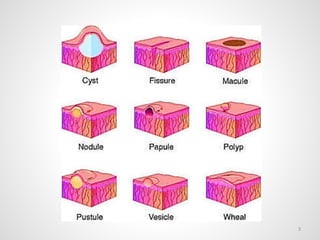
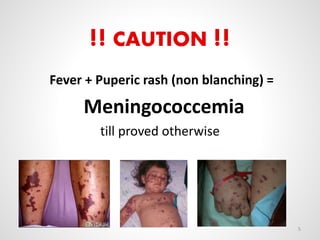
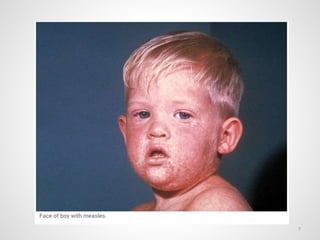
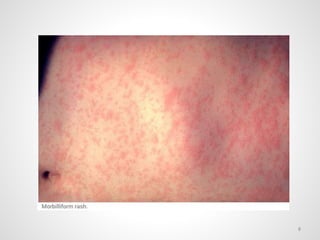
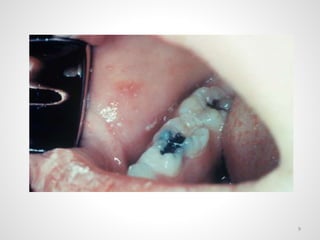
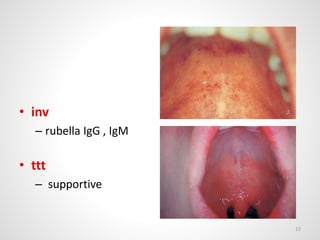
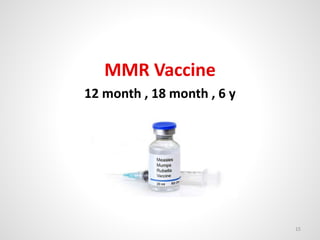
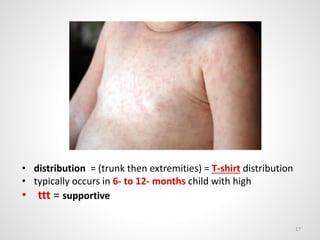
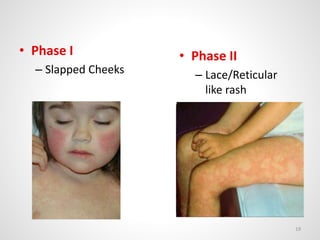
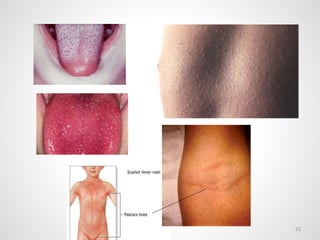
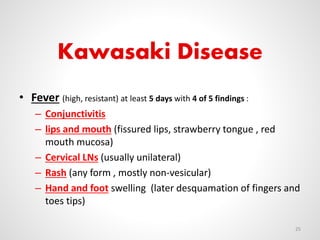
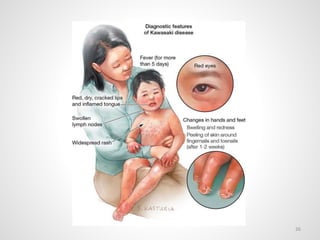
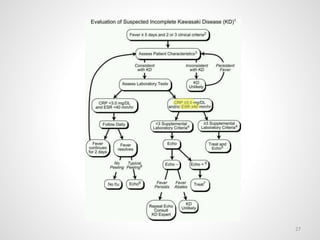
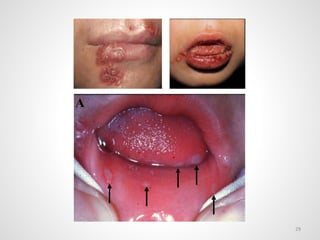
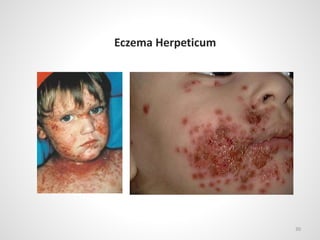
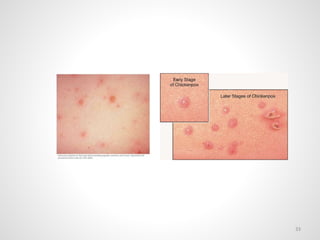
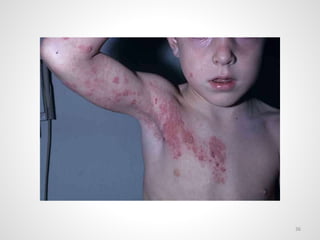
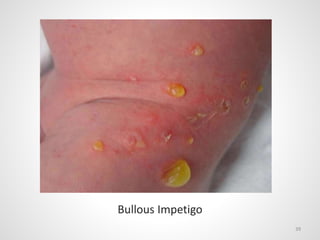
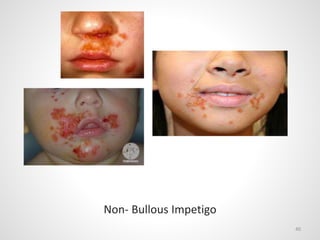
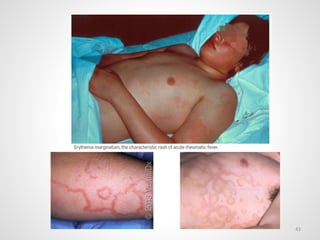
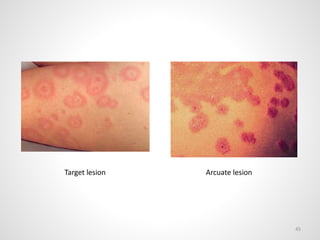
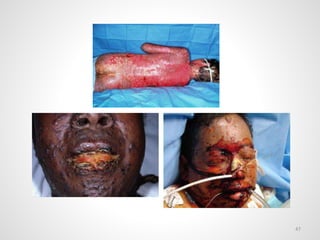
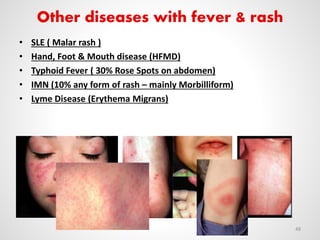
The document provides an overview of various infectious diseases associated with fever and rash, including their symptoms, diagnostics, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of differentiating between conditions such as measles, rubella, mumps, and chickenpox while outlining specific warning signs like purpuric rashes and complications. Additionally, it covers disease management, including the role of vaccinations and supportive care.