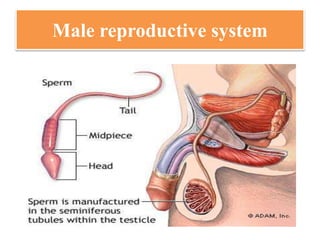
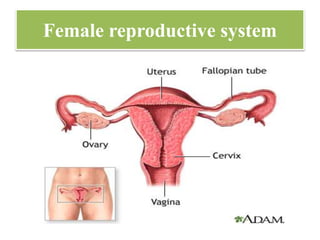
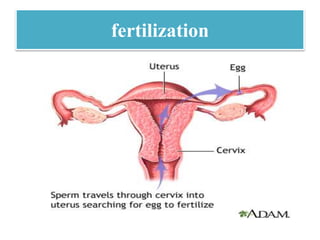
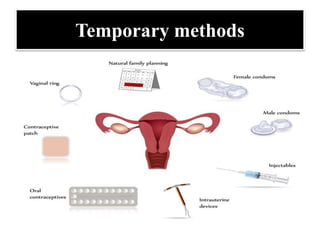
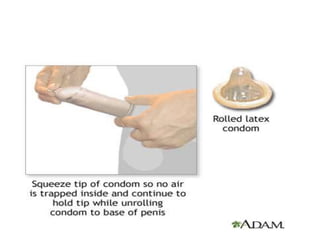
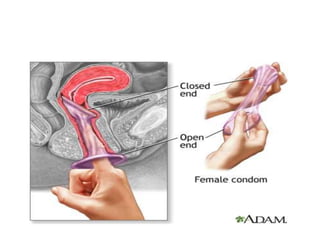
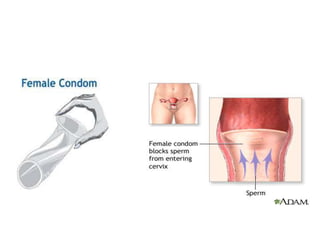
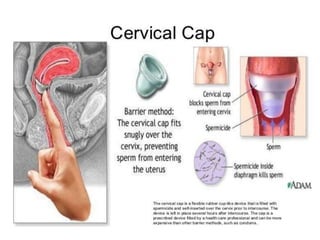
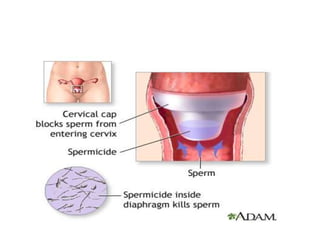
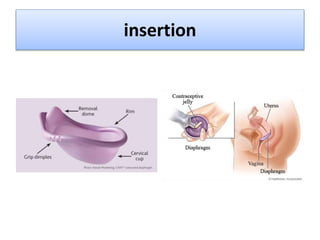
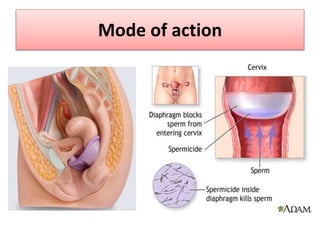
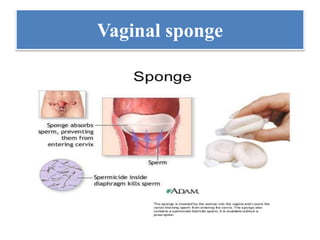
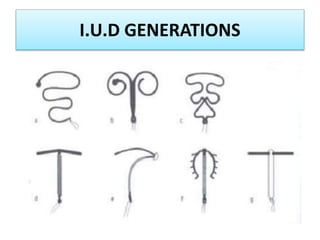
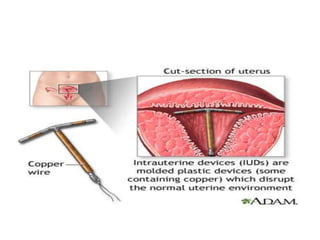
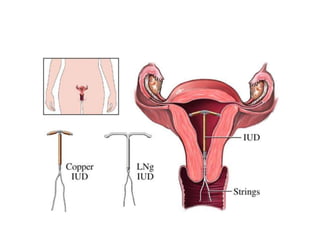
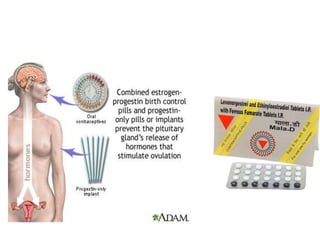
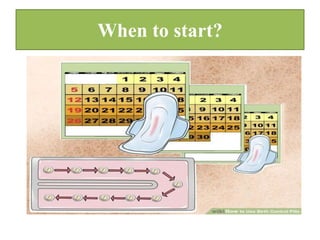
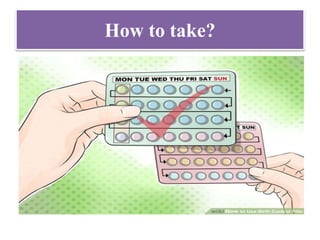
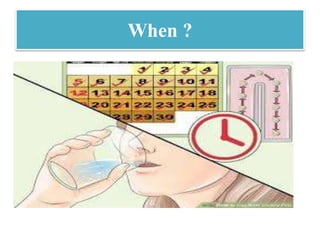
