This document provides a summary of valvular heart disease, including:
1. Descriptions of the main valves affected - aortic, mitral, tricuspid, and pulmonary valves.
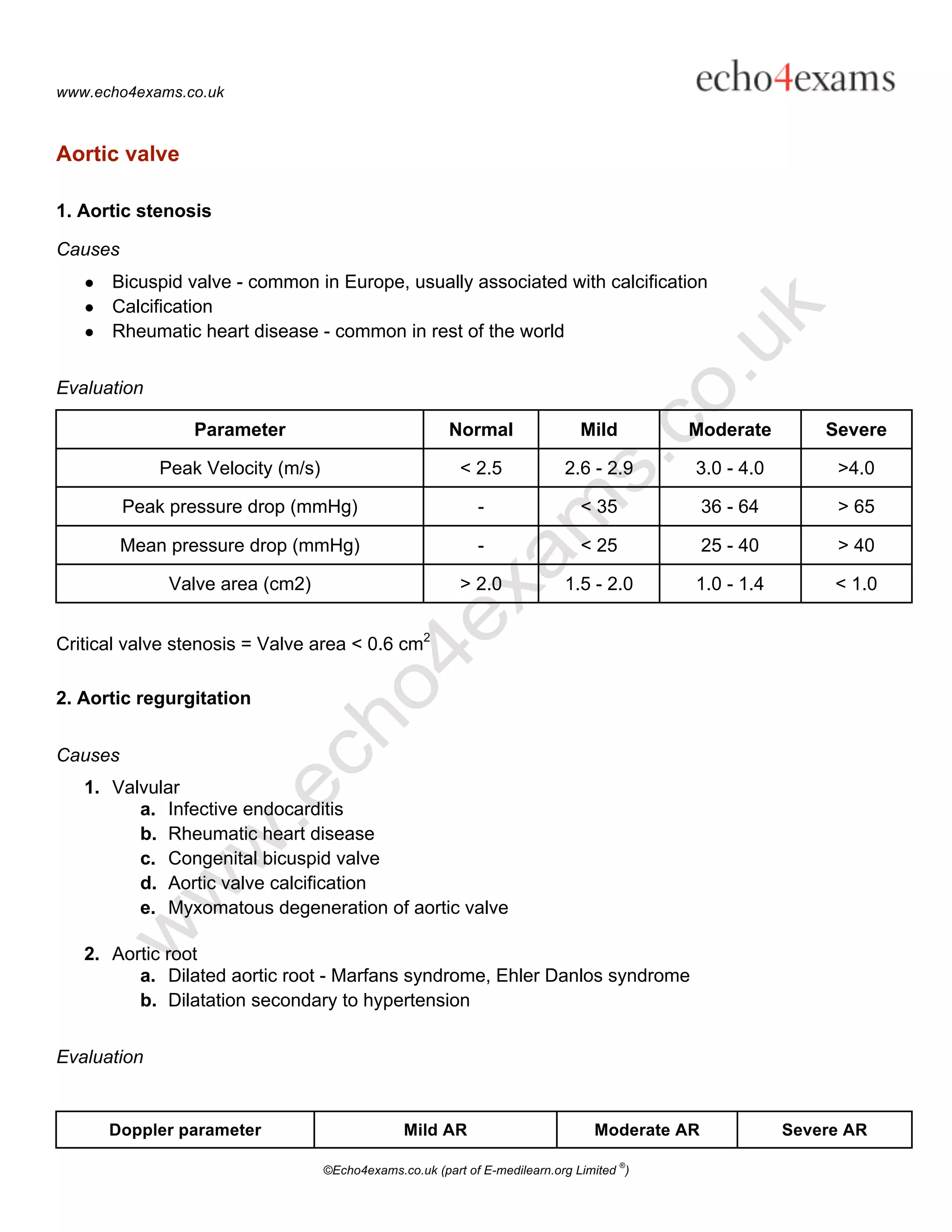
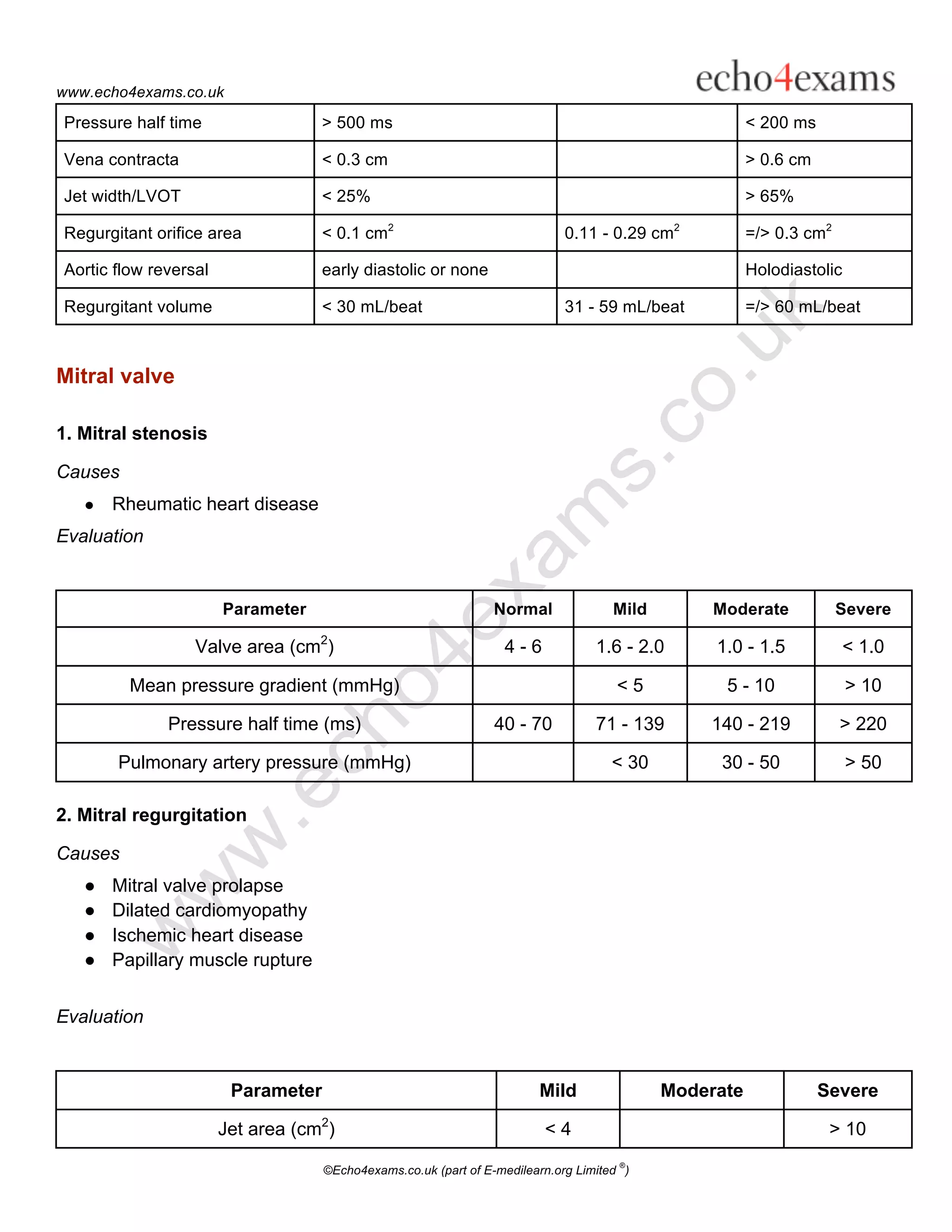
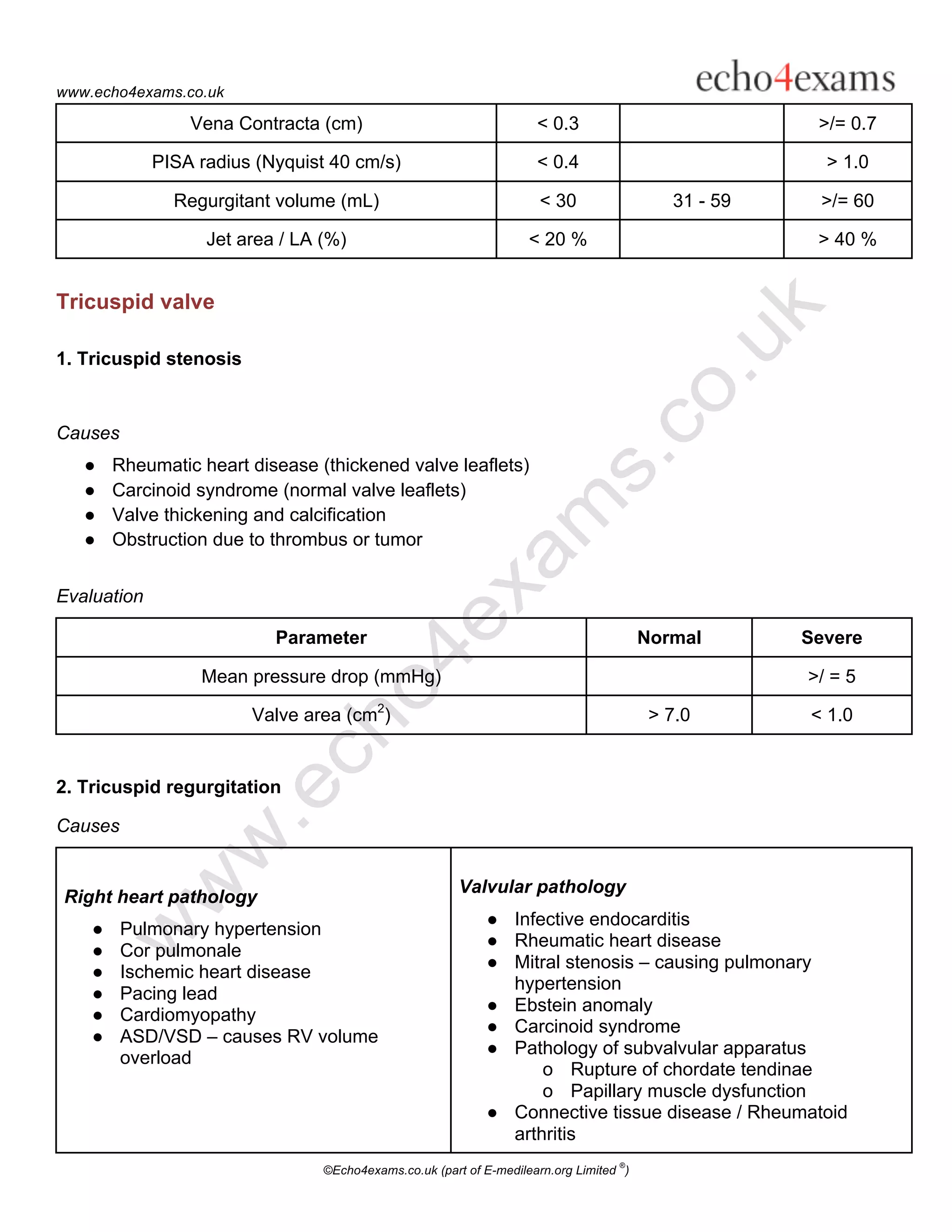
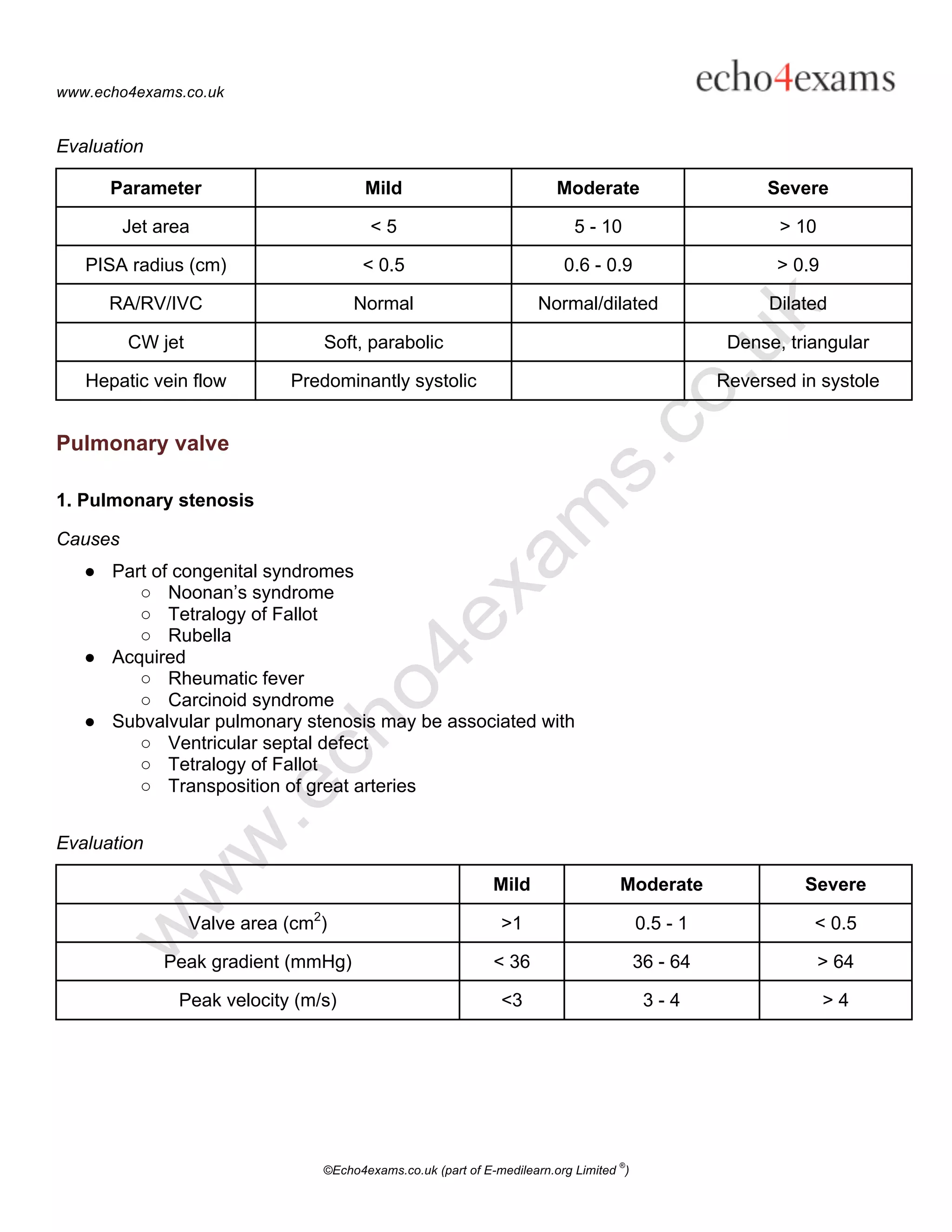
