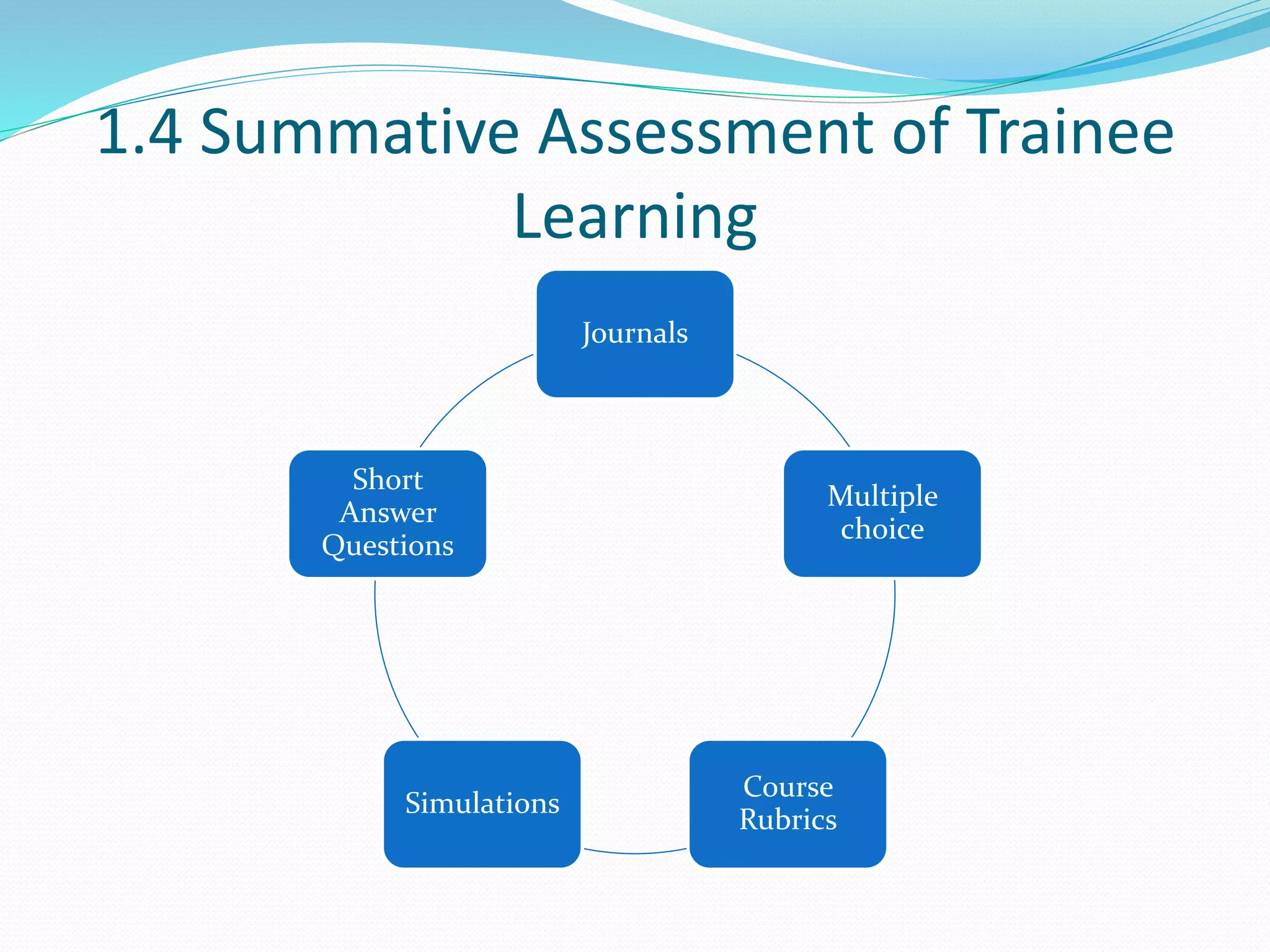
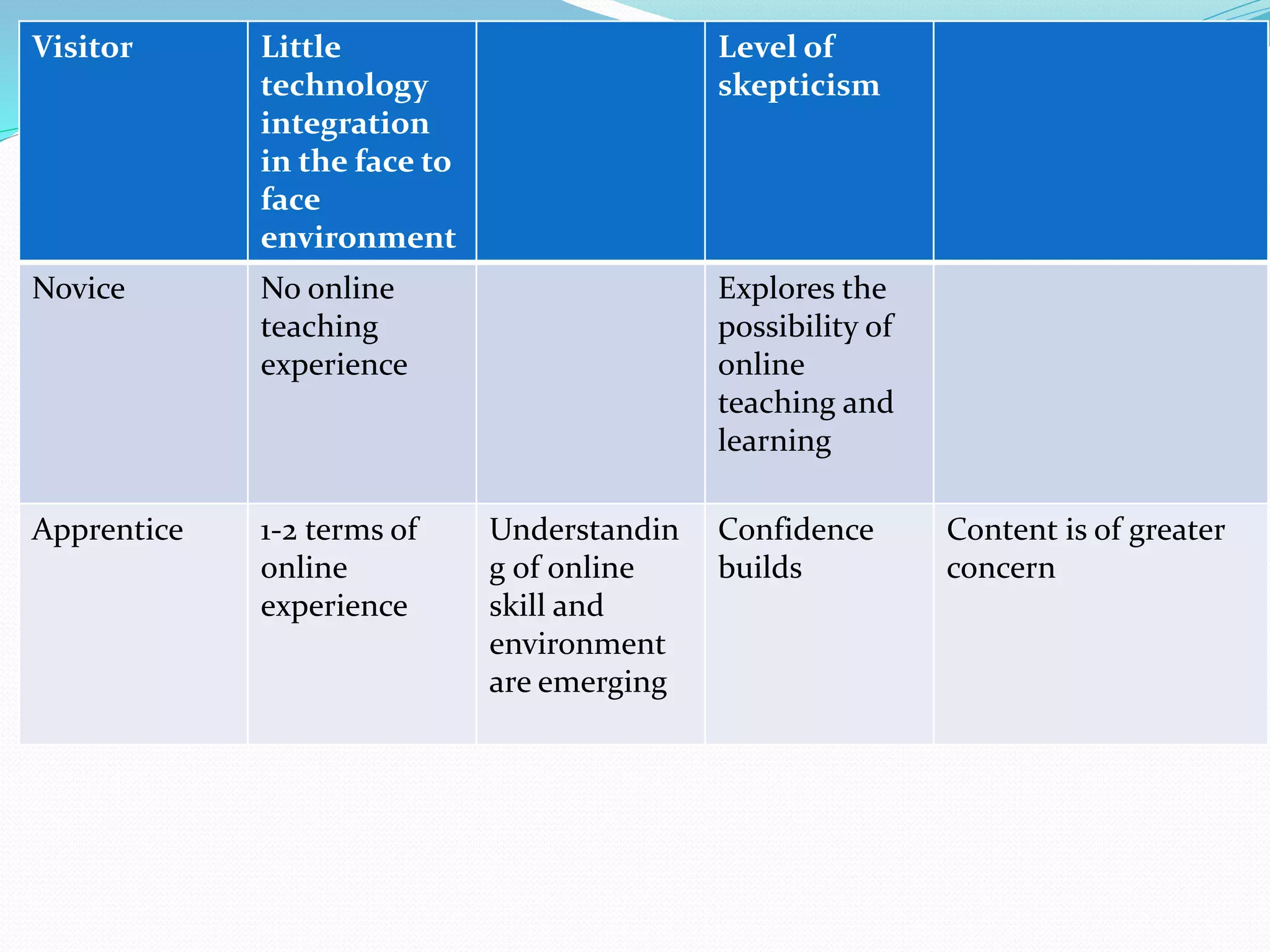
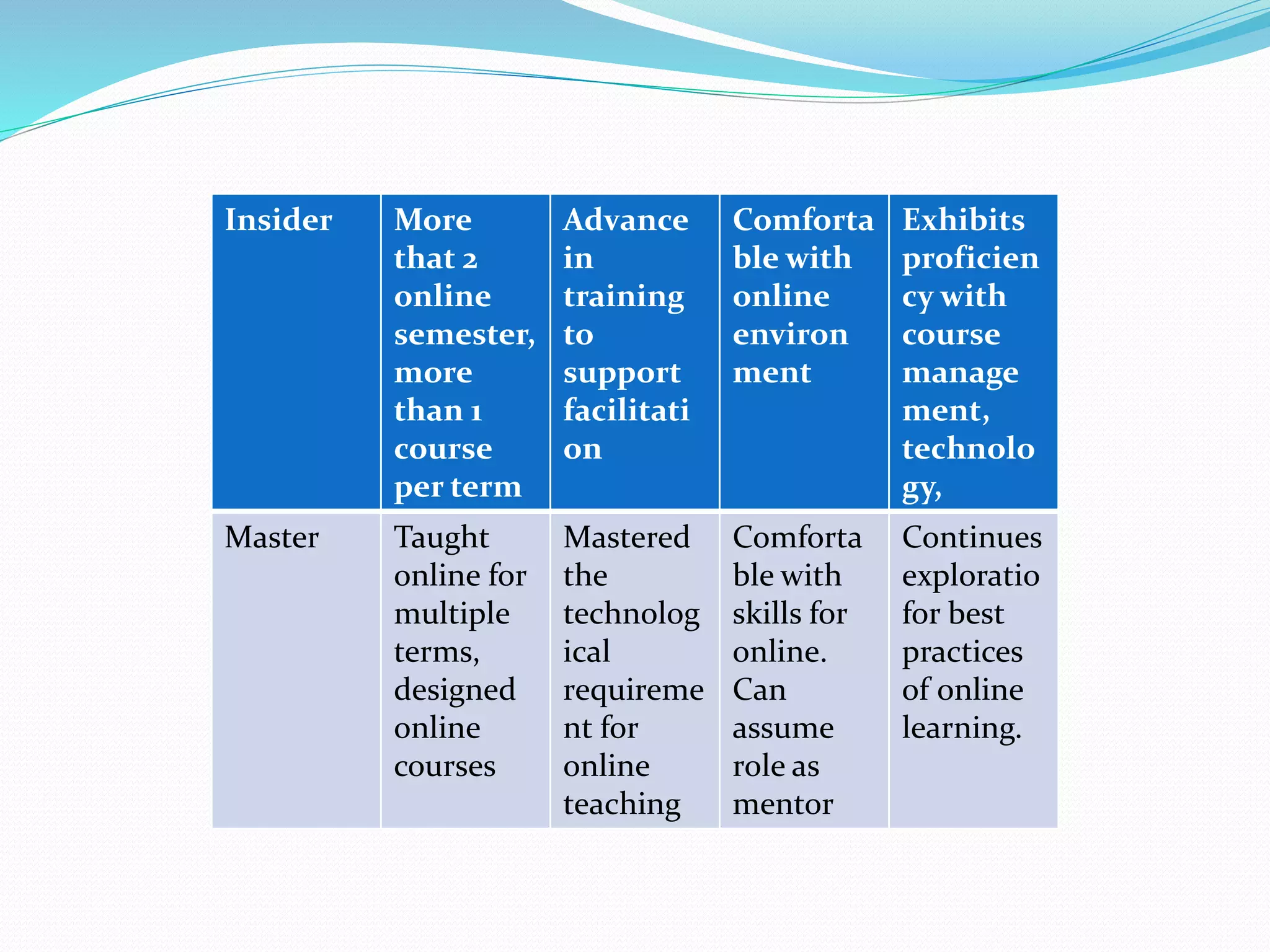
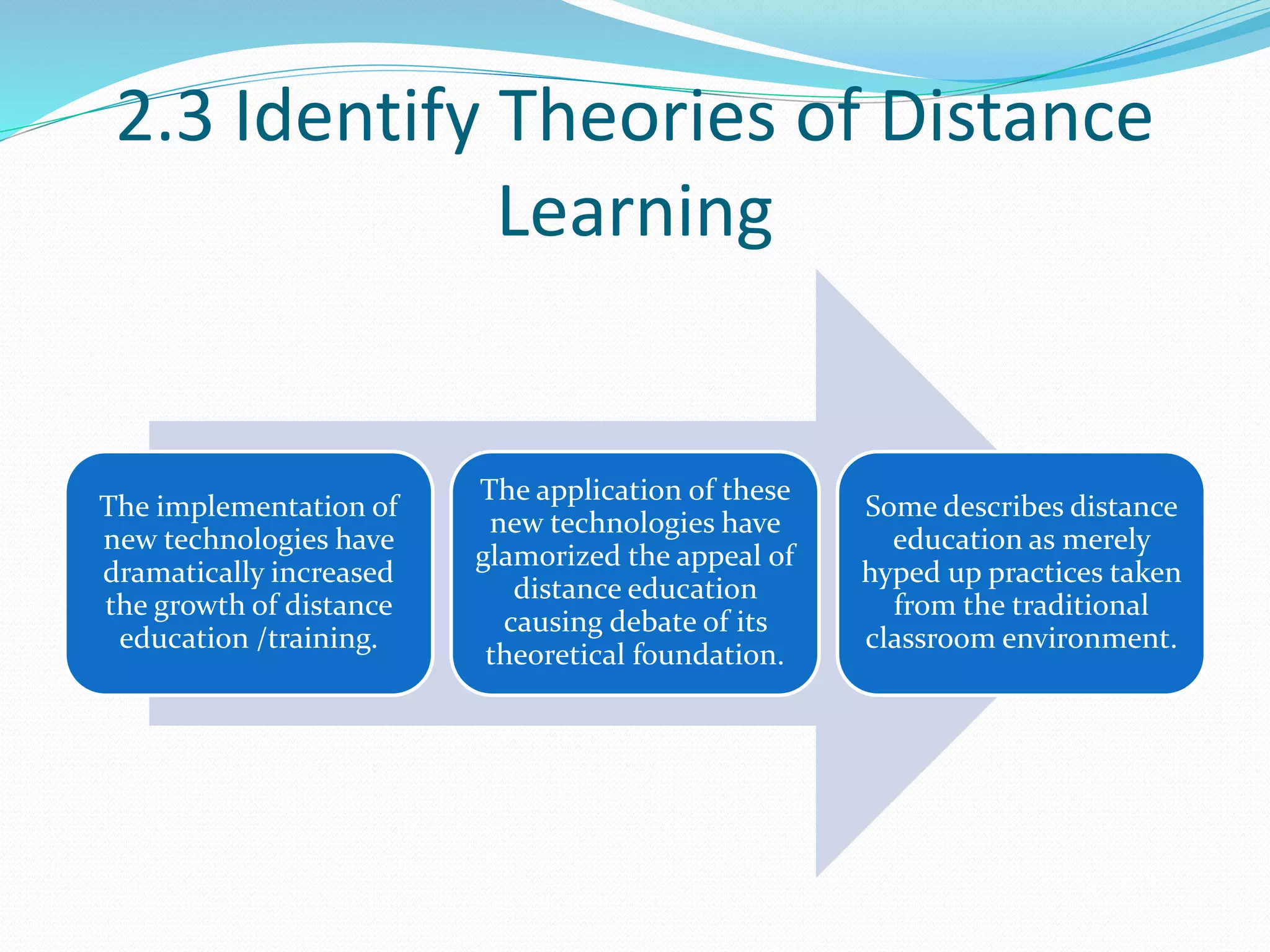
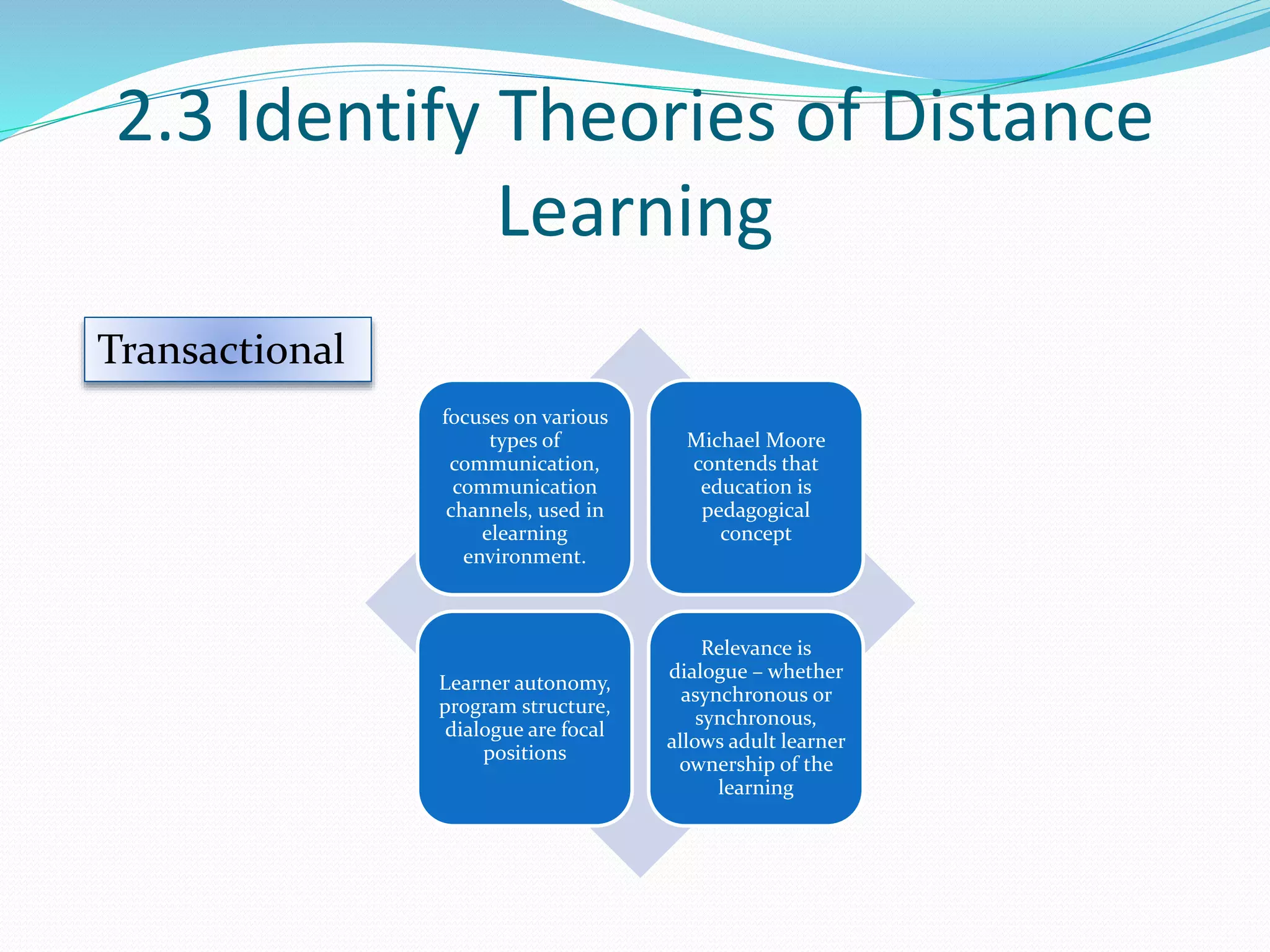
