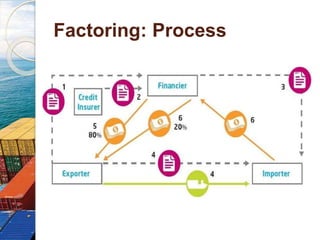
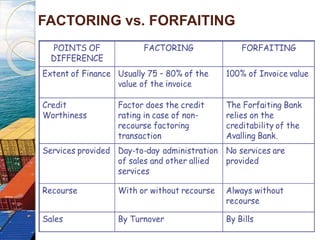
This document provides an overview of factoring and forfaiting processes used in international trade finance. It discusses that factoring involves the sale of book debts or invoices by an exporter to a factor, who provides financing and collects payment. Forfaiting involves the purchase of export receivables by a financial intermediary without recourse to the exporter. The key differences are that factoring may involve credit risk transfer, while forfaiting is done on a non-recourse basis. Both tools help companies raise working capital by discounting outstanding receivables. The document outlines the various parties, documents, costs and applicable regulations for these financial services.