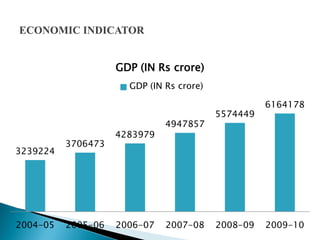
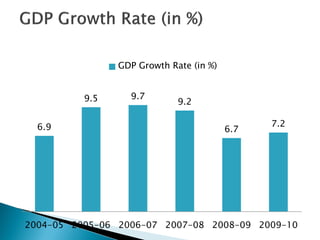
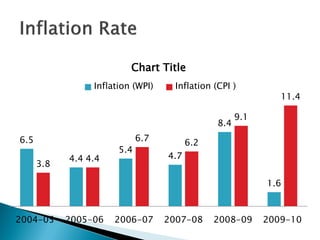
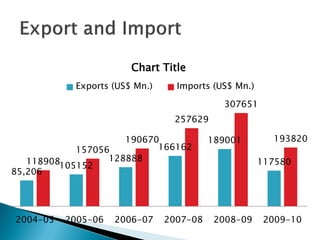
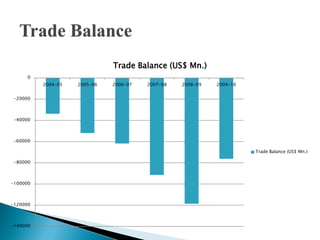
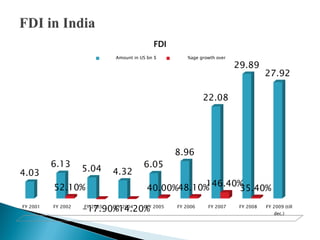
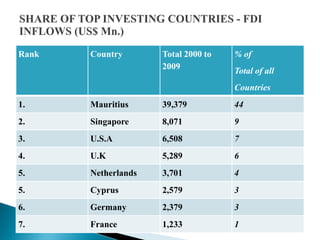
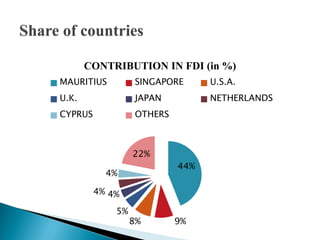
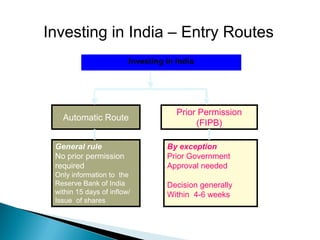
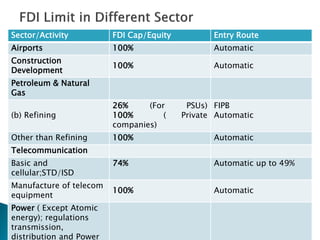
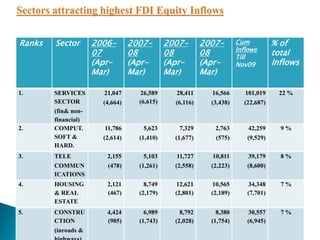
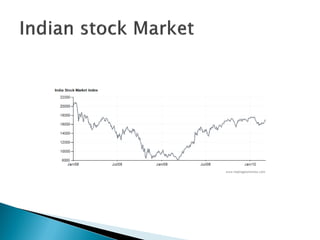
1) Foreign direct investment and foreign institutional investment are both types of cross-border investment but differ in nature. While FDI involves direct ownership in a business located in another country, FII refers to foreign investment in the stock markets of another country.
2) FDI provides greater control rights and is a longer term commitment, whereas FII is more short-term in nature and does not provide control over operations.
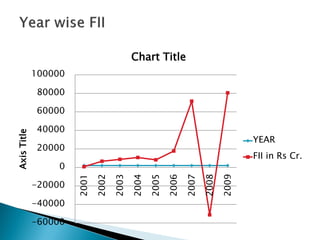
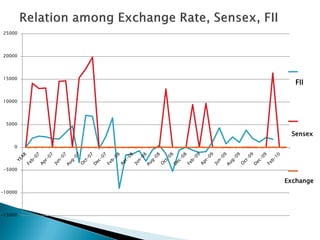
3) Both FDI and FII can provide benefits like increased capital flows and investment, but FII is more prone to being "hot money" that leaves quickly.