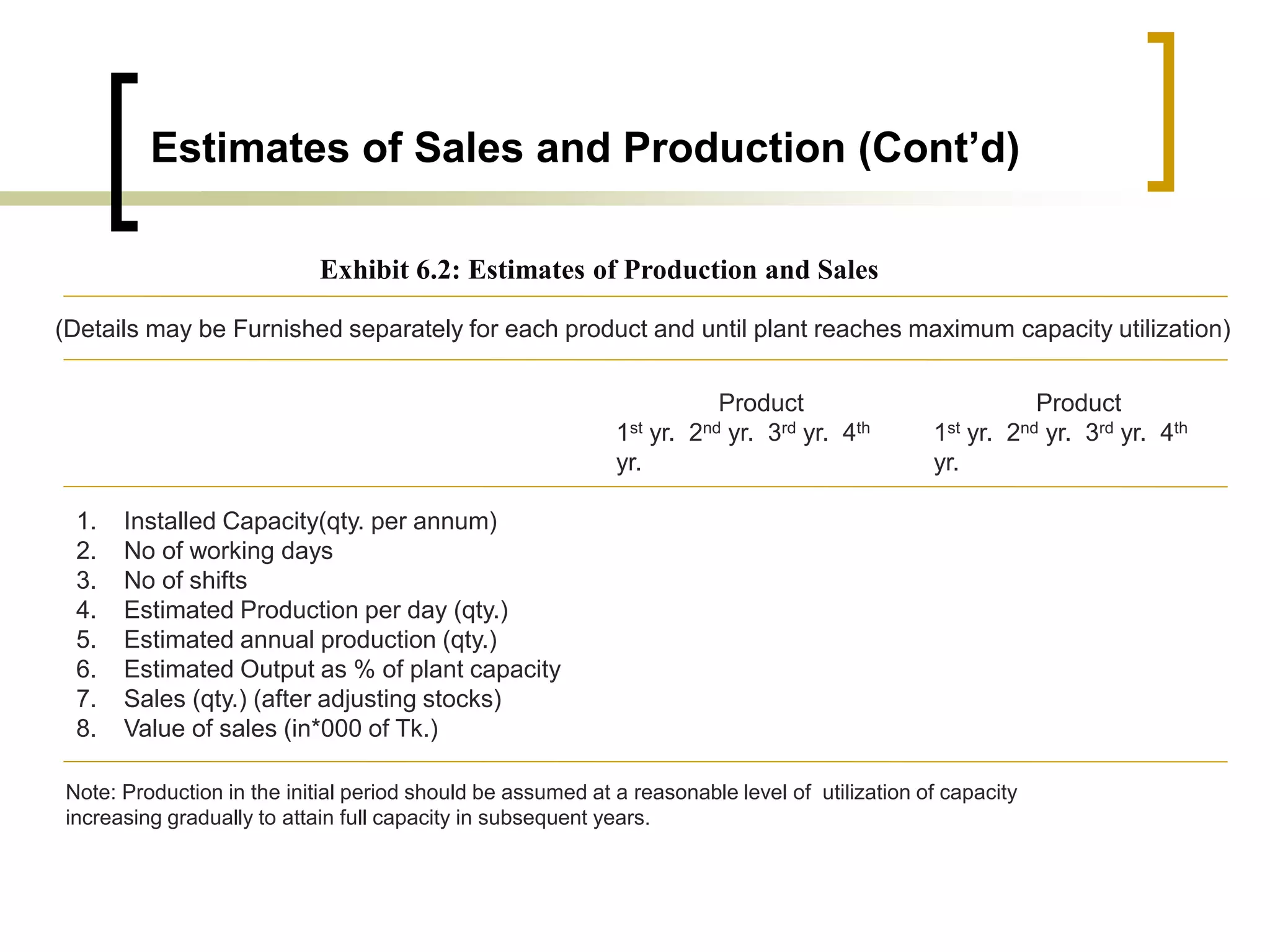
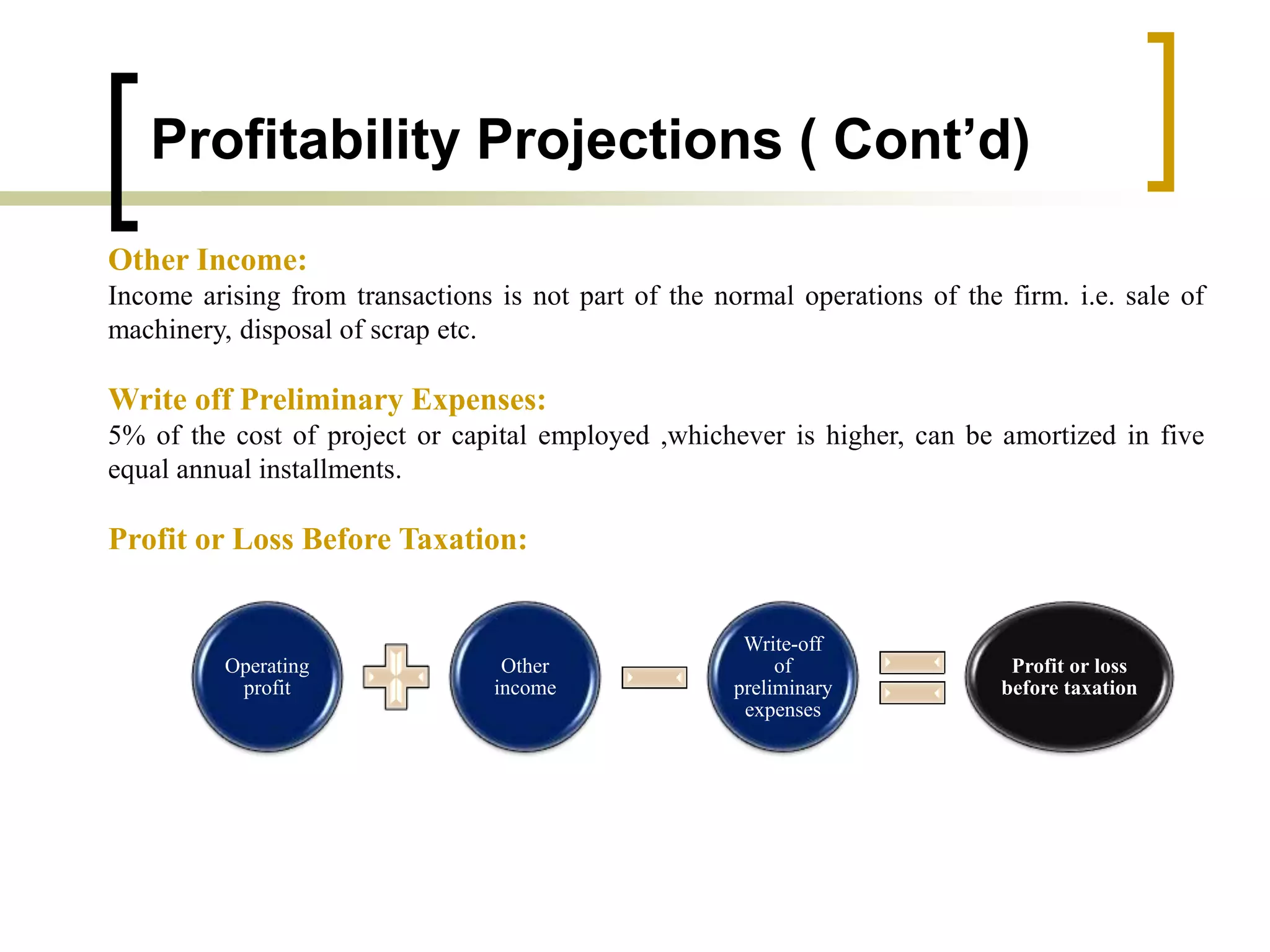
