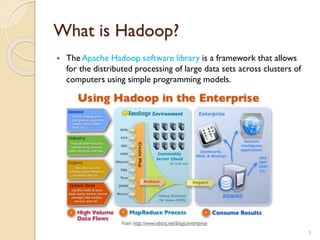
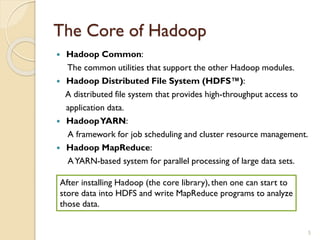
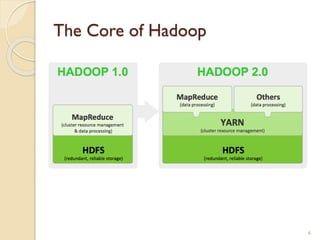
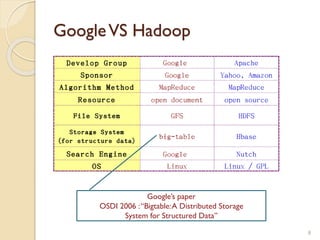
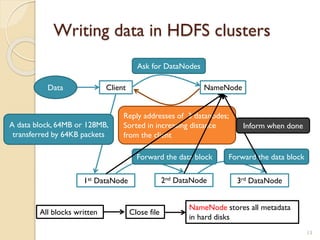
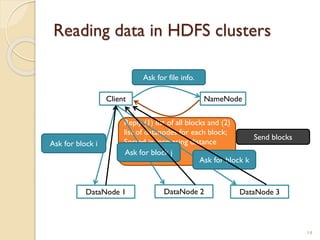
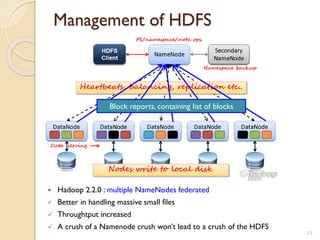
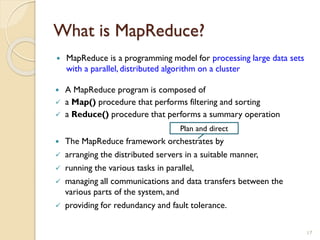
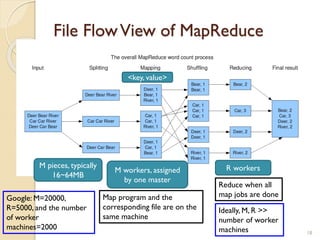
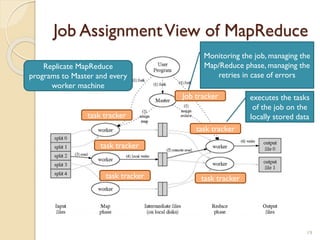
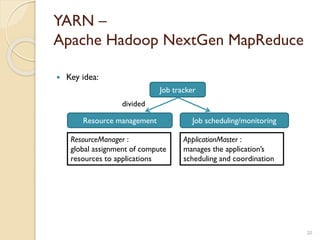
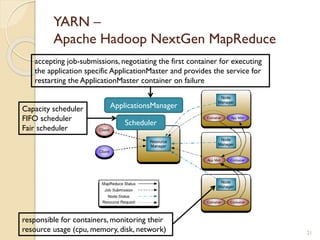
The document provides an overview of Hadoop, an open-source software framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets. It describes how Hadoop uses HDFS for distributed file storage across clusters and MapReduce for parallel processing of data. Key components of Hadoop include HDFS for storage, YARN for resource management, and MapReduce for distributed computing. The document also discusses some popular Hadoop distributions and real-world uses of Hadoop by companies.