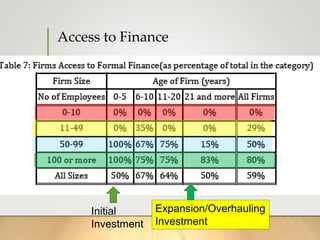
This document discusses various sources of financing for businesses. It notes that access to financing is often cited as a barrier to starting or growing a business, especially for women and minority entrepreneurs. Internal financing from family and friends is one source, but businesses may also seek external loans, equity investment, or retained earnings. In Pakistan specifically, most new investment and working capital for SMEs comes from internal financing rather than banks due to conservative lending practices. The document outlines some microfinancing options provided by non-profit organizations in Pakistan.