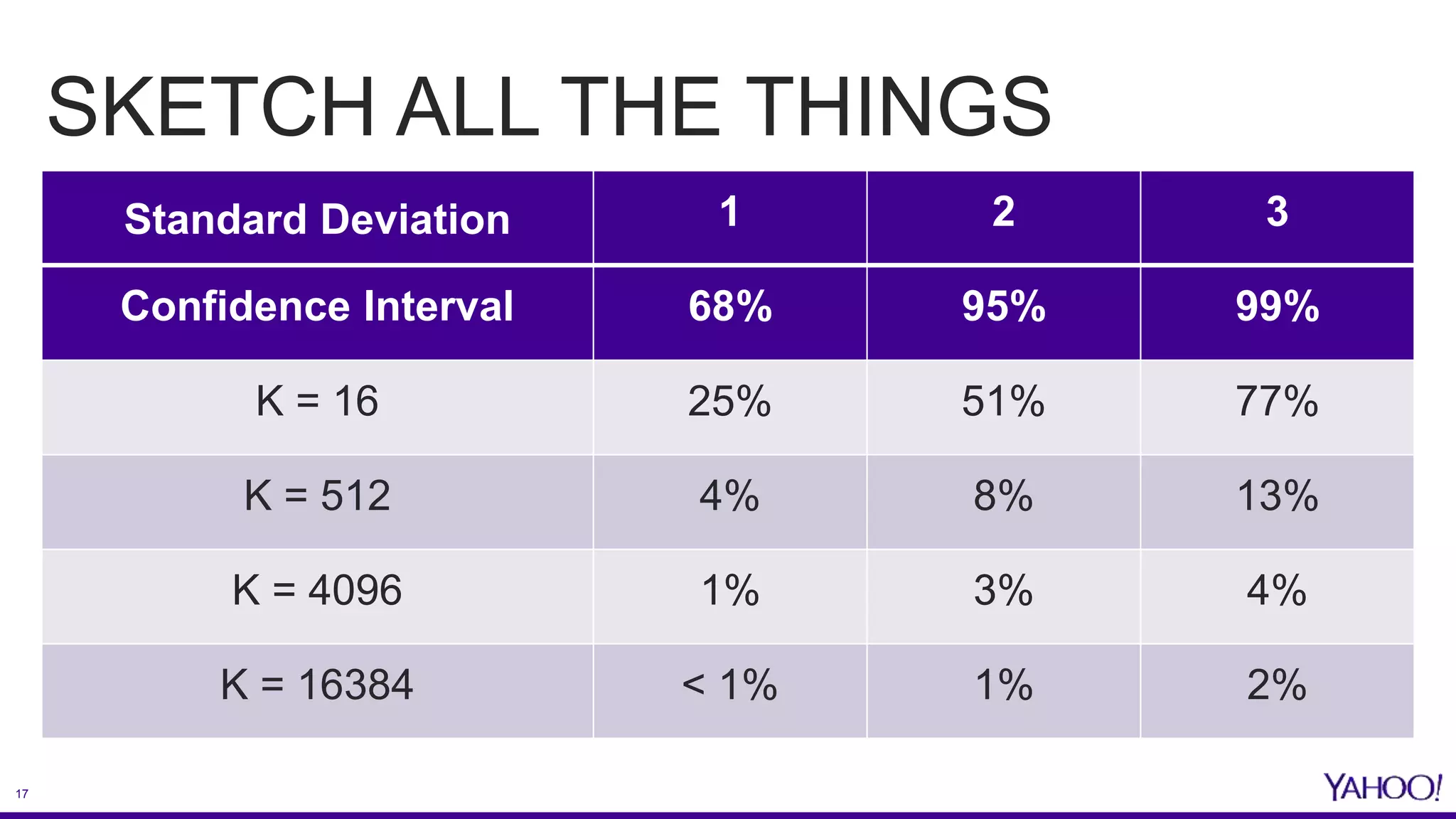
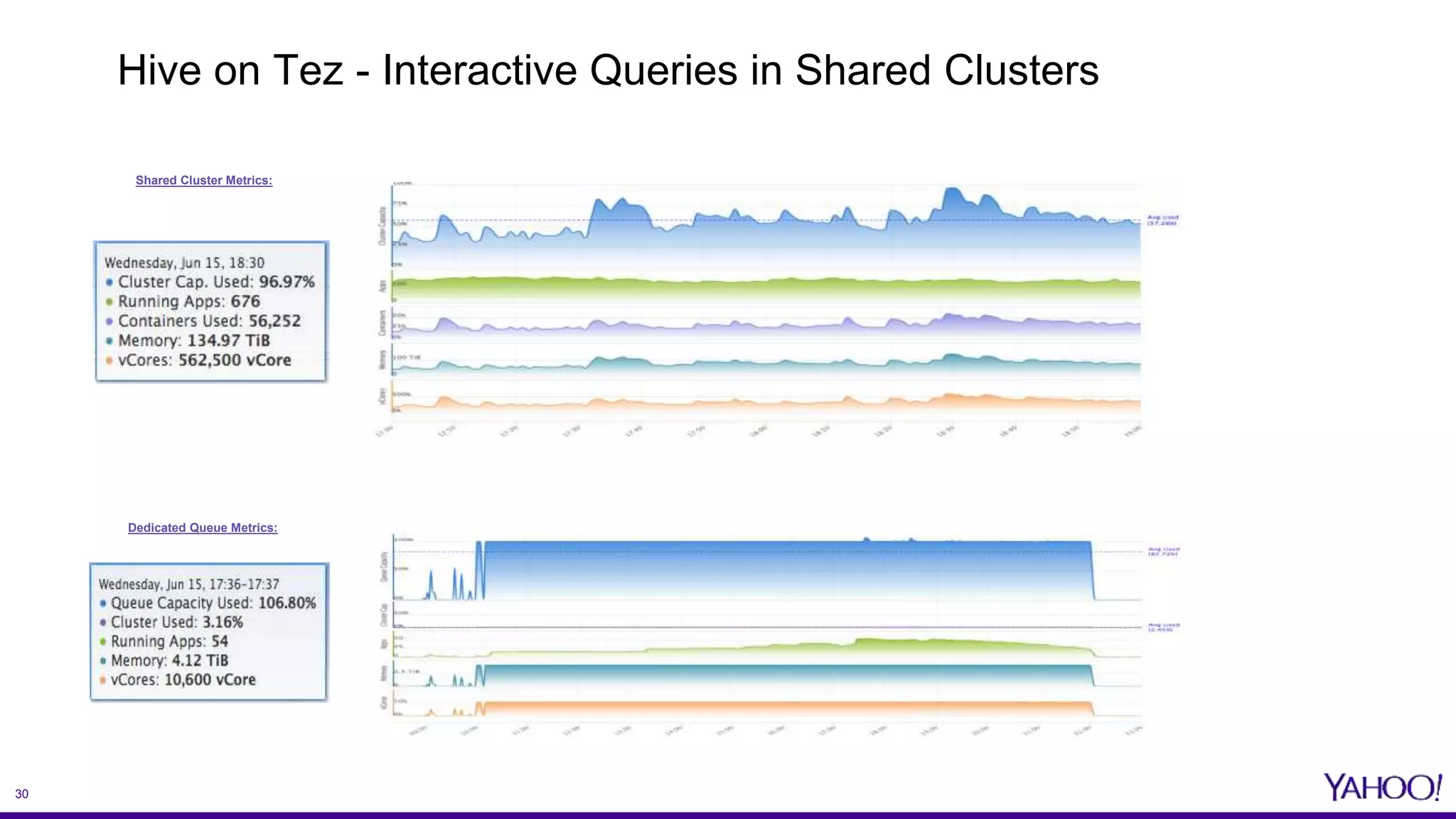
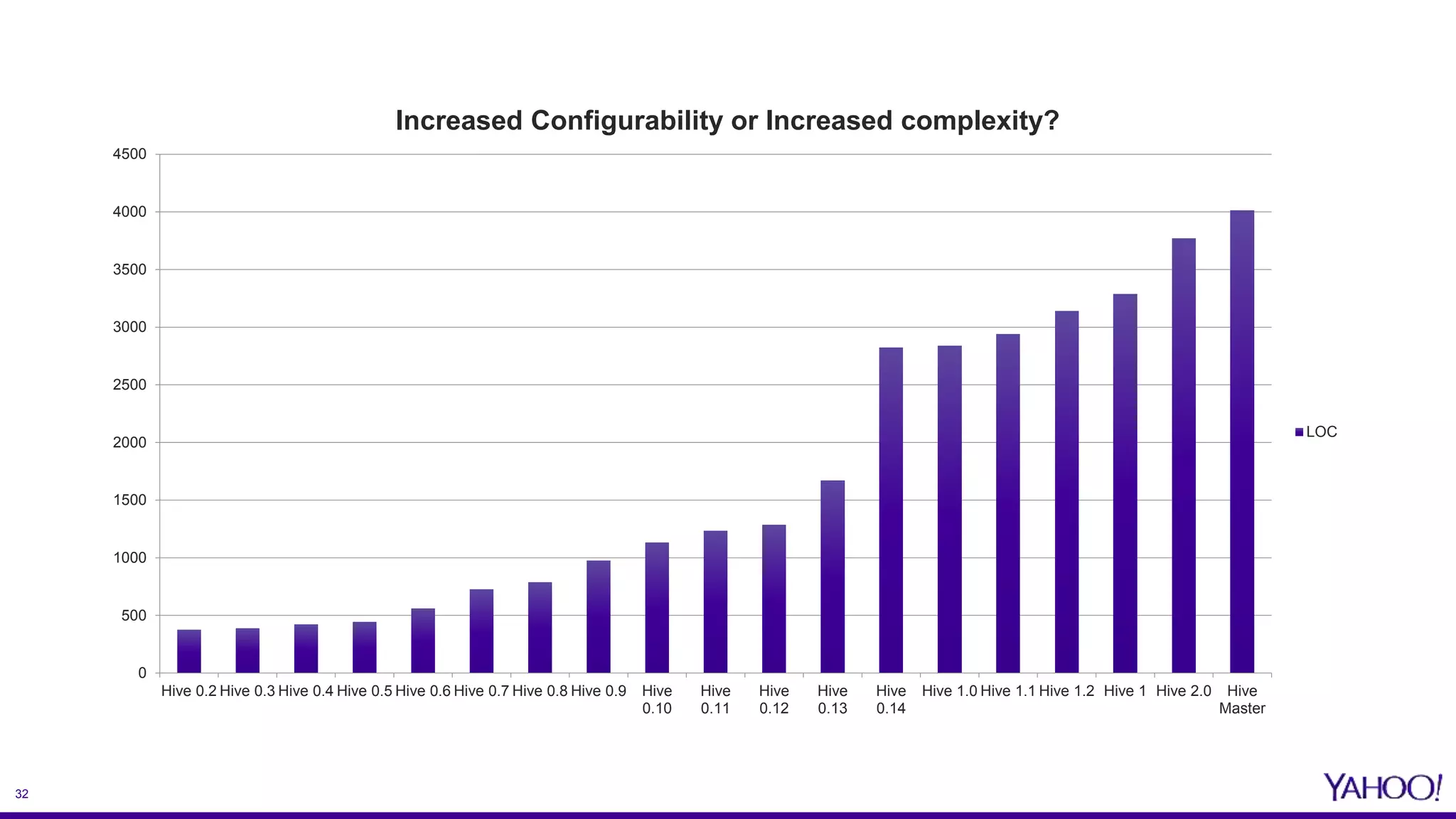
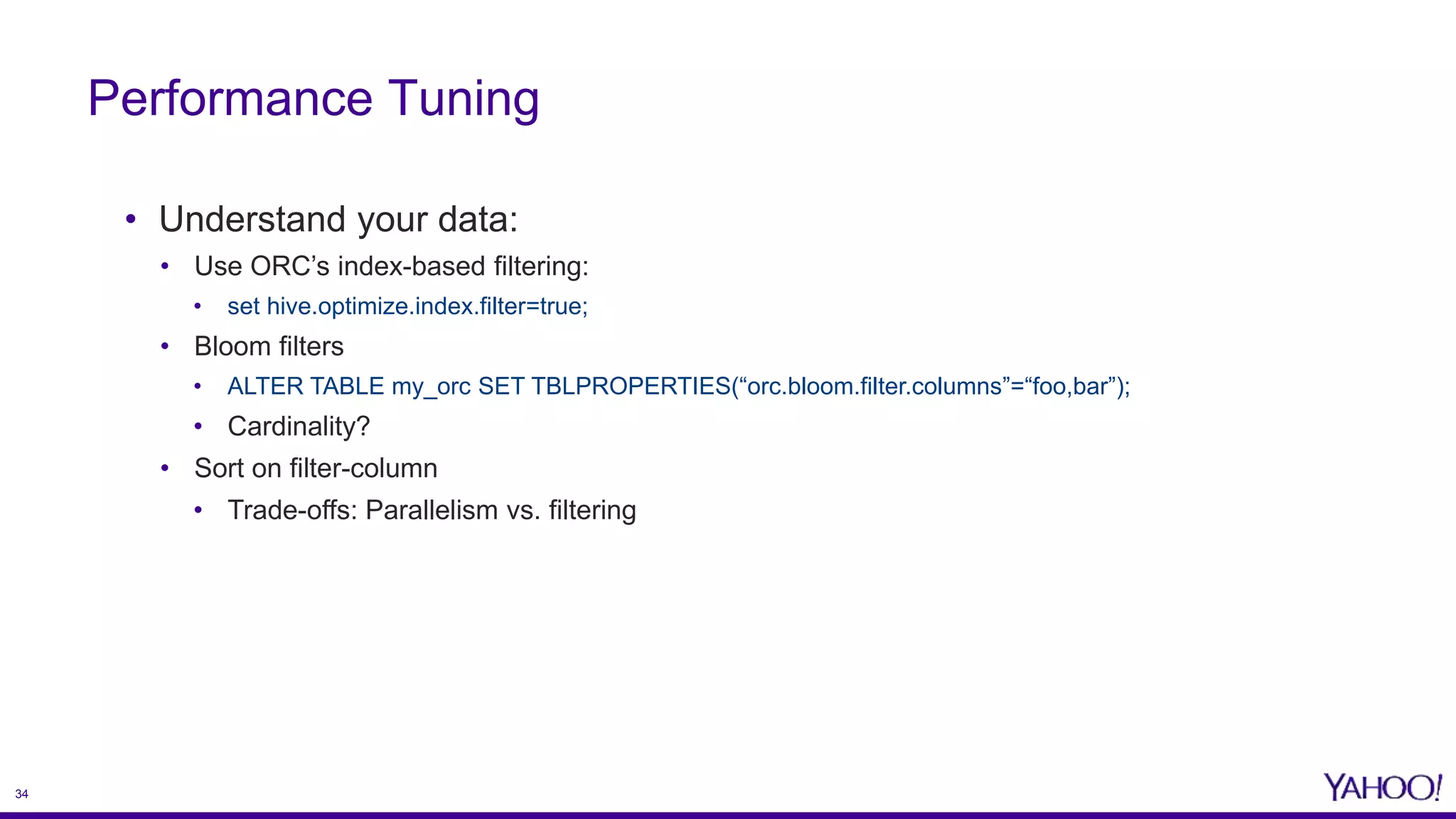
The document discusses the challenges and solutions related to enhancing mobile analytics performance at Yahoo using a data mart on Hive. Key strategies include optimizing ETL processes, leveraging deep partitioning, employing ORC format for efficient storage, and utilizing sketch algorithms for faster query execution. It also emphasizes the need for tailored data marts and collaborative infrastructure improvements to streamline data handling and analysis.





![6
From: The [REDACTED] ETL team
To: The Yahoo Hive Team
Subject: A small matter of size...
Dear YHive team,
We have partitioned our table using the following 6 partition keys:
{hourly-timestamp, name, property, geo-location, shoe-size, and so on…}.
For a given timestamp, the combined cardinality of the remaining
partition-keys is about 10000/hr.
If queries on partitioned tables are supposed to be faster, how come
queries on our table take forever just to get off the ground?
Yours gigantically,
Project [REDACTED]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fasterfasterfaster-datamartswithhiveatyahoo-160629231052/75/Faster-Faster-Faster-Datamarts-with-Hive-at-Yahoo-6-2048.jpg)


















![40
“There is no mature, no stable. The only constant is change…
... [Our] work on feeds often involves new columns, several times a day.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fasterfasterfaster-datamartswithhiveatyahoo-160629231052/75/Faster-Faster-Faster-Datamarts-with-Hive-at-Yahoo-40-2048.jpg)