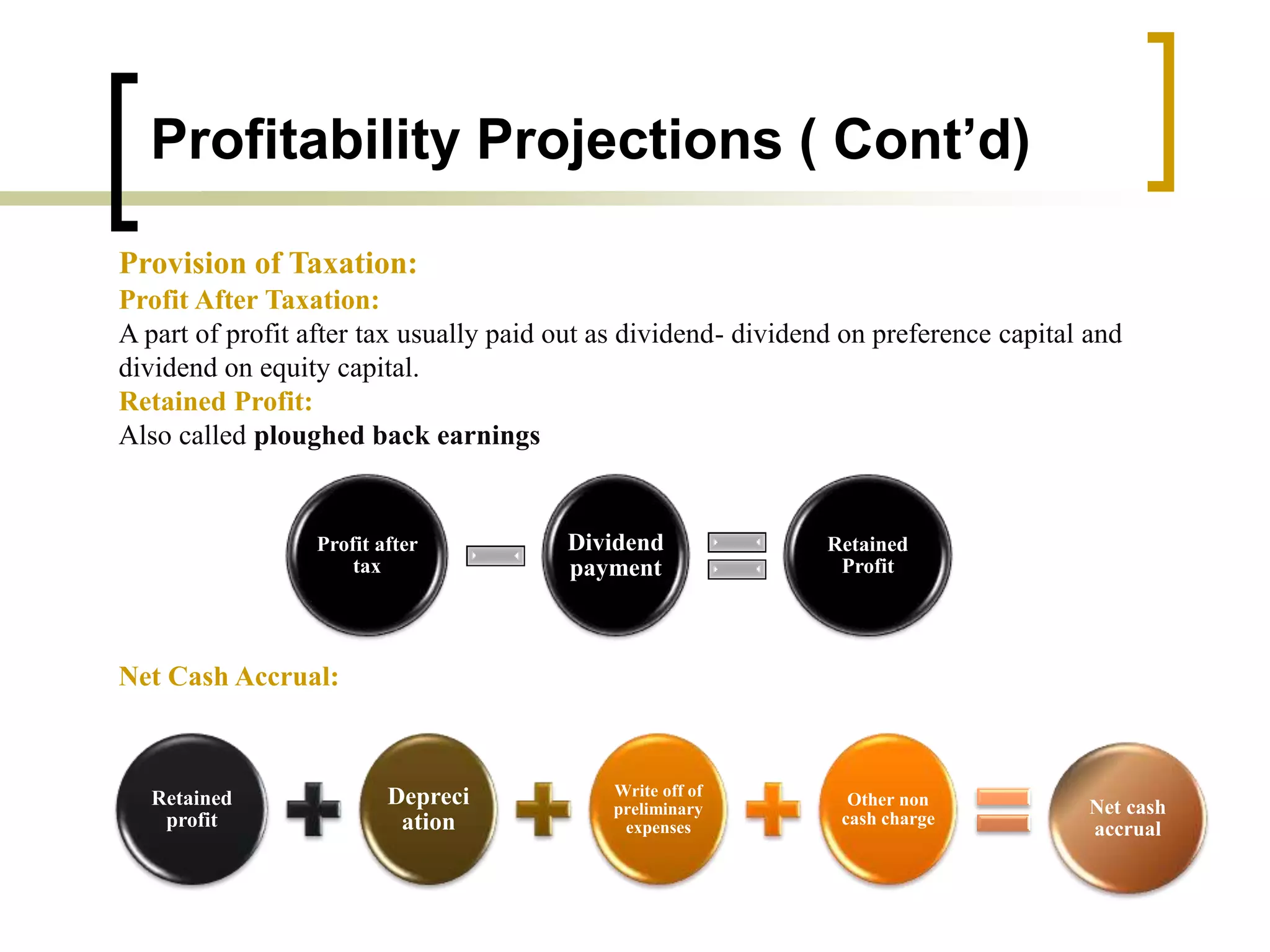
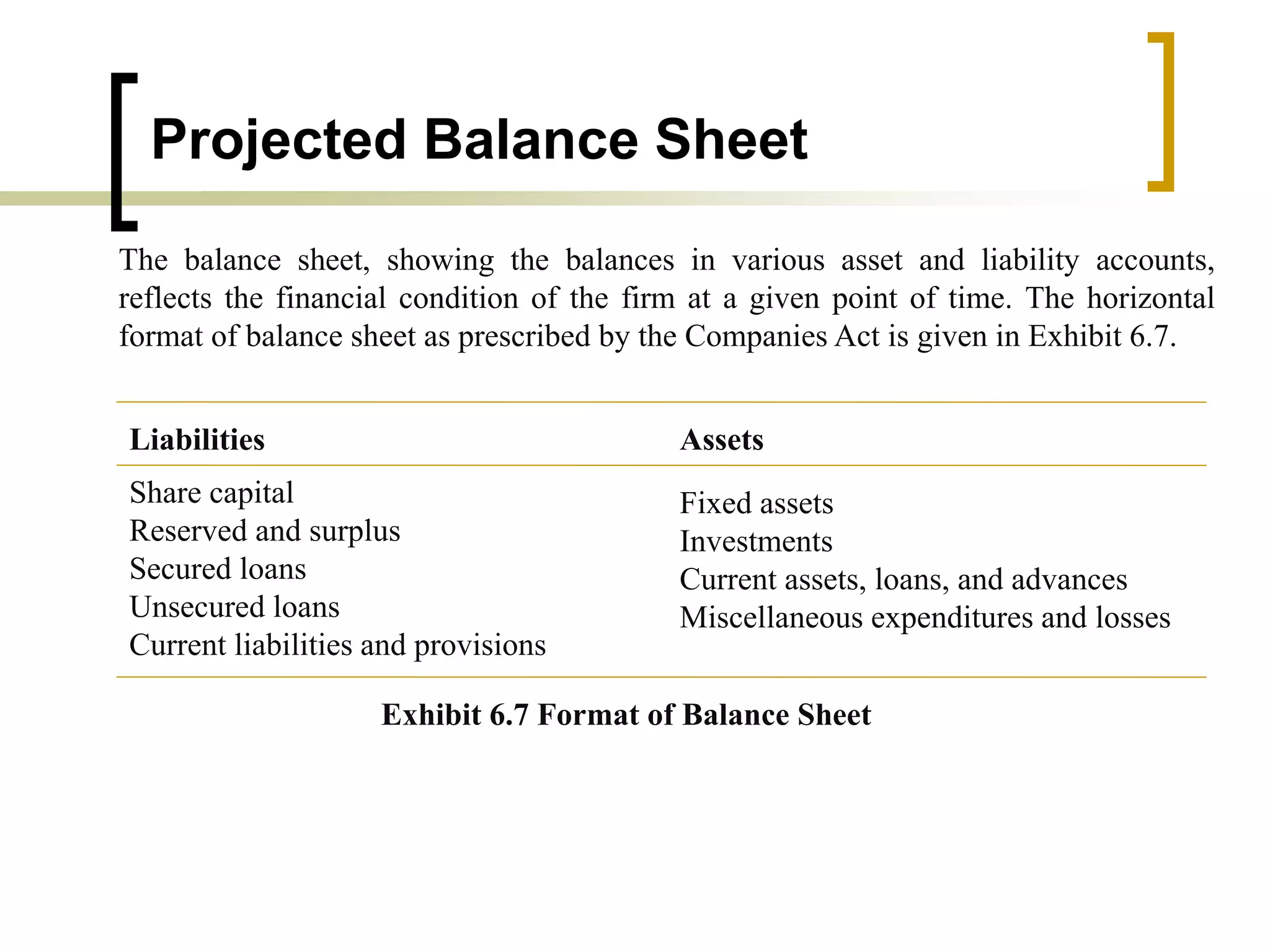
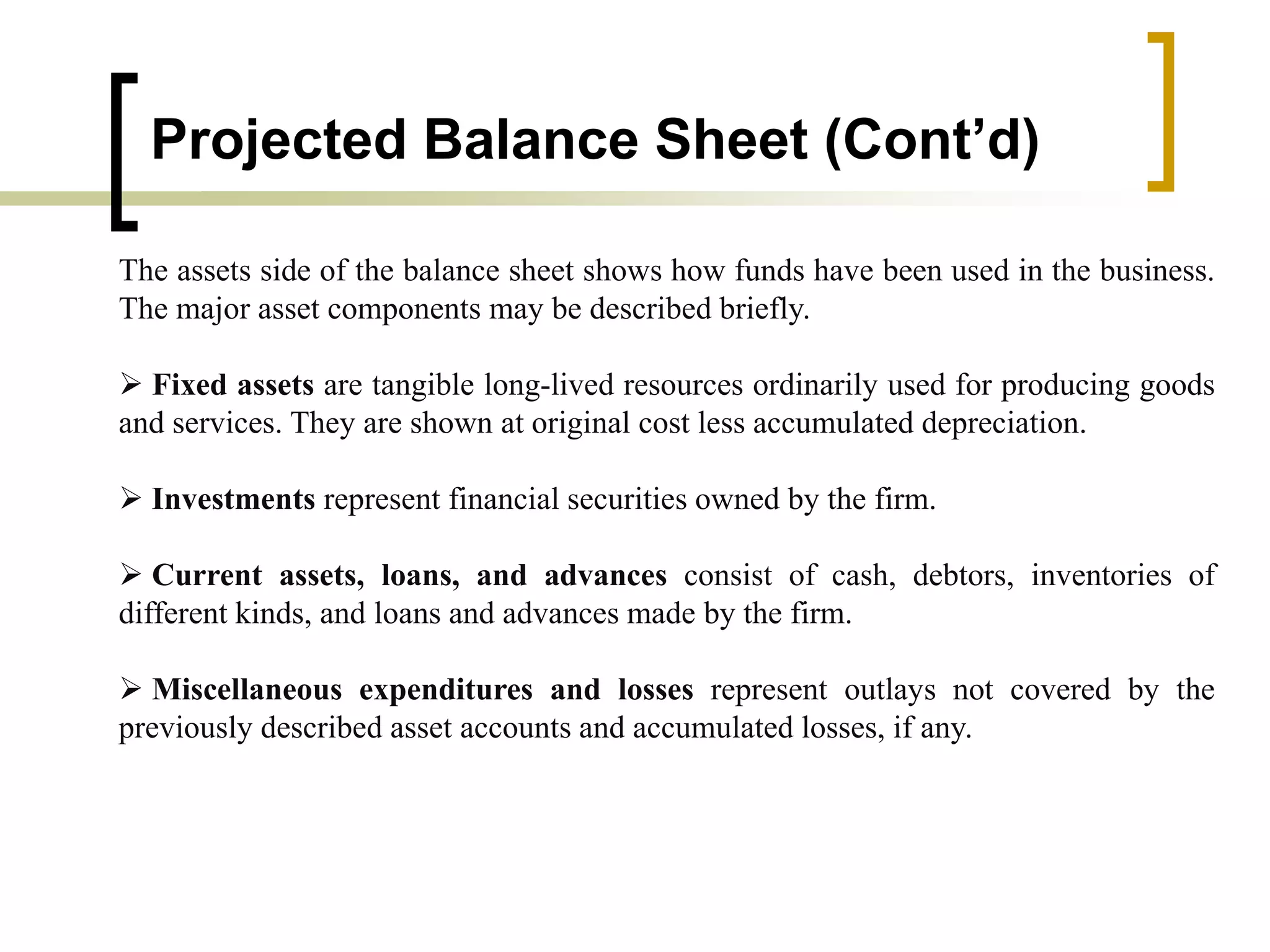
