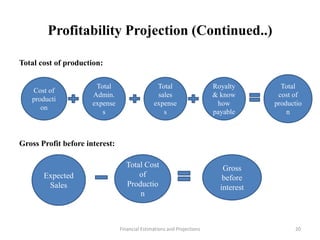
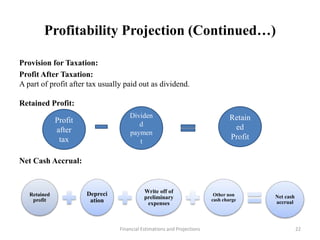
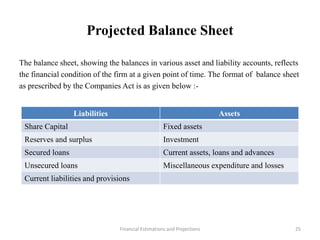
This document discusses various aspects of conducting a financial analysis for a project. It covers estimating project costs such as land, buildings, machinery, fees, and contingencies. It also discusses means of financing a project through share capital, loans, debentures, and incentives. The document outlines how to estimate sales, production costs, working capital requirements and financing, and profitability projections through calculating costs, revenues, expenses, profits and cash flows. The overall aim is to assess the viability, stability and profitability of a proposed project.