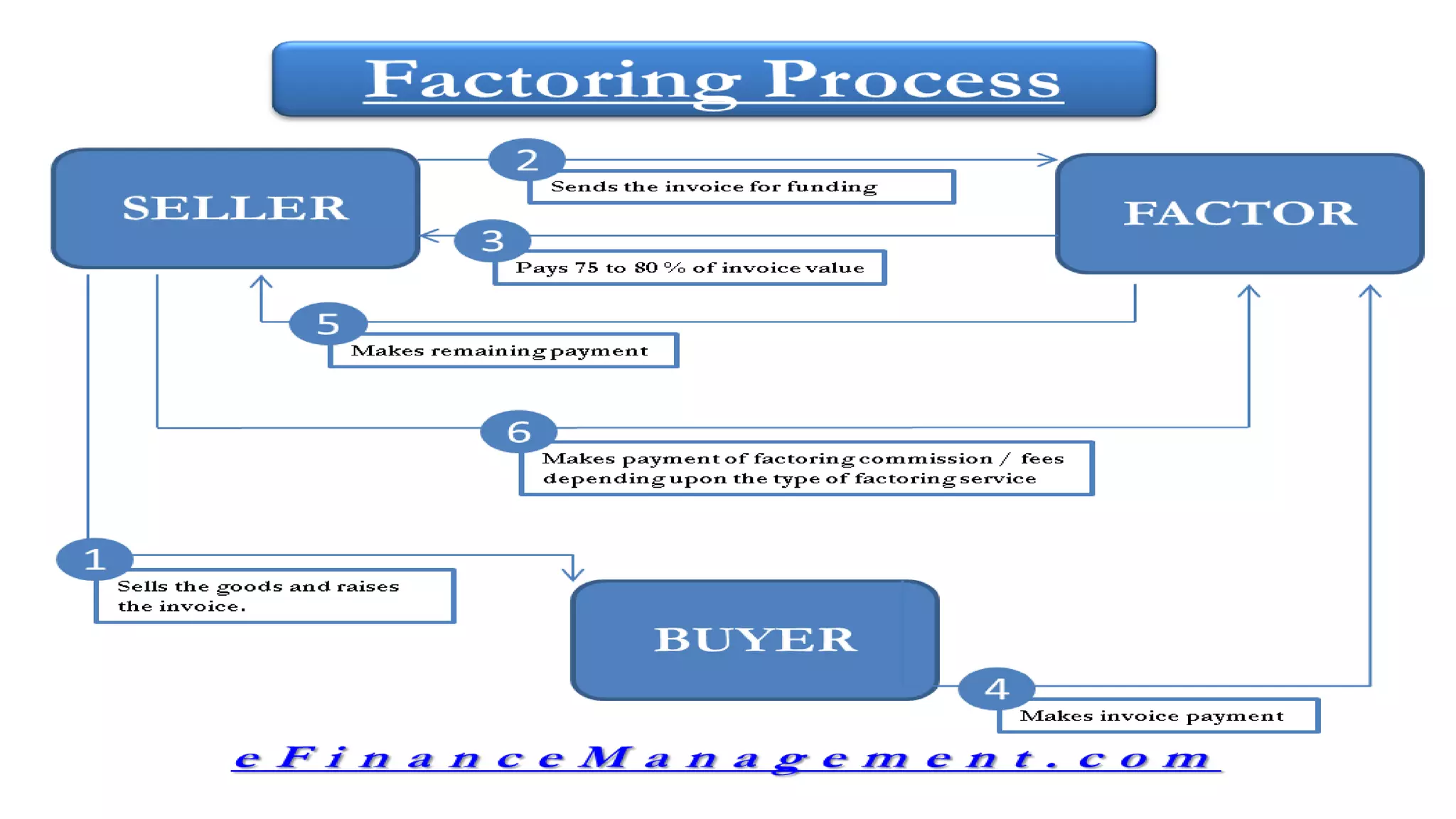
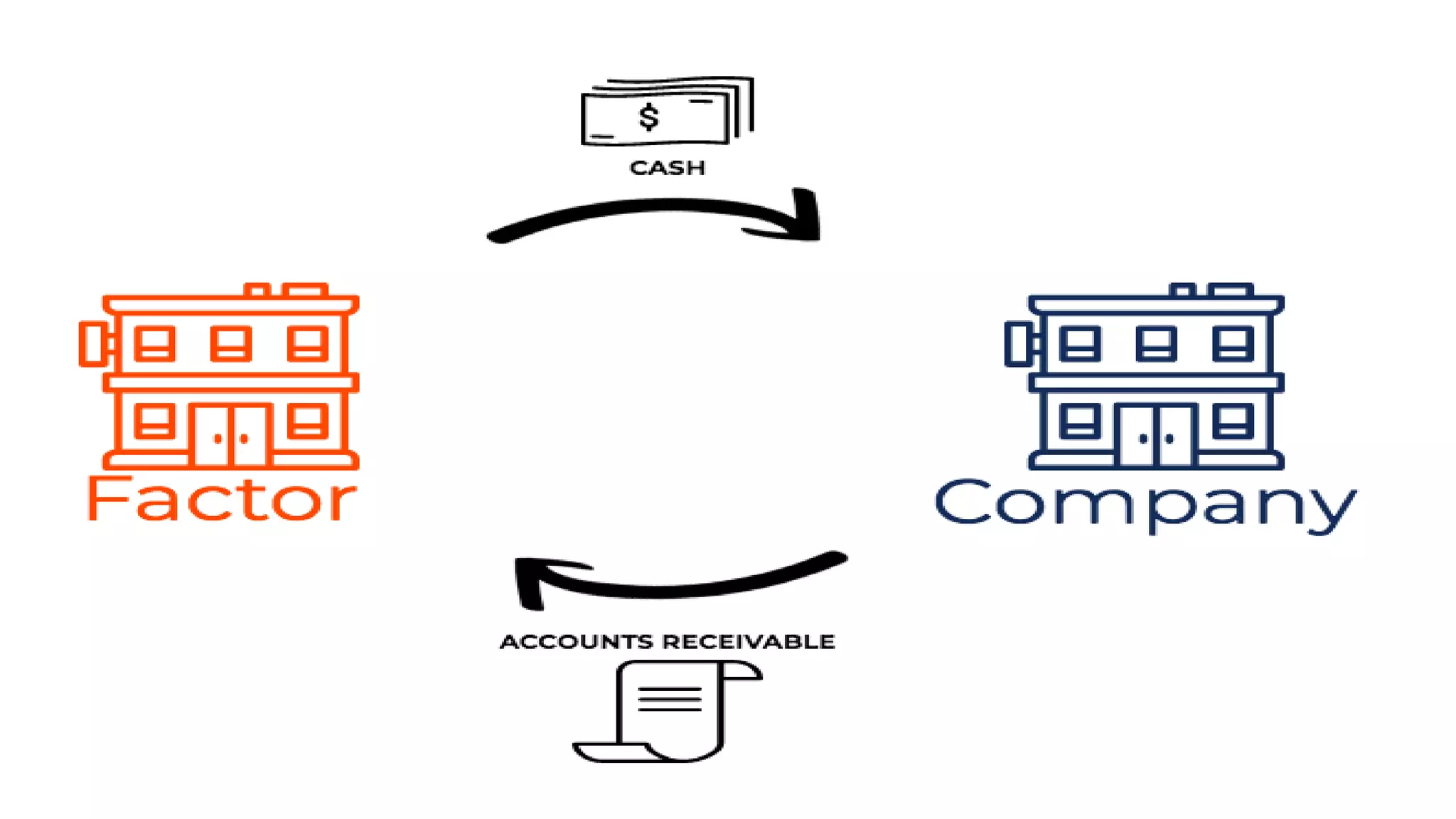
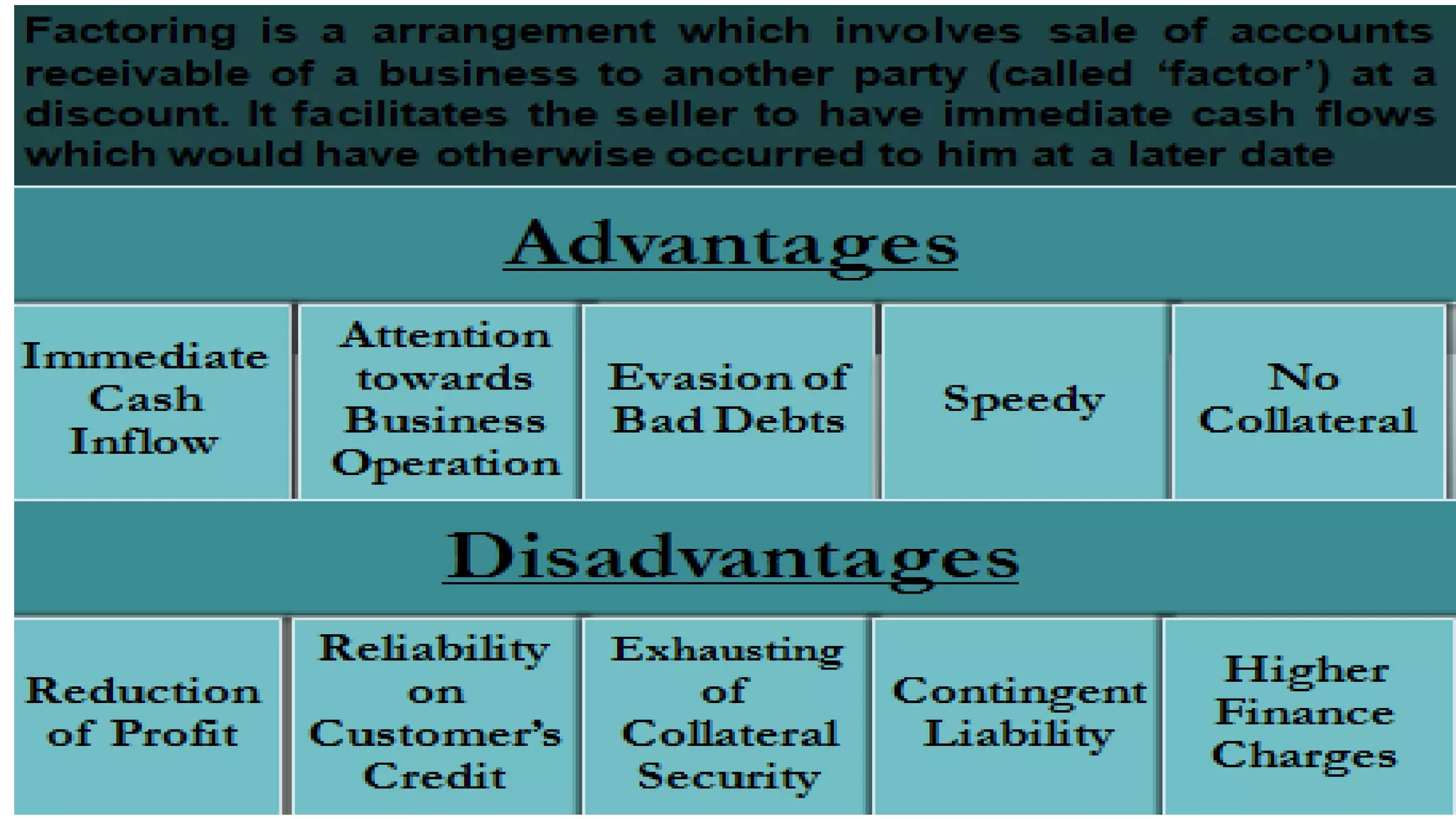
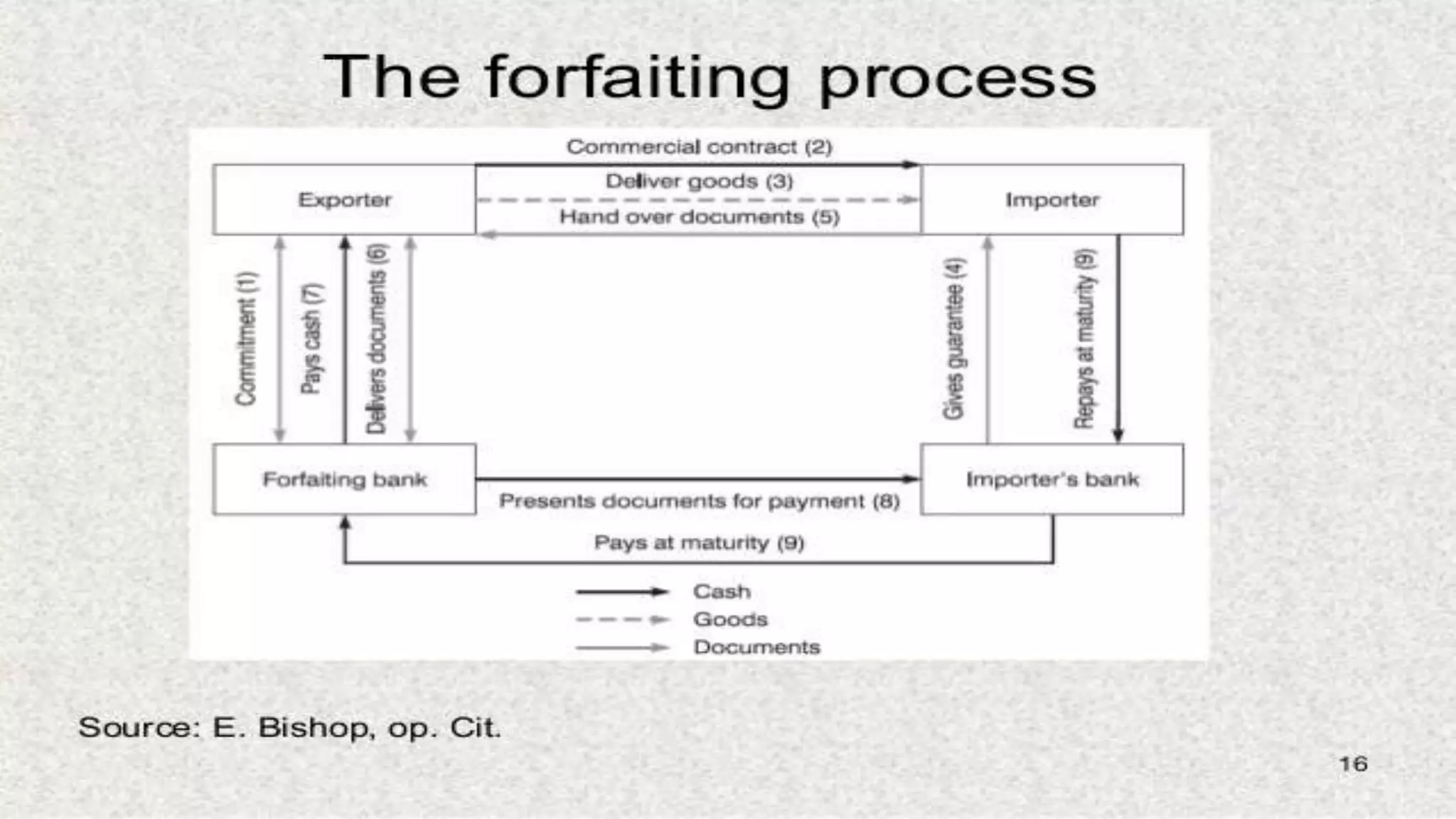