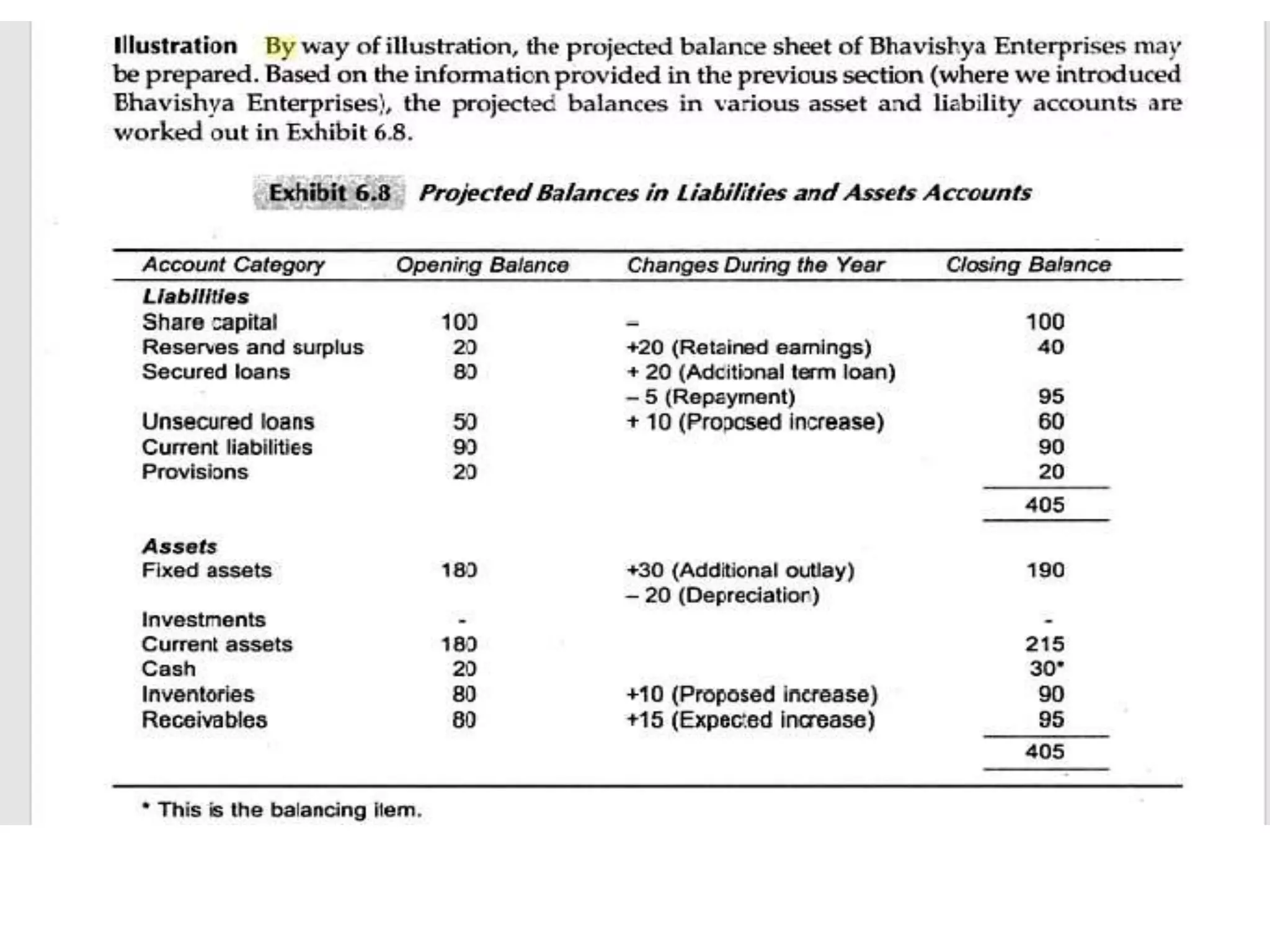
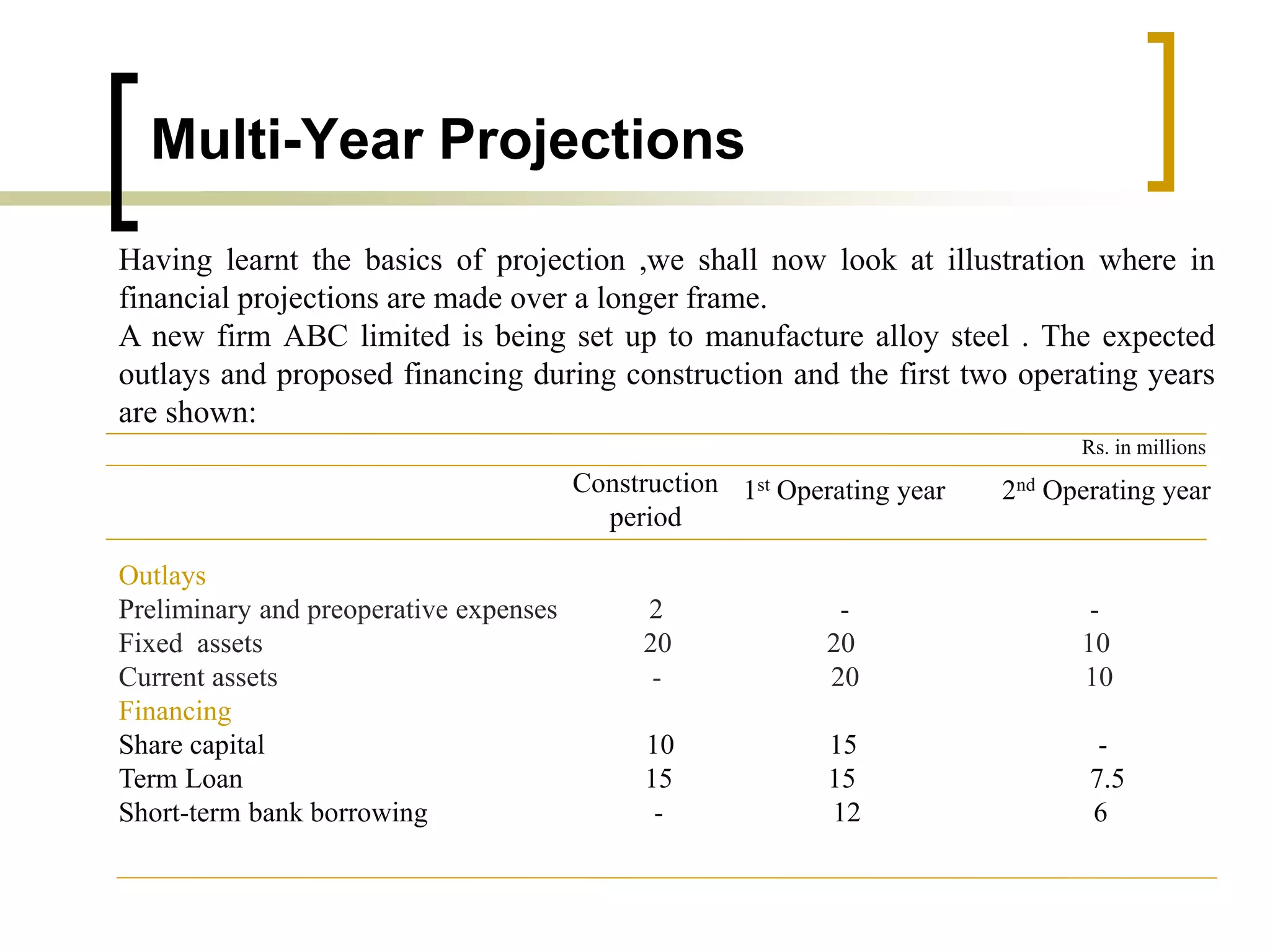
