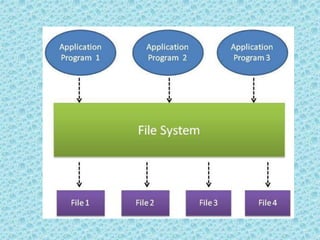
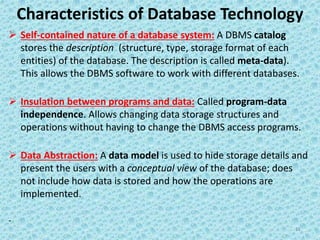
The document provides an introduction to databases and database management systems (DBMS), discussing traditional file systems and their limitations, such as data redundancy, inconsistency, and security issues. It highlights the benefits of using a DBMS, including program-data independence, data abstraction, and support for multiple user views. The document also emphasizes the importance of DBMS in various applications like banking and universities for efficient data management.