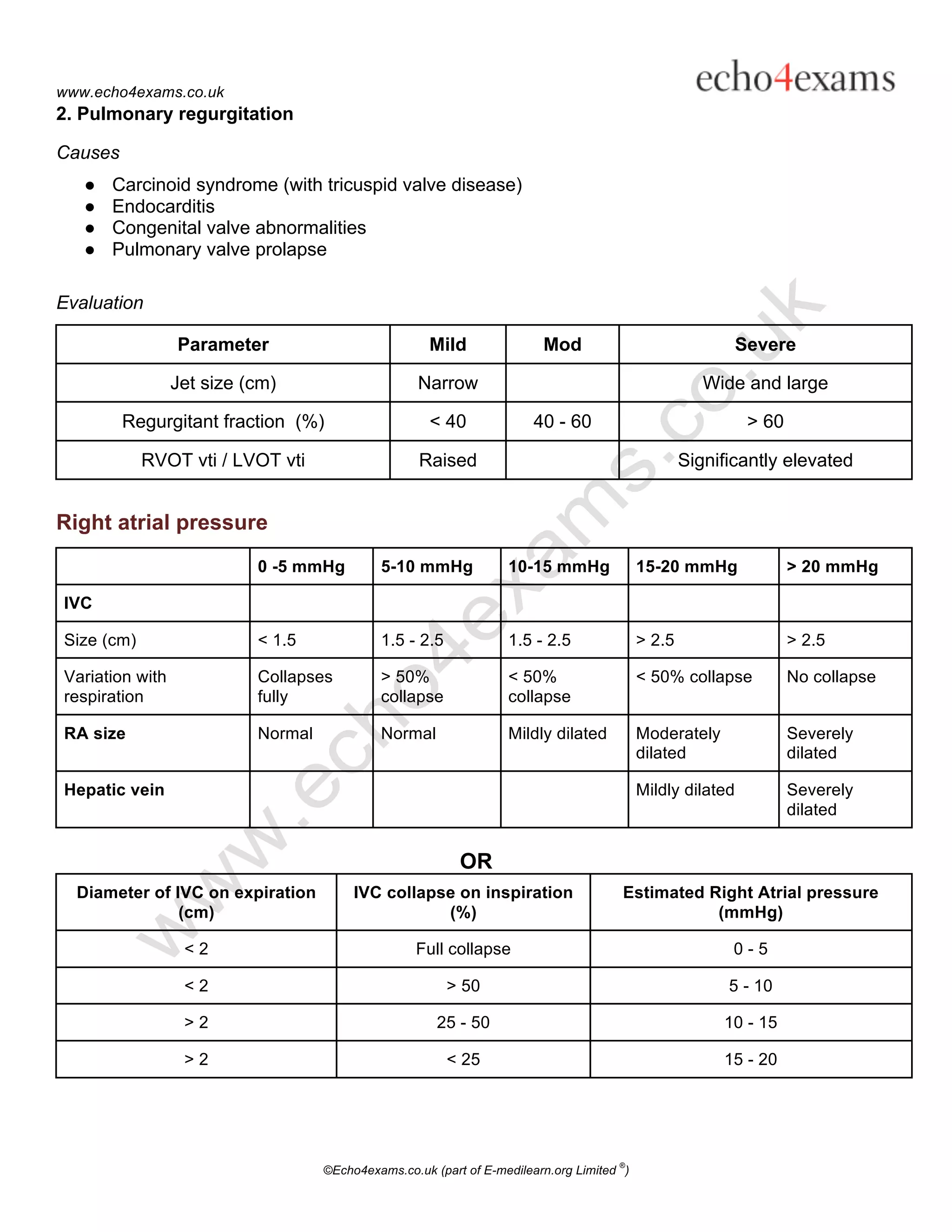
2. Causes and parameters to evaluate the severity of common valve lesions for each valve.
3. Guidance on estimating right atrial pressure based on inferior vena cava size and variability.
The full document contains additional detail on evaluating each type of valve disease.