1) Project finance sources funds for long-term infrastructure projects through a special purpose vehicle (SPV) formed by corporates and development authorities.
2) The SPV funds 30% of projects through equity and 70% through debt from several banks and financing institutions.
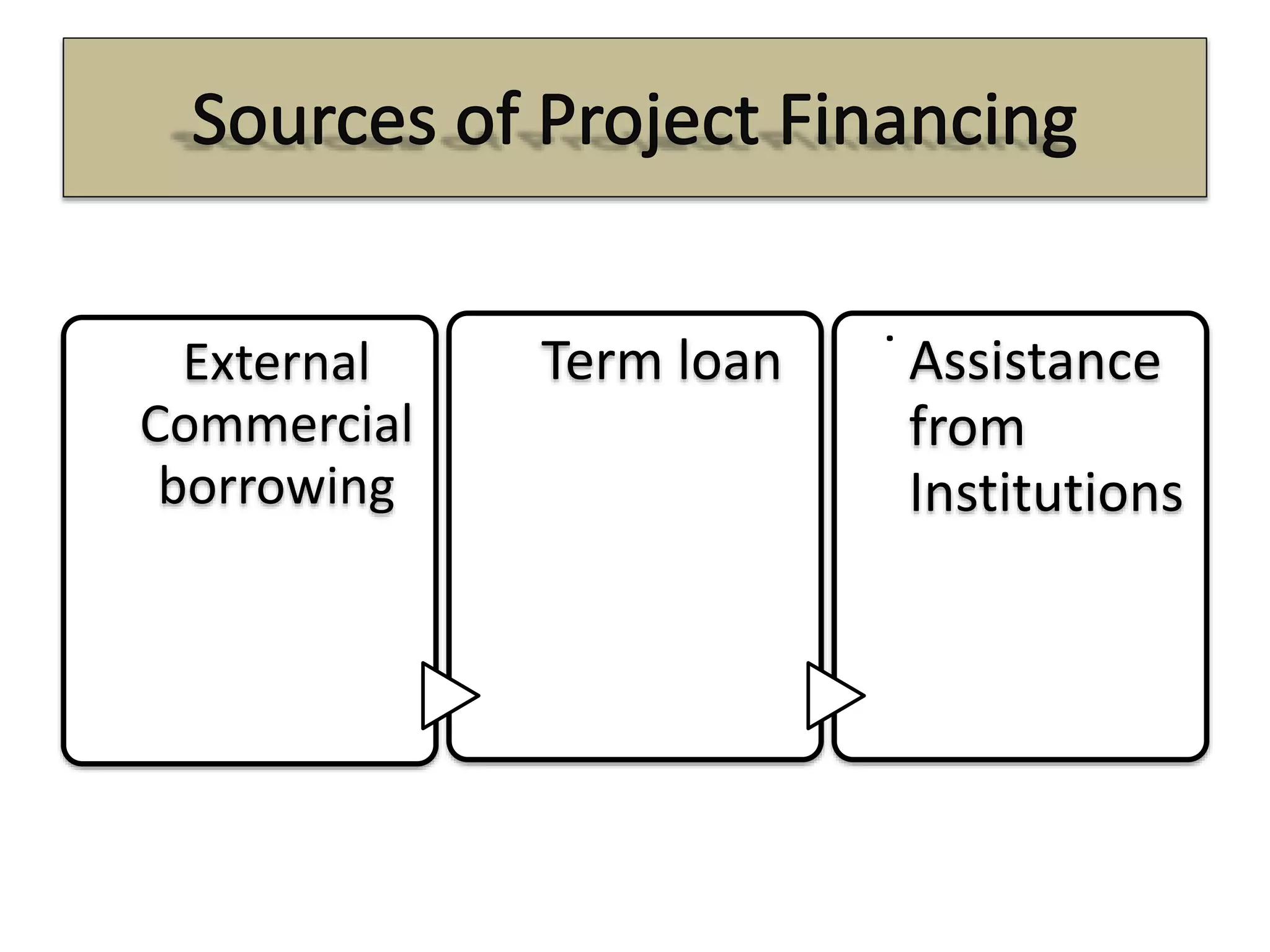
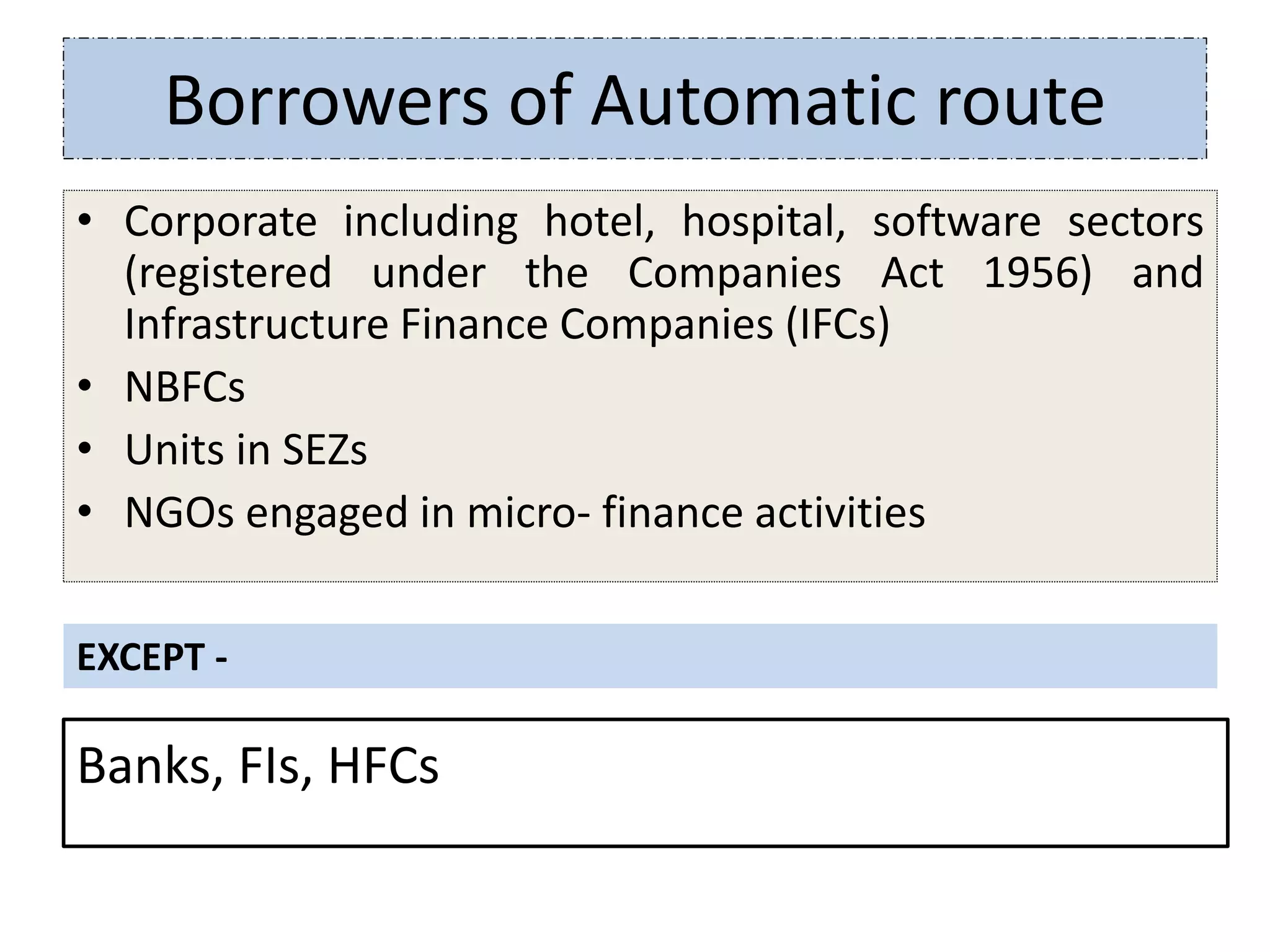
