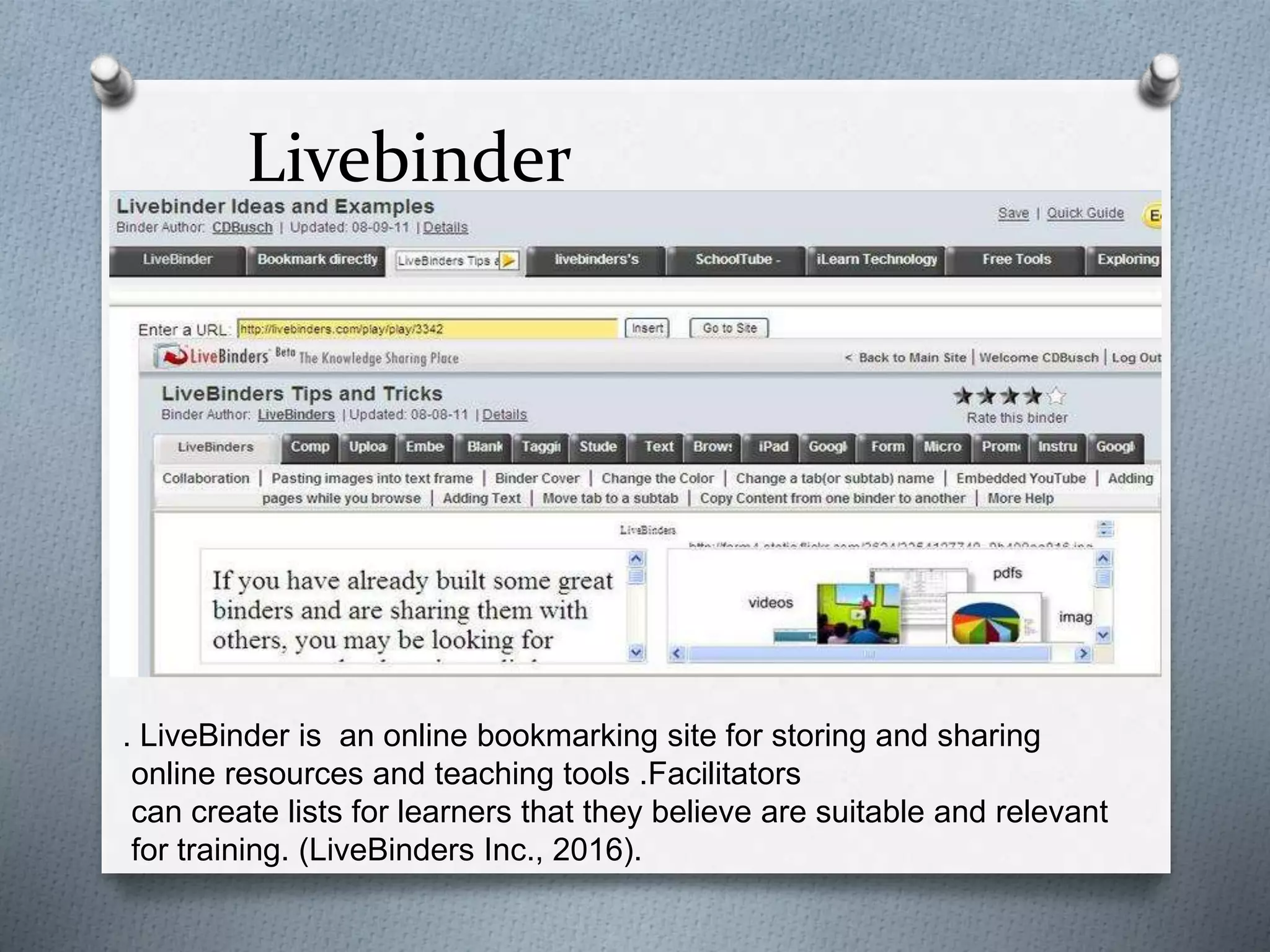
This document provides an overview of a facilitator training program for new hire trainers at Skyview Airlines. It includes the following:
- The training program will have 50 asynchronous participants and use an online asynchronous model.
- The goals are to prepare trainers for online facilitation by providing skills in establishing presence, facilitation, feedback, and maintaining a learning community.
- Modules will cover presence, facilitation skills, feedback skills, and building a learning community. Formative and summative assessments will evaluate participant learning.