Embed presentation
Download to read offline





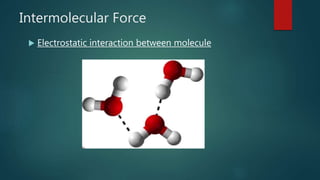













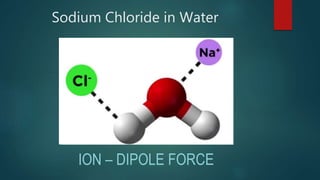





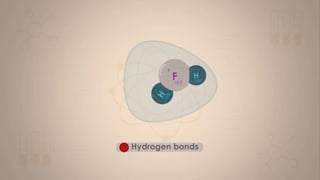


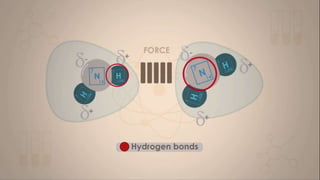
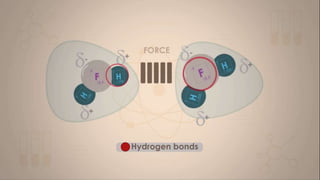
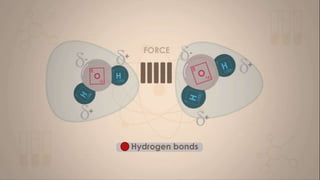
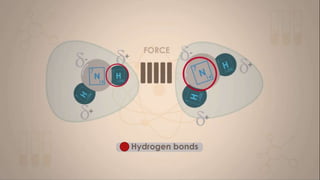


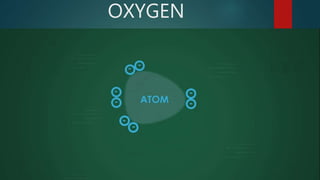
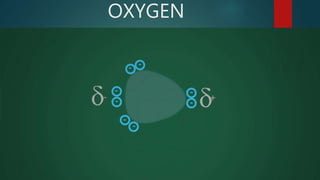
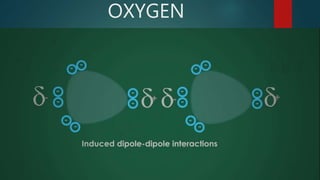


This document discusses intermolecular forces, including what they are and different types. The main types discussed are ion-dipole forces, dipole-dipole forces, and Van der Waals forces. Ion-dipole forces occur between an ion and a molecule with a dipole. Dipole-dipole forces occur between polar molecules that have partial charges, like water molecules. Van der Waals forces are weak electrostatic attractions between all molecules, even non-polar ones, due to temporary charge distributions. These intermolecular forces are important for determining the properties of liquids and solids.






