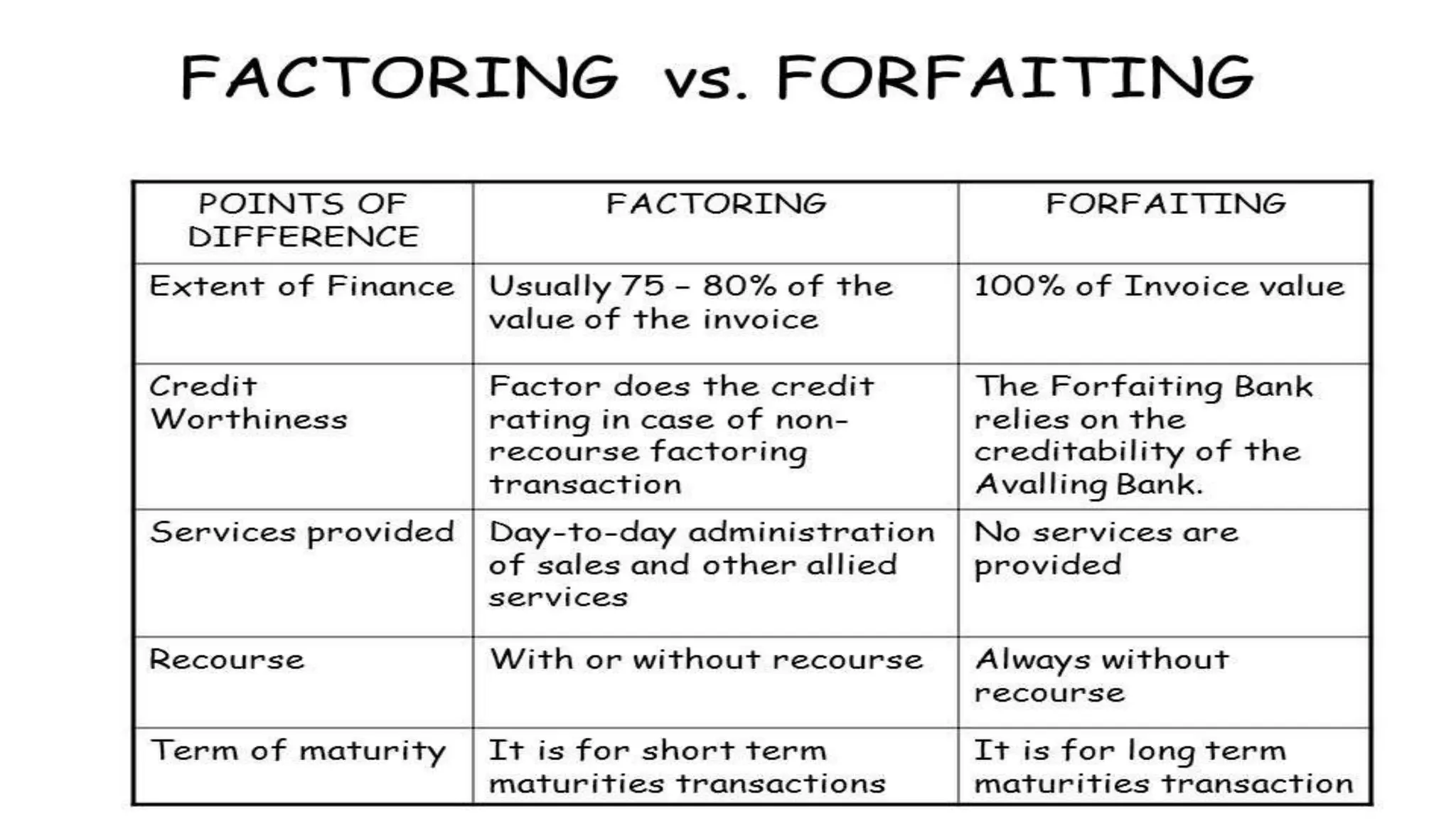
This document provides an overview of factoring and forfaiting. It defines factoring as the financial transaction where a business sells its accounts receivable to a third party called a factor at a discount. Forfaiting refers to the financing of receivables related to international trade where the right to export receivables is purchased by a financial intermediary without recourse. The document outlines the key parties involved in factoring and forfaiting, the different types of factoring arrangements, the functions of a factor, and the information and documents required by a forfaiter.