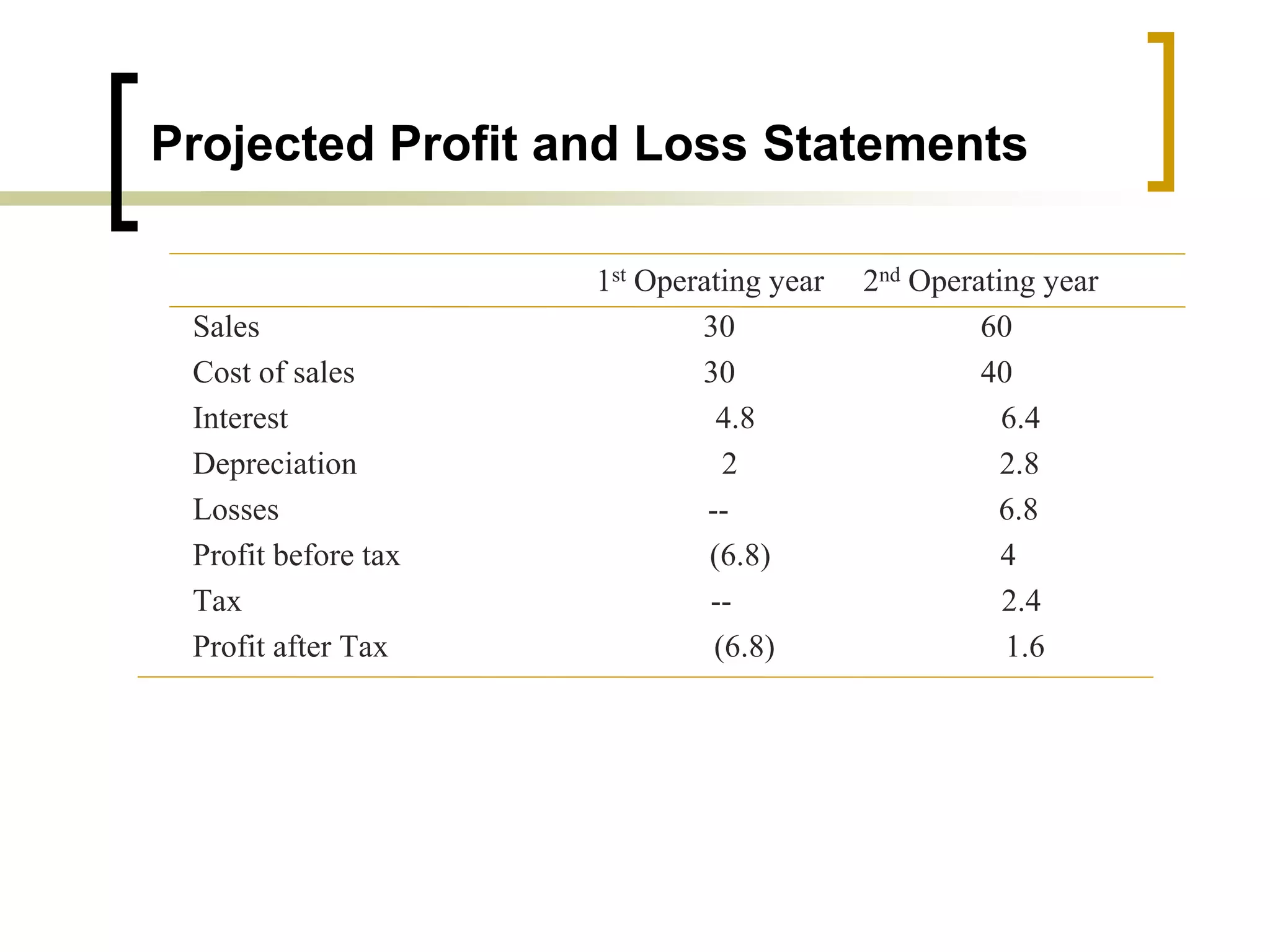
The document outlines financial estimates and projections for a project, detailing the components of project costs such as land development, machinery, and working capital. It covers means of financing, including share capital, loans, and government incentives, as well as projections for revenues, costs, and profitability. It also addresses cash flow statements and balance sheets to monitor financial health over time.