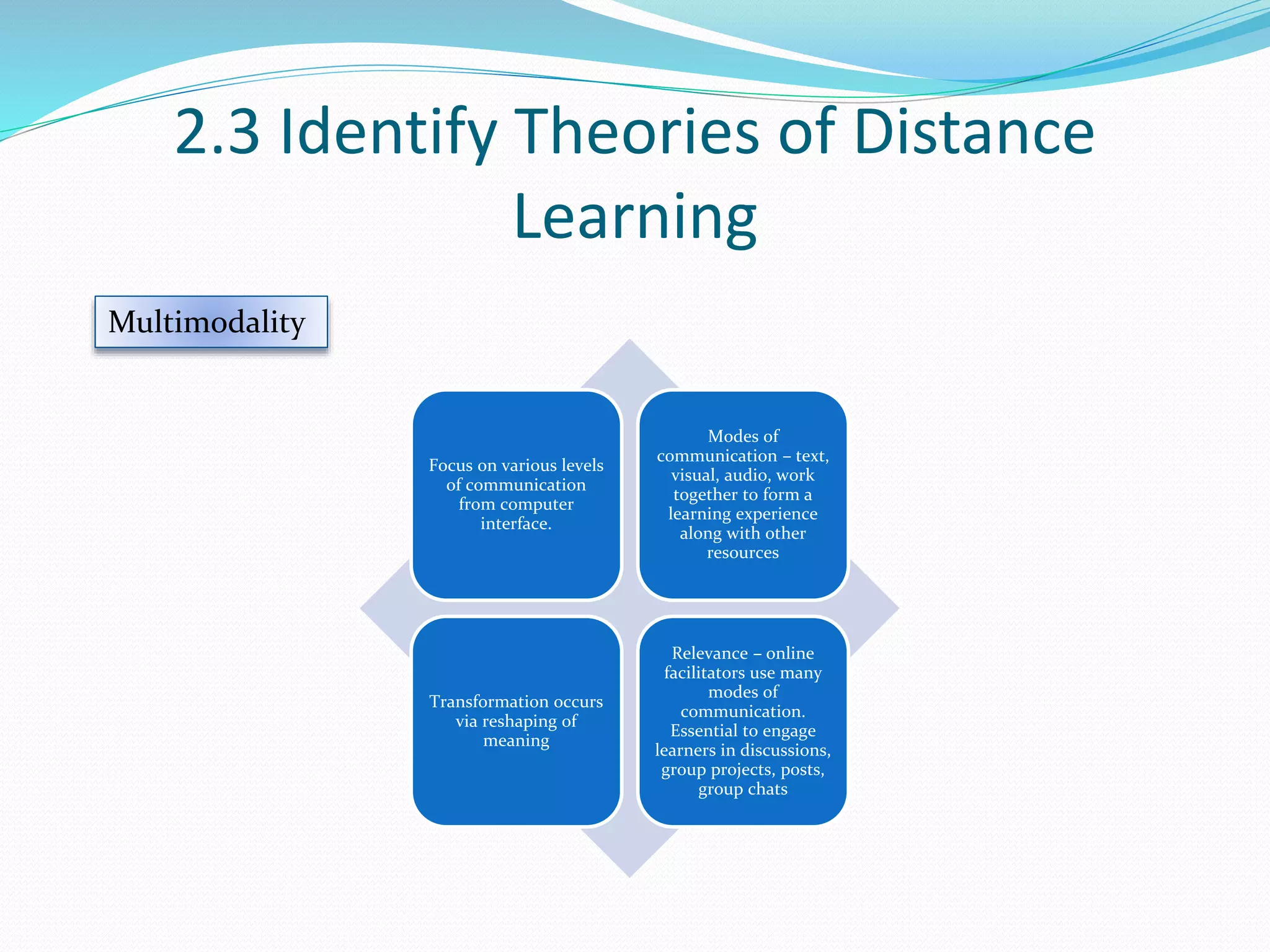
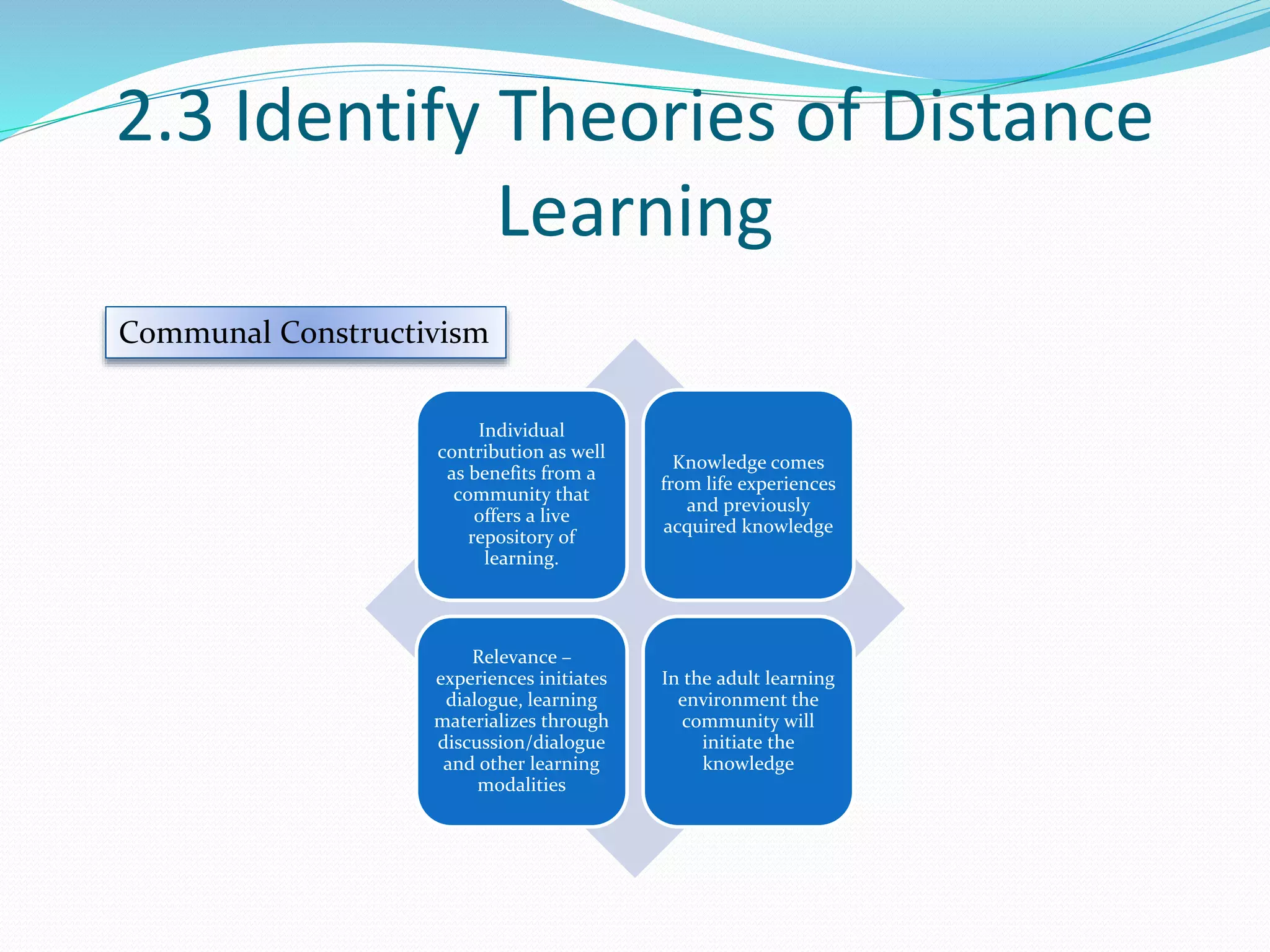
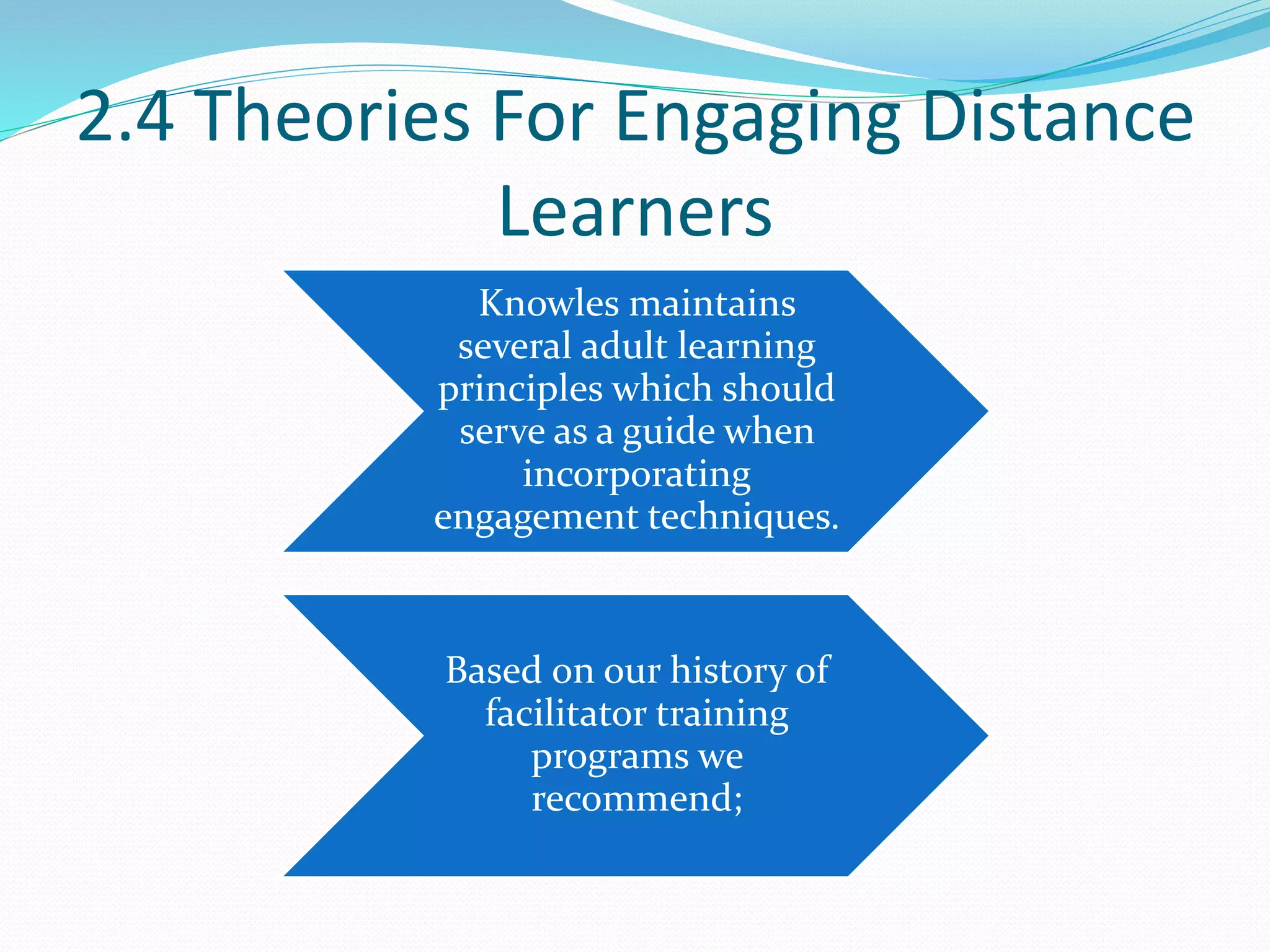
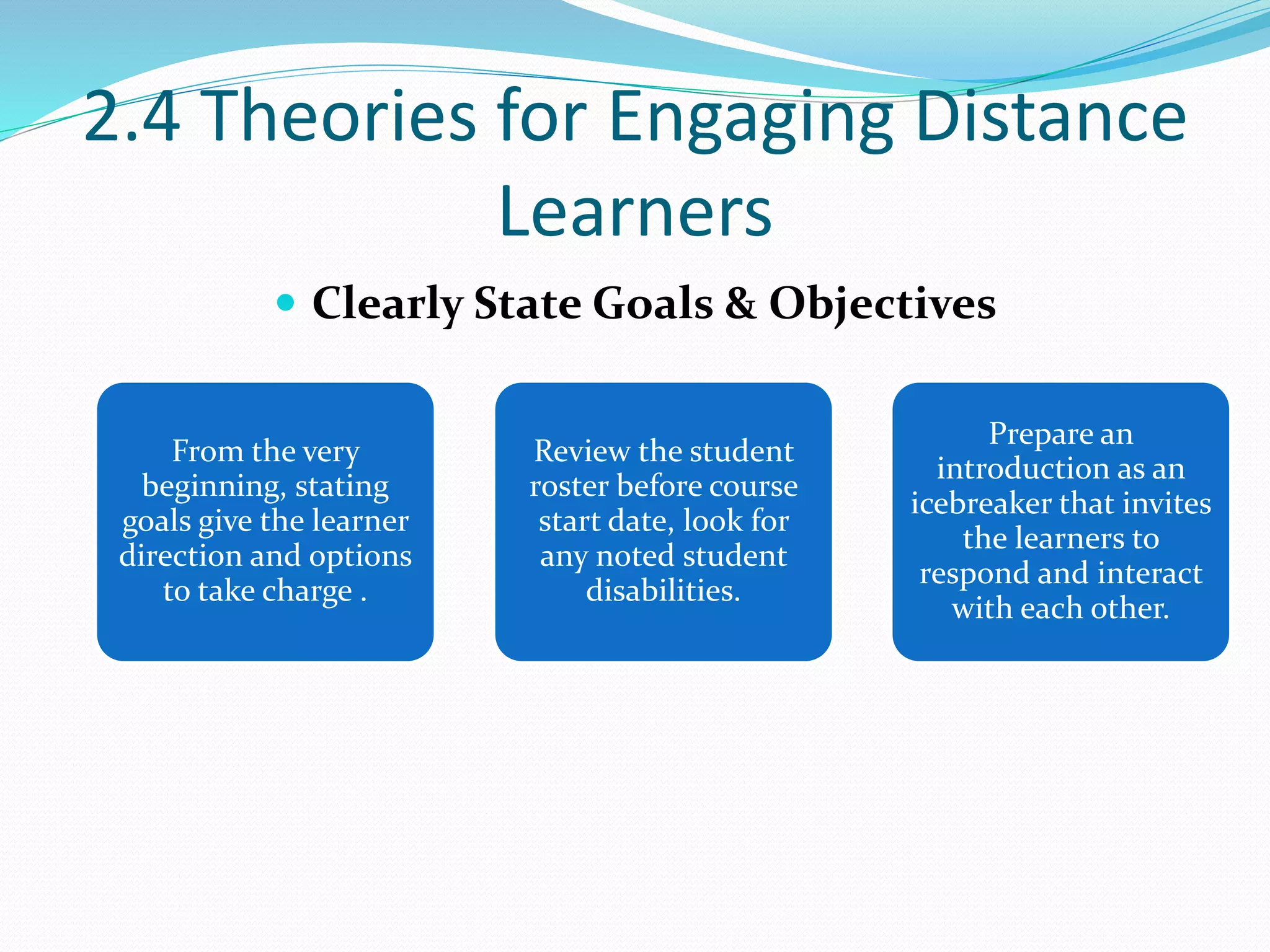
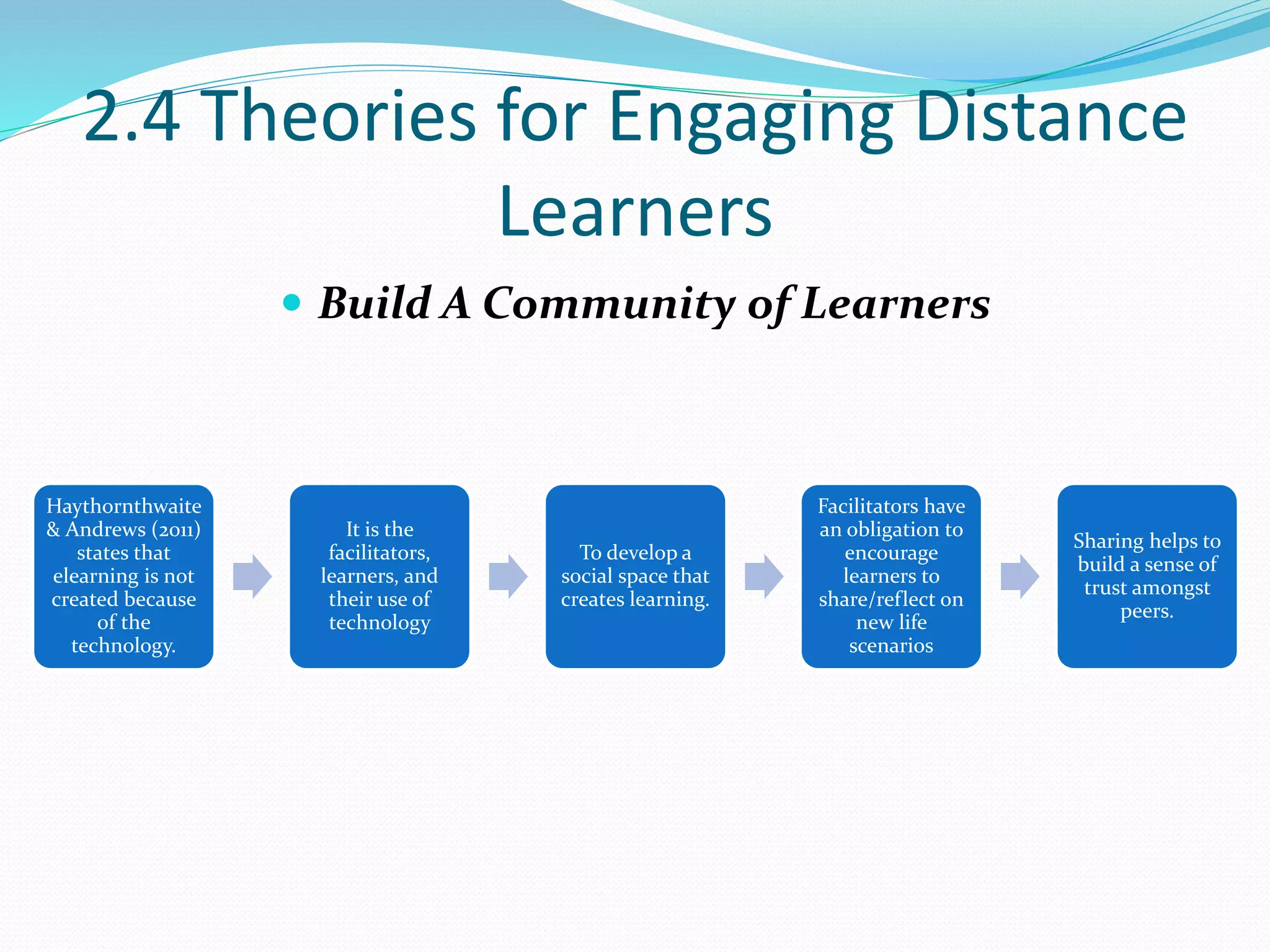