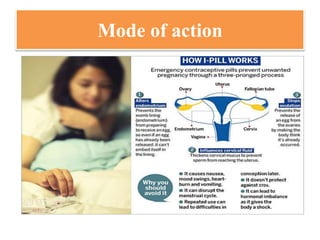
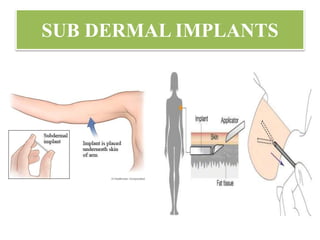
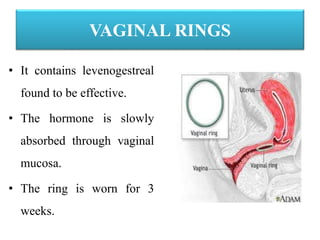
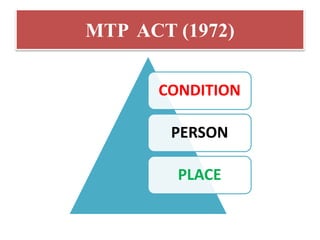
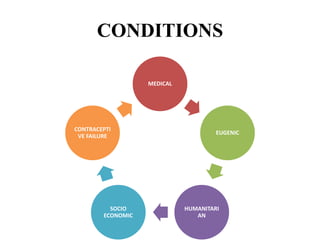
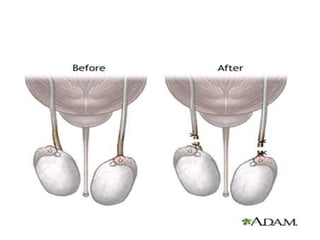
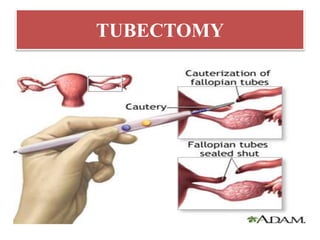
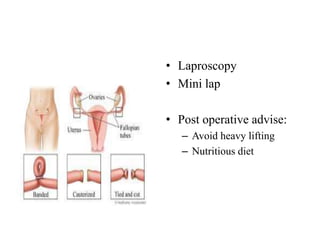
The document discusses various family planning methods including temporary methods like condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, sponges, and IUDs. It also covers hormonal methods like birth control pills, injections, implants, and rings. Emergency contraception, natural family planning methods, and permanent sterilization methods like vasectomy and tubectomy are described. The objectives, effectiveness, use instructions, and risks of each method are provided in detail.