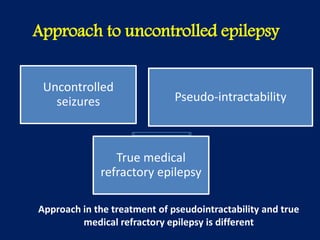
1) Uncontrolled epilepsy can be due to pseudointractability or true refractory epilepsy, requiring different treatment approaches.
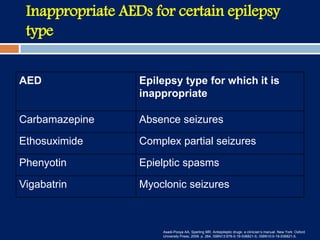
2) For uncontrolled epilepsy, the first step is a careful diagnosis to correctly classify the epilepsy type and exclude other conditions, followed by proper antiepileptic drug (AED) selection, dosing, and ensuring compliance.
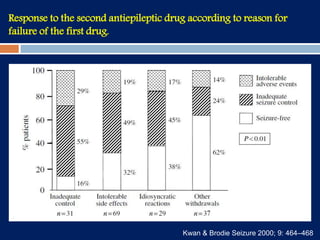
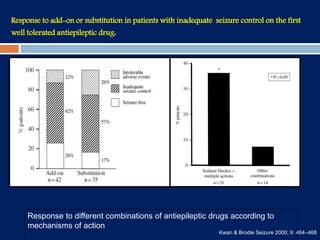
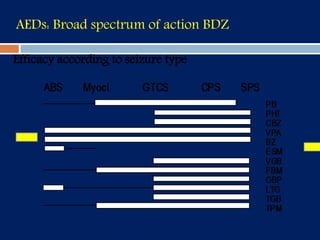
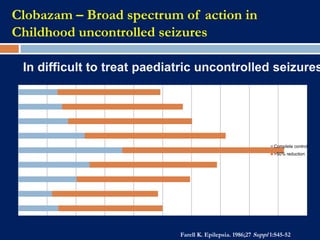
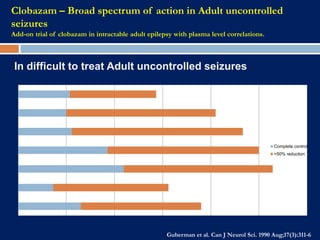
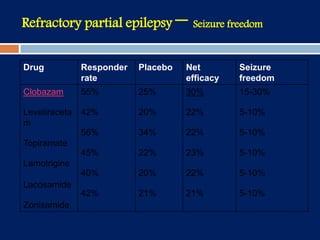
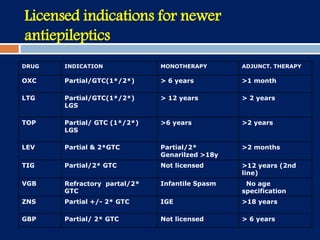
3) Clobazam is an effective add-on treatment for both generalized and focal epilepsies due to its broad spectrum of action, and can provide long-term seizure control when used as an adjunct to other AEDs.