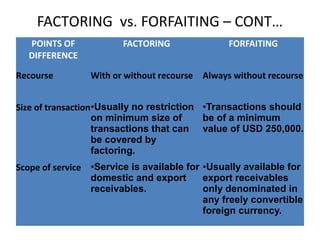
Factoring and forfaiting are forms of invoice financing that provide liquidity to companies. Factoring involves the sale of accounts receivable to a factor at a discount, who then takes on the responsibility of collection and provides financing against the receivables. Forfaiting specifically refers to financing of international trade receivables without recourse to the exporter. Key differences are that forfaiting provides 100% financing without recourse and guarantees against political and exchange rate risks, for longer tenors of 3-5 years, while factoring also includes receivables administration and is for shorter terms. Factoring is more widely used in India while forfaiting remains less developed due to issues like high costs and lack