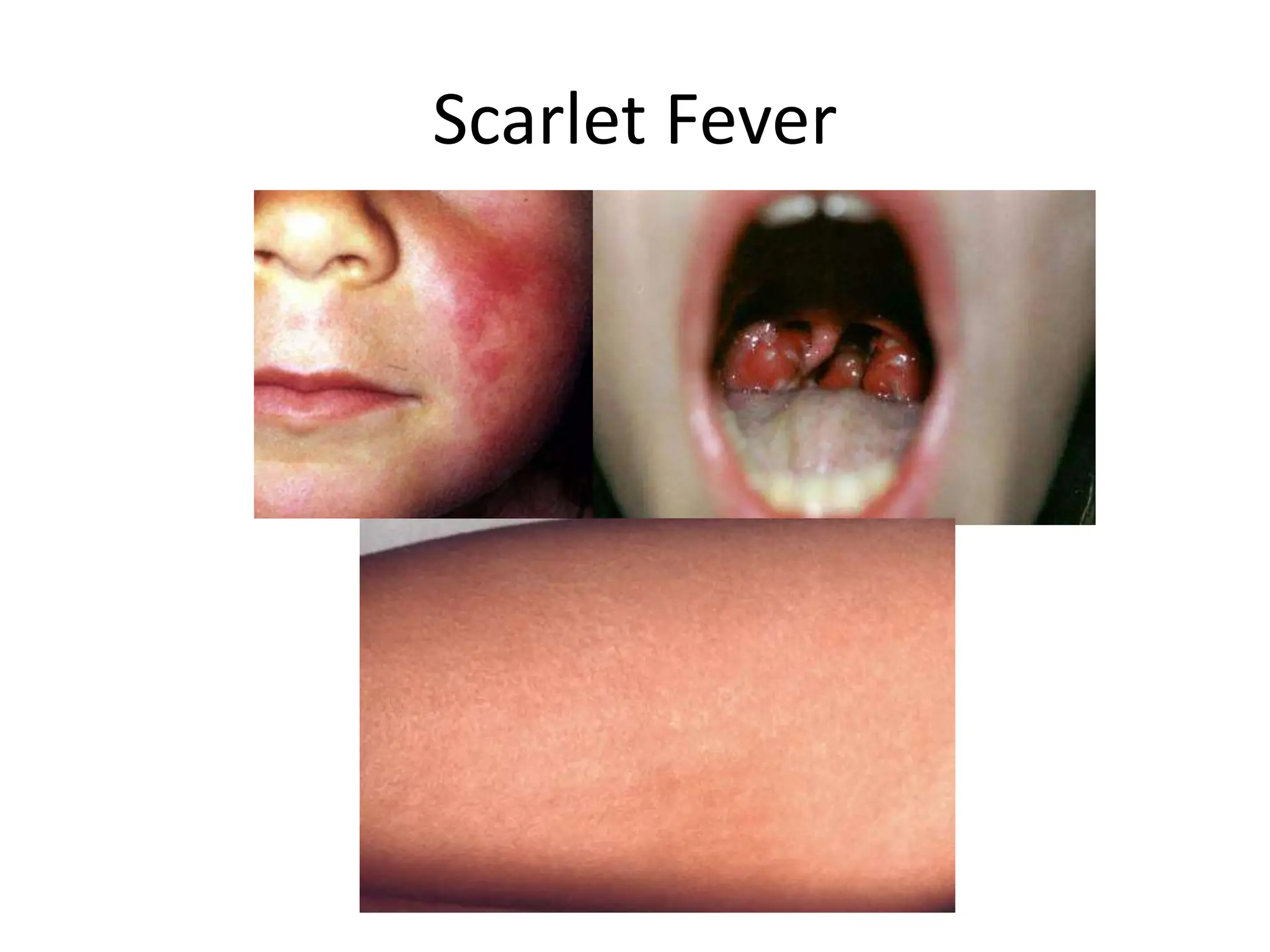
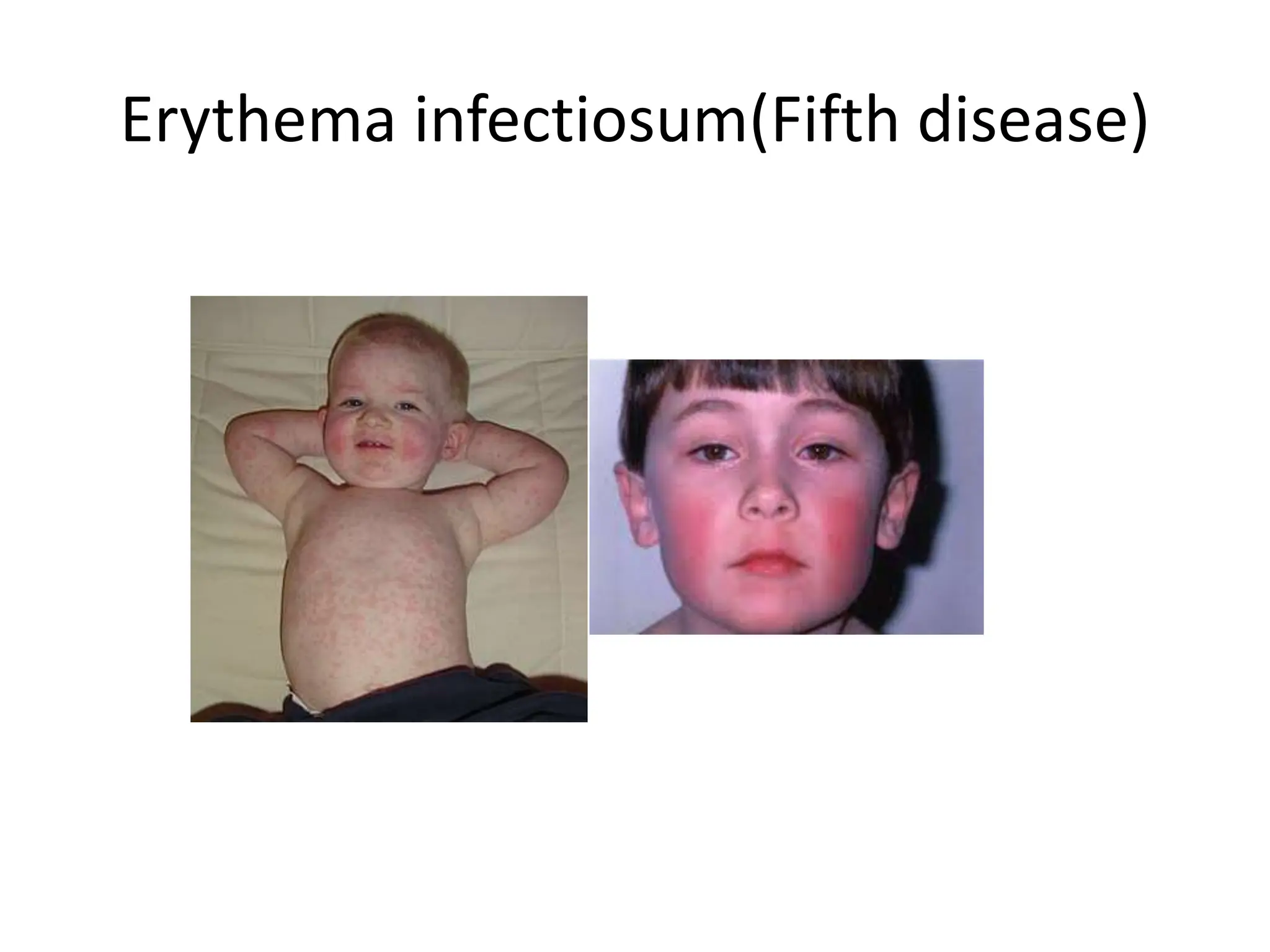
The document outlines various common pediatric rashes, detailing their clinical features, history, and progression. It covers specific conditions such as measles, rubella, scarlet fever, meningococcemia, and others, highlighting their prodromal symptoms and characteristic rashes. Additionally, it discusses the appearances of drug eruptions and papulovesicular rashes like chicken pox and herpes zoster.