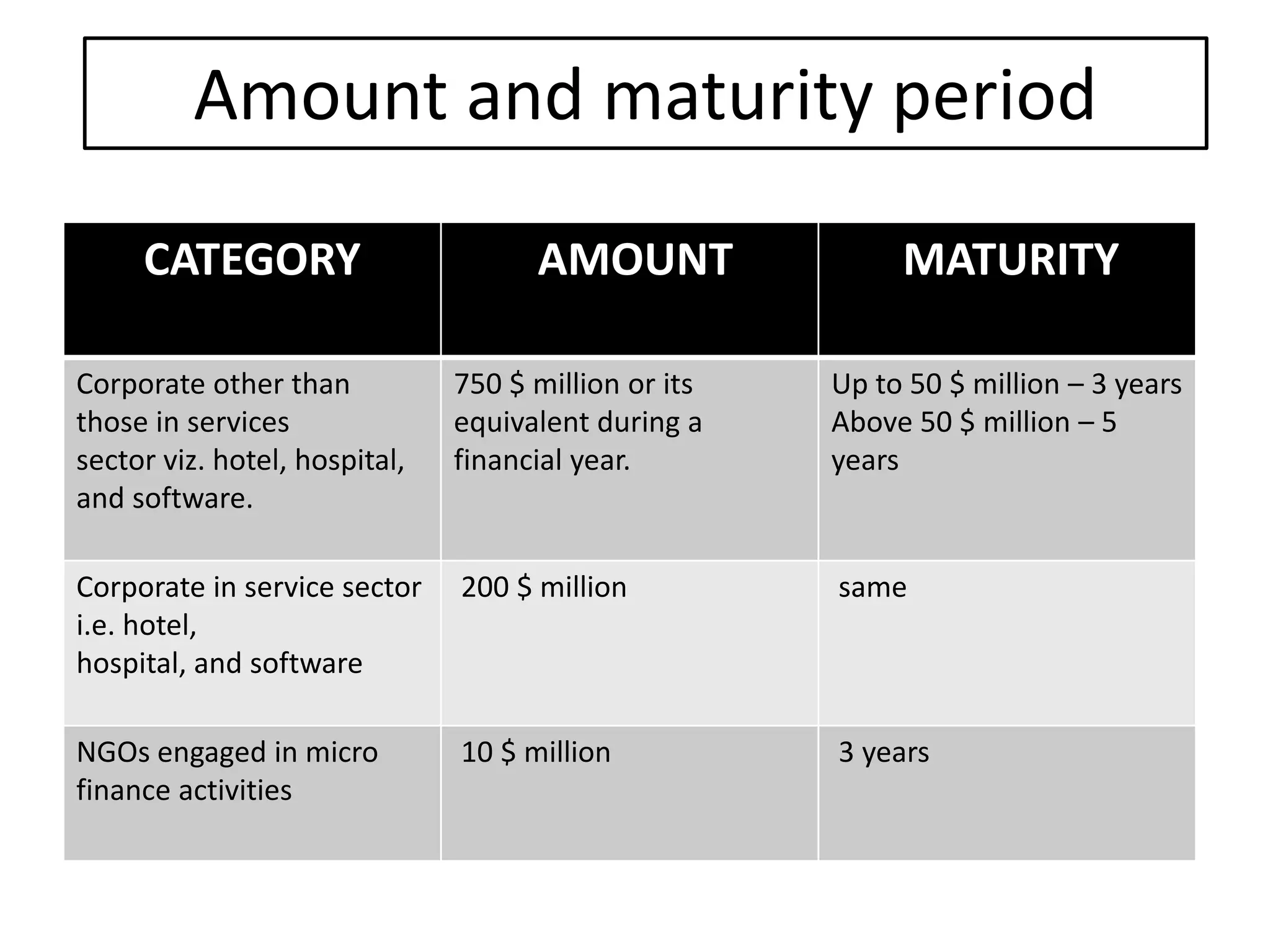
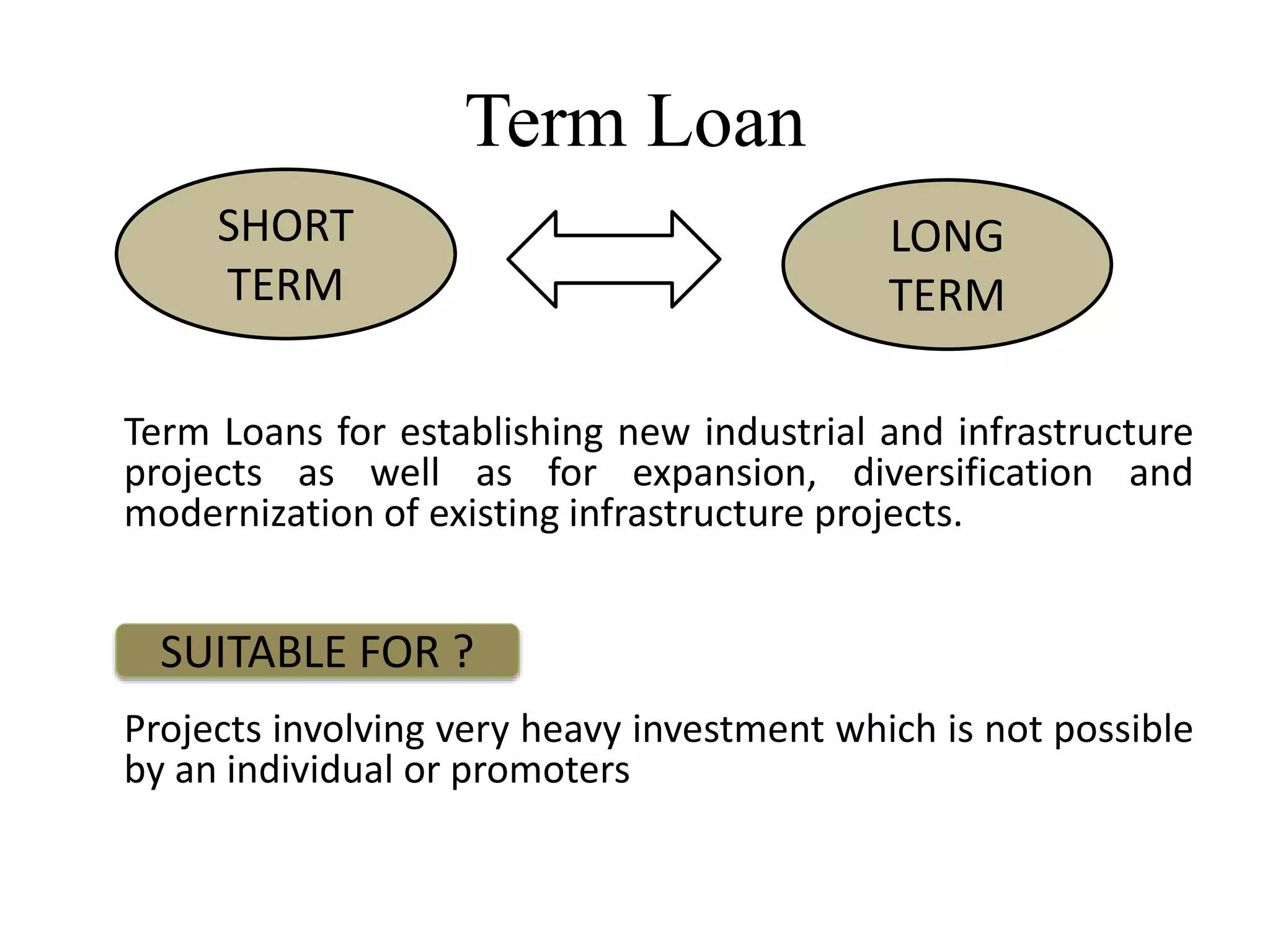
3) Key sources of project financing include external commercial borrowing, term loans, and assistance from institutions like commercial banks, IFCI, SFCs, UTI, and IIBI which provide medium to long-term financing for infrastructure projects.