Embed presentation
Download to read offline

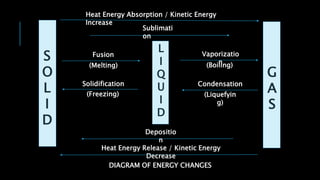







This document discusses phase changes of matter. It defines key phase changes - melting, freezing, vaporization, boiling, condensation, sublimation, and deposition - and explains the energy changes that occur during these processes. A diagram shows the phase changes between solid, liquid, and gas phases, and how heat absorption or release causes kinetic energy to increase or decrease during these transitions. Reverse phase changes occur at the same temperature, and when they occur at the same rate the phases are said to coexist in dynamic equilibrium at the triple point.