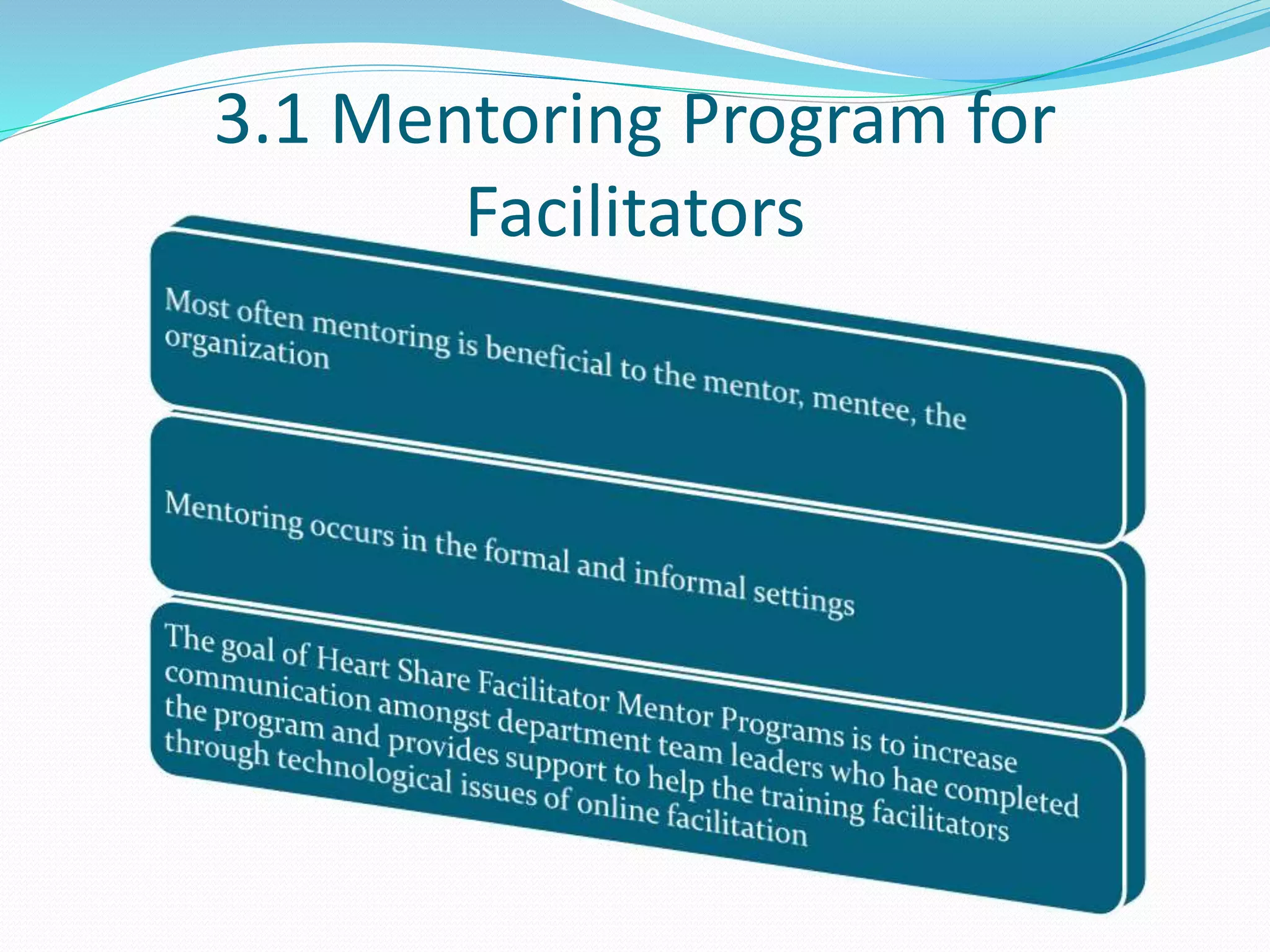
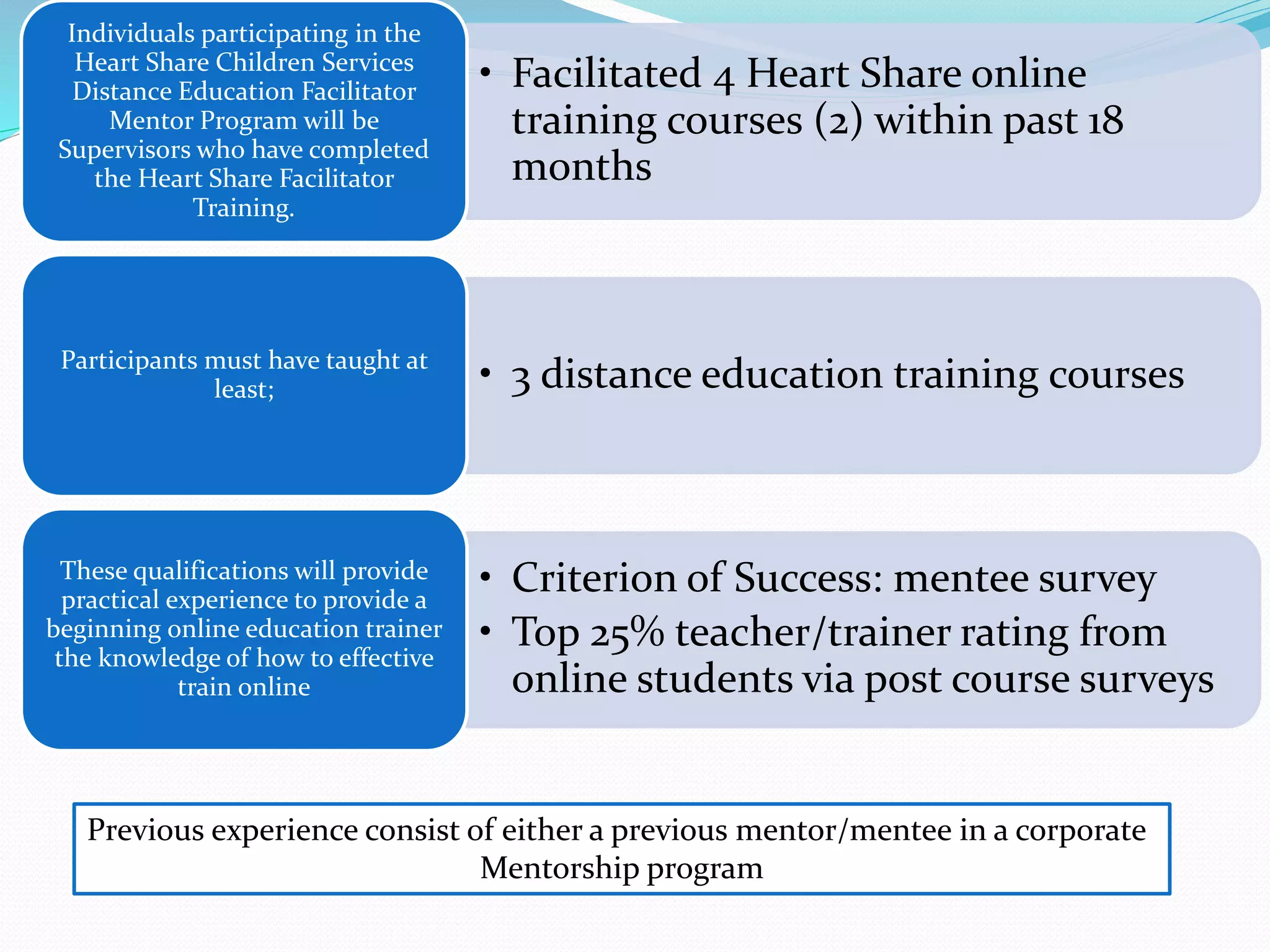
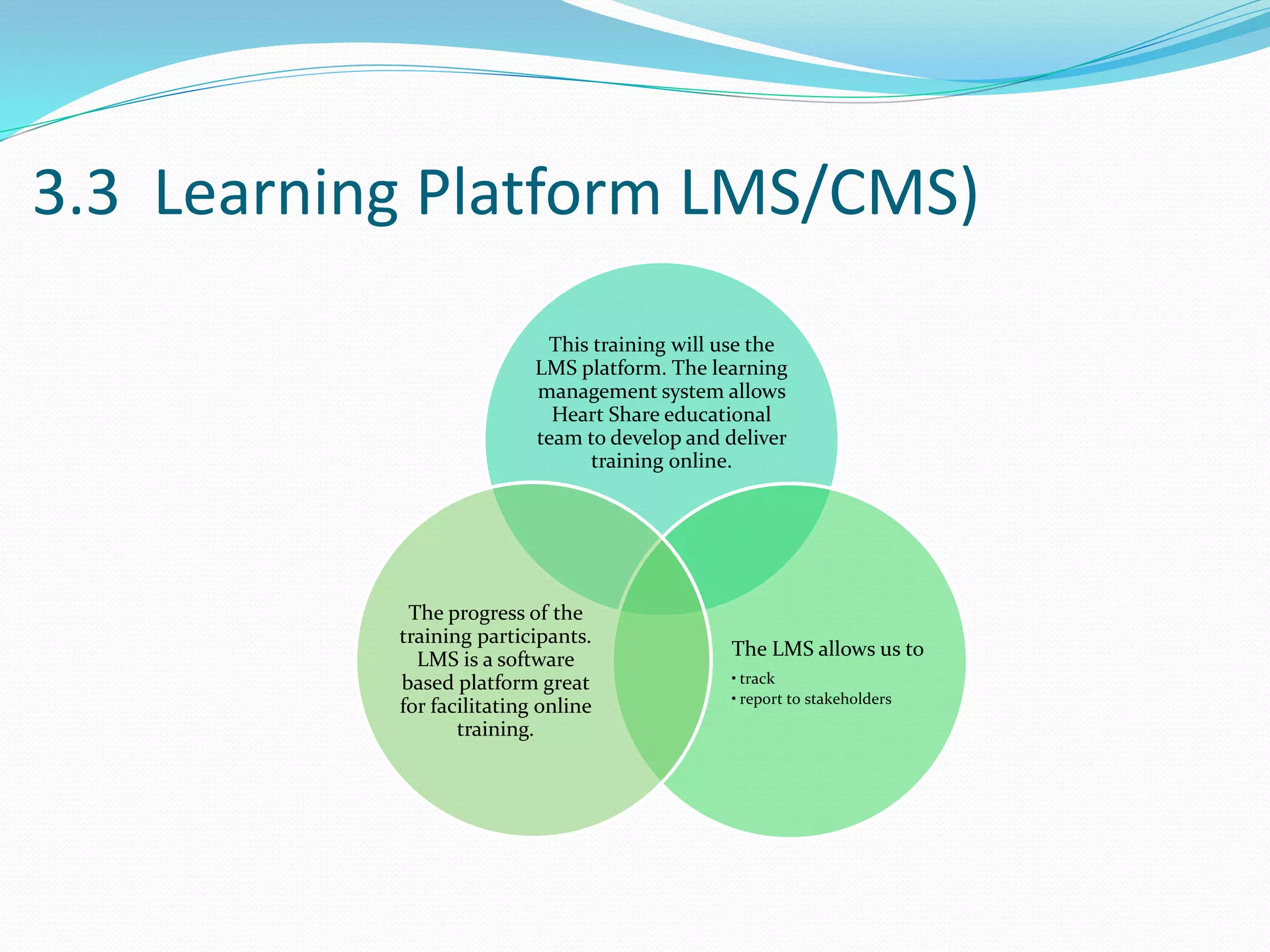
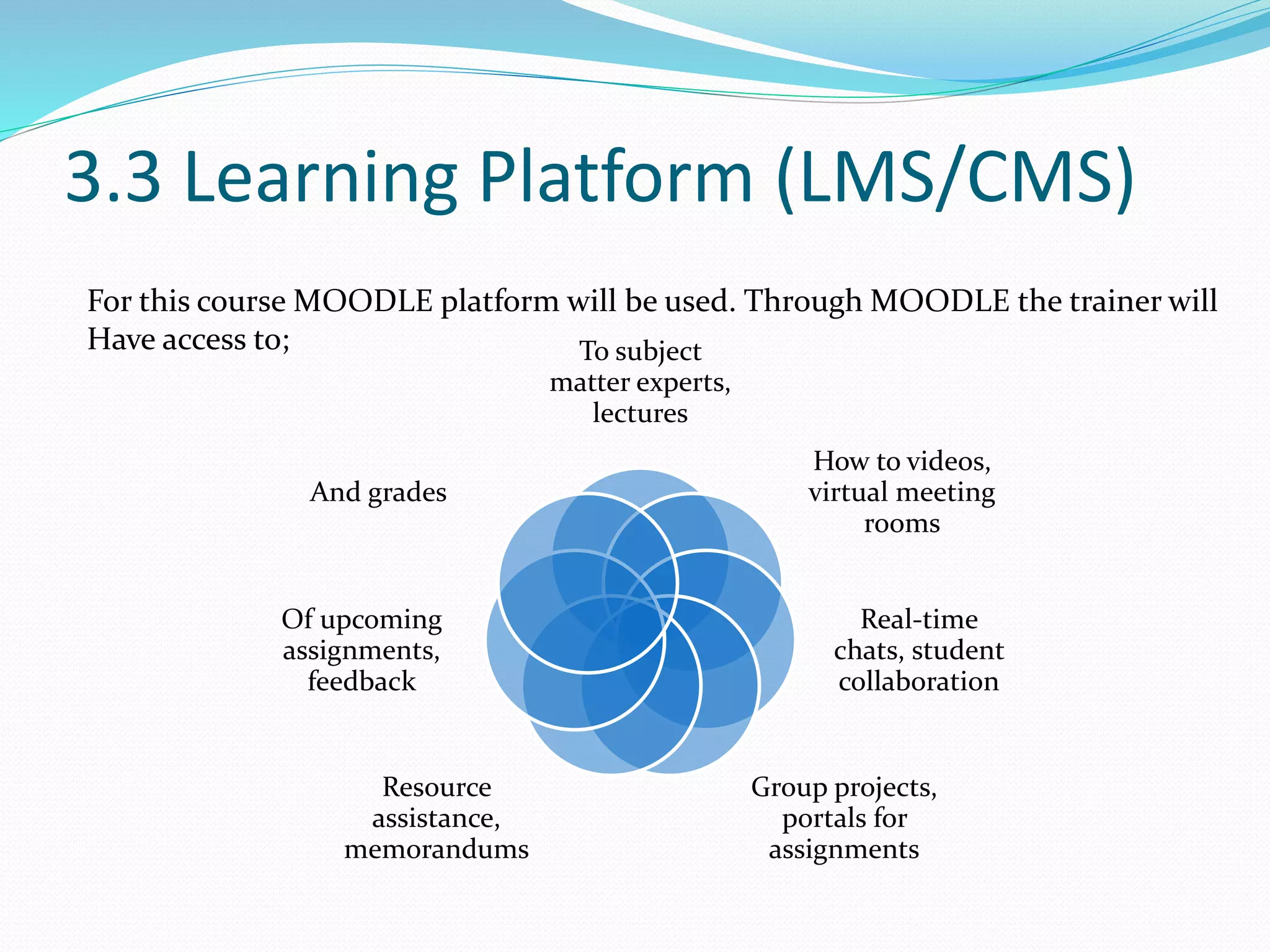
