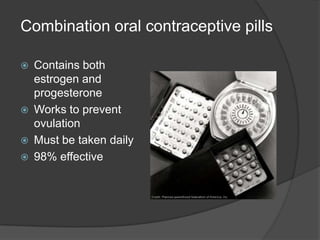
This document discusses various forms of birth control, including hormonal methods like combination oral contraceptives and Depo-Provera injections, long-acting reversible methods like implants and IUDs, barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms, and natural family planning. It provides information on how each method works, how effective it is at preventing pregnancy, and factors to consider when choosing a method, such as effectiveness, effort required, cost, and protection from STDs. Forms of birth control range in effectiveness from about 75% for withdrawal and natural family planning to over 99% for female and male sterilization.