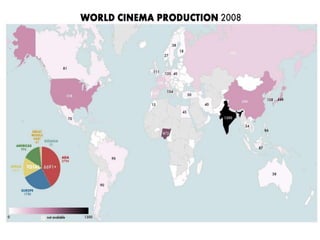
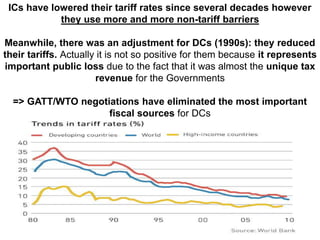
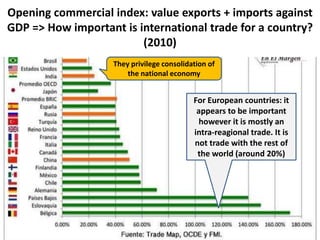
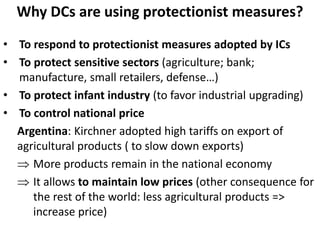
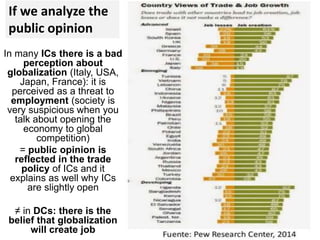
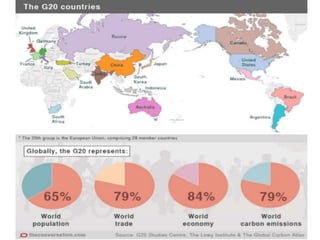
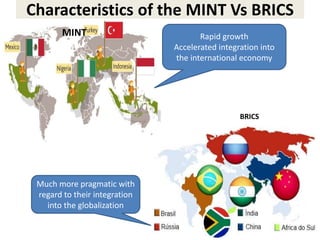
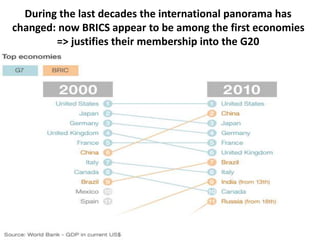
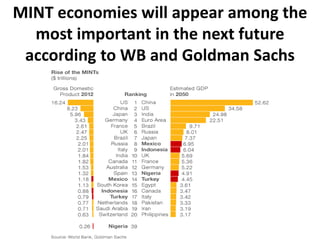
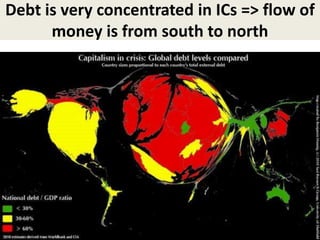
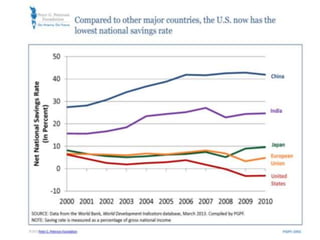
This document discusses protectionism between developed and developing countries. It notes that while developed countries have lowered tariffs, they increasingly rely on non-tariff barriers like technical standards to protect strategic industries and jobs. Developing countries face pressure to open their markets more than developed countries. The document argues that current international trade rules are not equally applied and developed countries have more autonomy in decision making compared to developing nations.