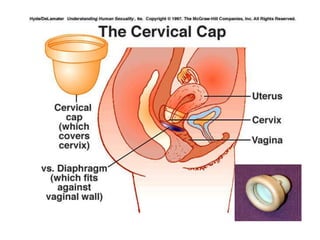
The document details various contraceptive methods, including natural, mechanical, chemical, hormonal, and surgical options, highlighting their effectiveness, safety, and user acceptance. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each method, including barriers, IUDs, oral contraceptives, injectable options, and emergency contraception. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding ovulatory cycles and user compliance for successful contraceptive use.