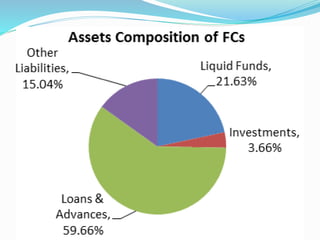
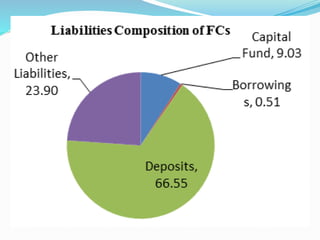
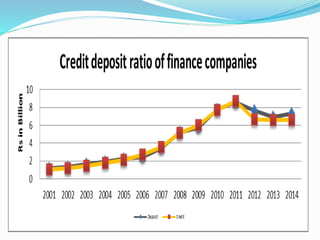
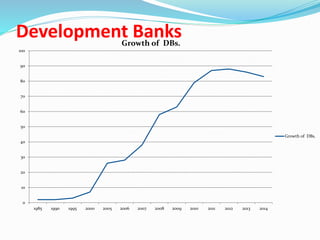
Finance companies in Nepal serve as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, providing loans to individuals and businesses but do not accept deposits. They primarily finance their operations through loans from banks, commercial paper, bonds, and capital from retained earnings. Key challenges include urban concentration of services, corporate governance issues, and borrowers' access to multiple banking facilities.