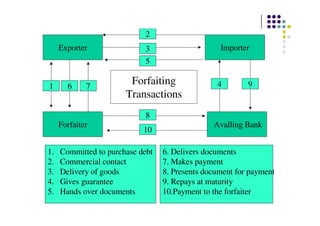
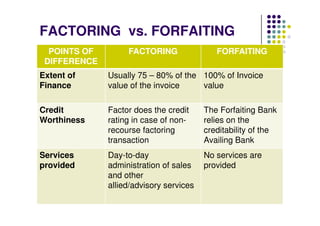
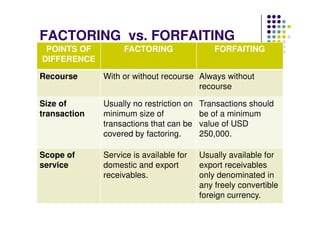
This document discusses factoring and forfaiting. It defines factoring as a transaction where a financial intermediary called a factor assumes responsibility for collecting receivables from a client's credit sales in exchange for a commission. Forfaiting is defined as the purchase of a client's export receivables by a financial intermediary called a forfaiter without recourse to the client. The document outlines the key differences between factoring and forfaiting such as the extent of finance provided, credit risk assessment, services offered, recourse, minimum transaction size, and scope of services.