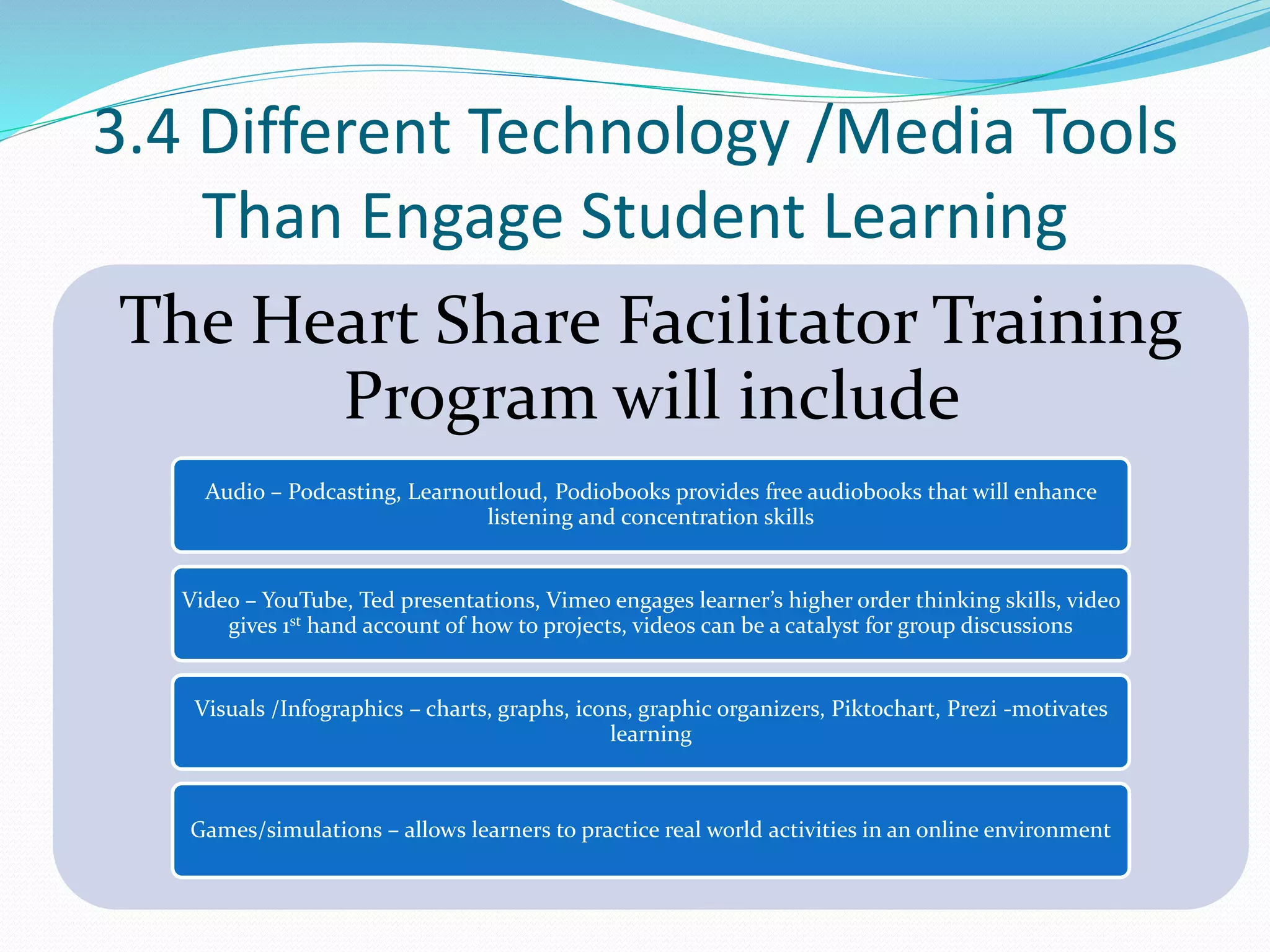
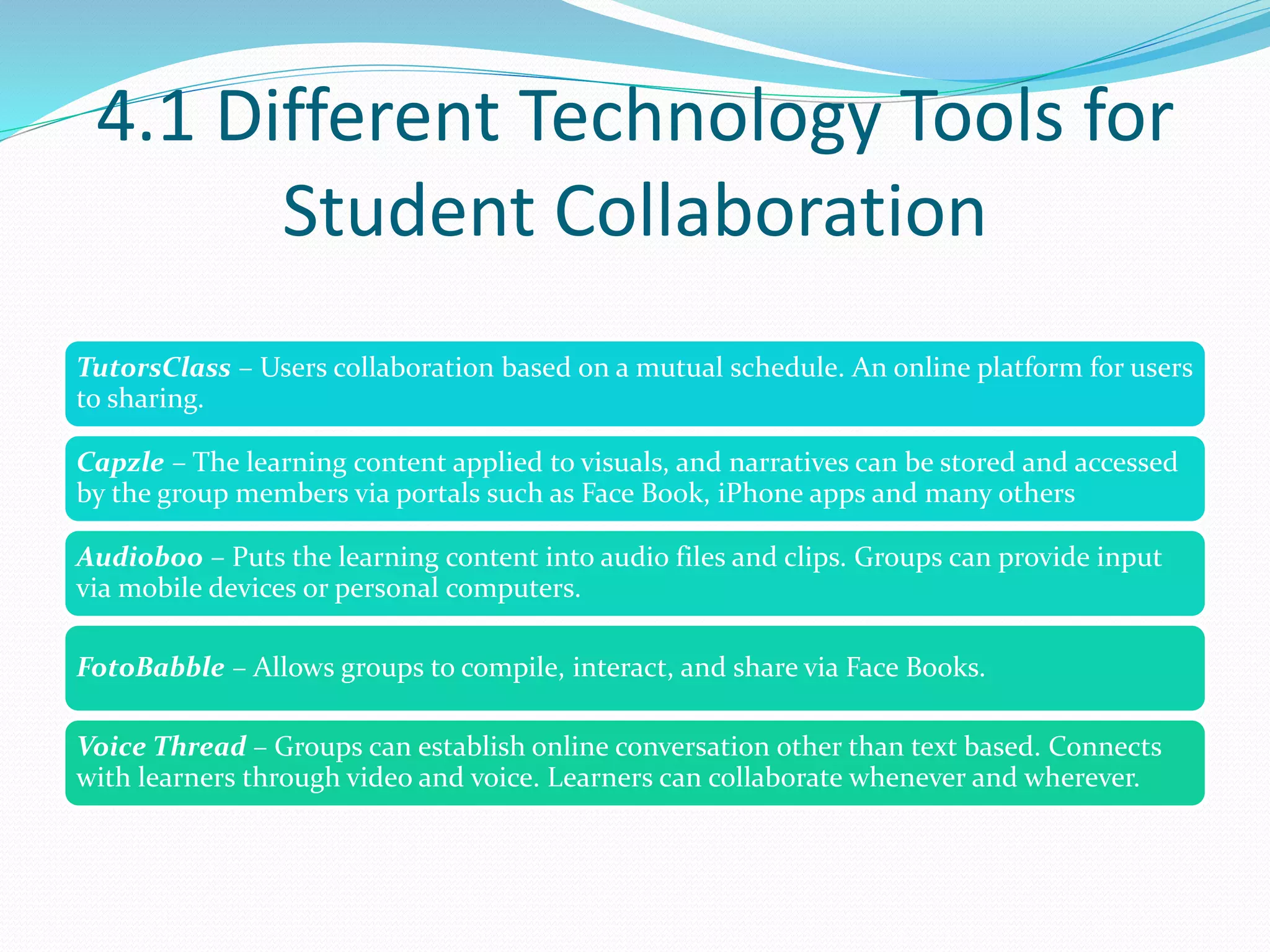
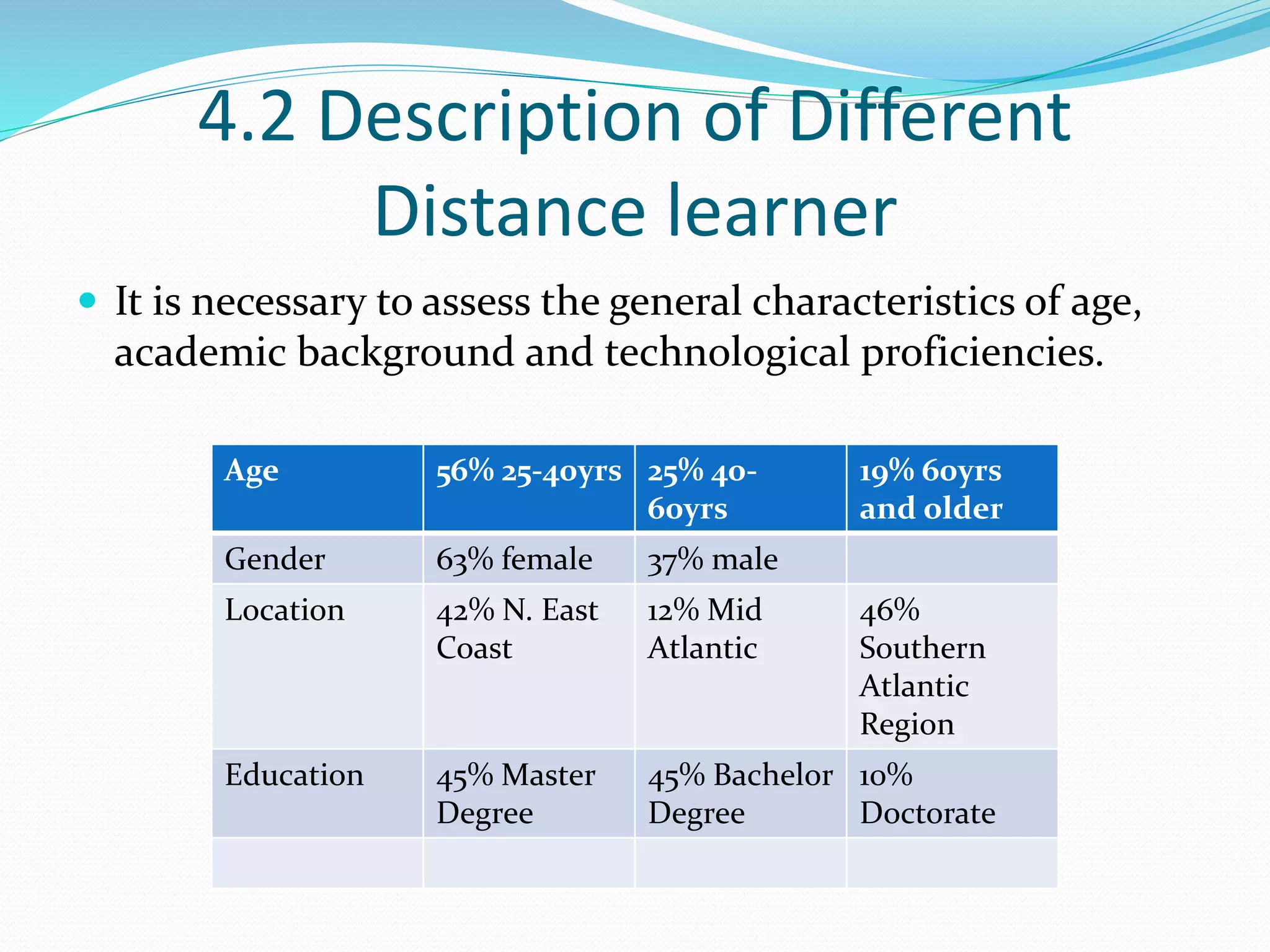
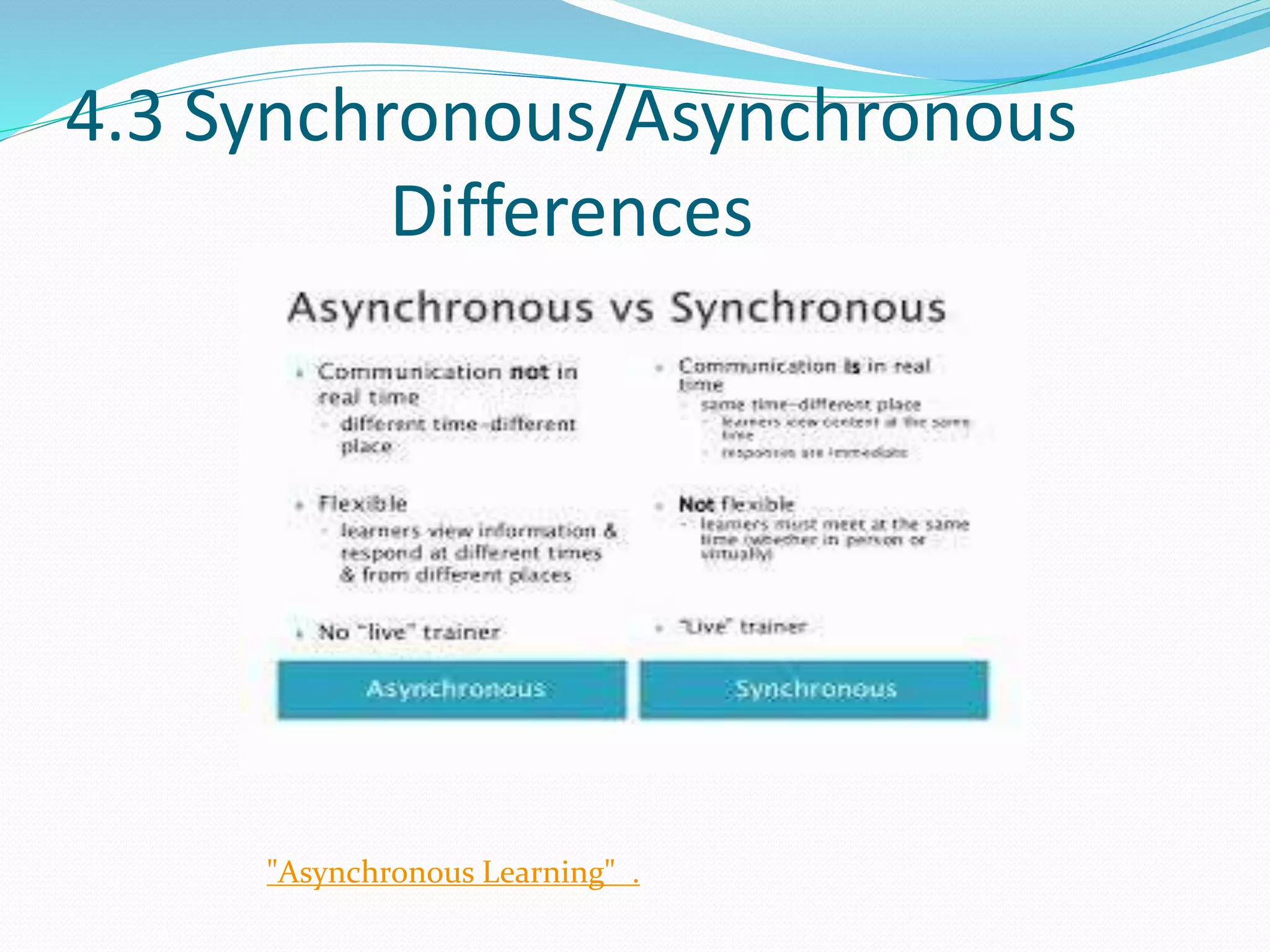
This document provides an overview of a 3-day facilitator training program for Heart Share Children Services supervisors. The training will be led by Lillian White and cover important topics to prepare supervisors to train others online. The training goals are to establish an online learning community, teach online engagement techniques, and help supervisors become proficient with online tools. Trainees will be assessed through journals, simulations, and peer collaboration. The training will explore best practices for online facilitation including maintaining an online presence, building a community of learners, and engaging adult learners. It will also cover management topics like mentoring programs and the learning platform used. A variety of technology and media tools will be introduced to enhance online learning.