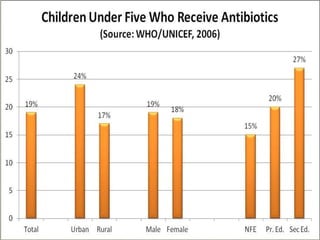
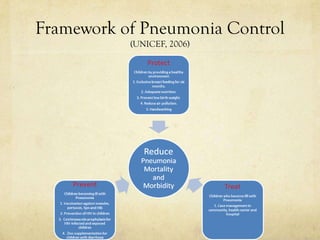
Pneumonia is one of the biggest killers of children under 5 globally, responsible for over 2 million deaths annually. It is caused by bacterial, viral and fungal infections which are often spread through airborne transmission. Those most at risk are young children and individuals with compromised immune systems. Efforts through programs like GAPP aim to increase vaccination coverage, improve access to healthcare and antibiotics, reduce indoor air pollution, and promote breastfeeding to help prevent and treat pneumonia cases. However, challenges remain in resource-limited settings where socioeconomic factors can create both liabilities and opportunities in controlling this disease.