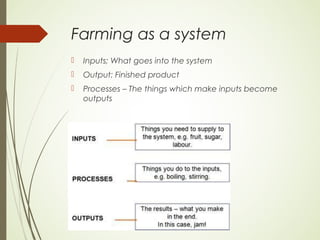
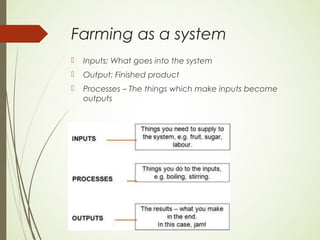
Farming involves collecting natural resources and products from the Earth. There are five main sections of primary activities: farming, fishing, forestry, energy, and mining. Farming operates as a system with inputs that go into the system, such as seeds, fertilizers, and machinery. The outputs are the finished agricultural products. The processes that transform inputs into outputs include planting, growing, harvesting, and transporting crops. Key factors that influence farming include rainfall, temperature, soil type, growing season, labor, technology, relief of the land, and market demand.