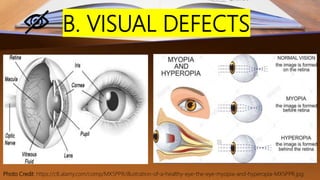
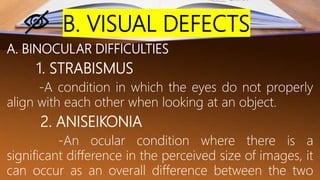
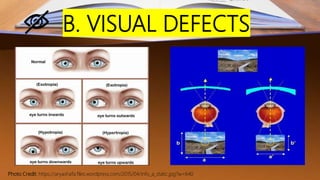
The document discusses various factors affecting reading skills, distinguishing between physical, physiological, neurological, psychosocial, and family-based risk factors. It highlights insights from experts regarding conditions such as poverty, teacher training, and specific learning disabilities like dyslexia. Additionally, it presents case studies of children facing reading challenges due to these diverse factors.