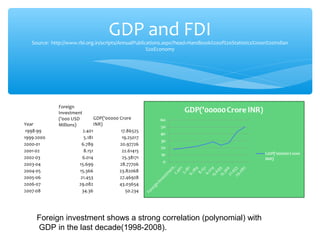
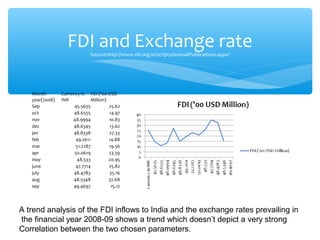
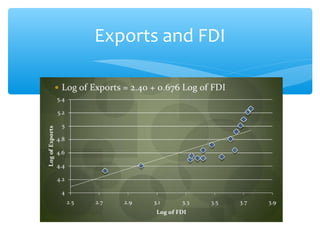
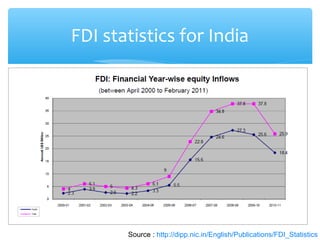
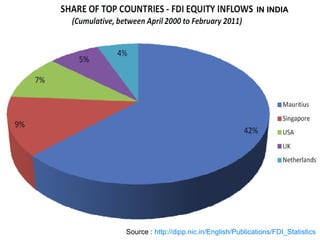
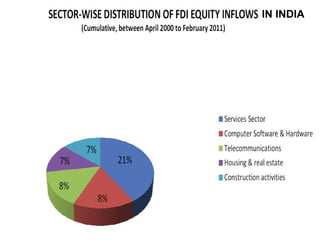
The document discusses factors that determine foreign direct investment (FDI) in India, including income, exchange rates, technology, human capital, and openness of the economy. It hypothesizes that FDI is a function of these country-specific factors. The methodology section outlines a model for FDI as a function of these variables. Trend analyses show some correlation between FDI and GDP and limited correlation with exchange rates. The conclusion emphasizes that the growth, size, and openness of the Indian economy as well as currency exchange rates are important determinants of FDI inflows.